Related Research Articles

Silicon Graphics, Inc. was an American high-performance computing manufacturer, producing computer hardware and software. Founded in Mountain View, California, in November 1981 by James Clark, its initial market was 3D graphics computer workstations, but its products, strategies and market positions developed significantly over time.

SATA is a computer bus interface that connects host bus adapters to mass storage devices such as hard disk drives, optical drives, and solid-state drives. Serial ATA succeeded the earlier Parallel ATA (PATA) standard to become the predominant interface for storage devices.

In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM), also called intercellular matrix (ICM), is a network consisting of extracellular macromolecules and minerals, such as collagen, enzymes, glycoproteins and hydroxyapatite that provide structural and biochemical support to surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM.

The IRIS-T is a medium range infrared homing missile available in air-to-air and surface-to-air variants. It also is called AIM-2000.
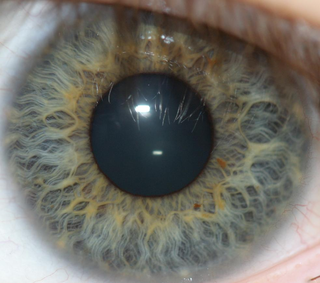
Iris recognition is an automated method of biometric identification that uses mathematical pattern-recognition techniques on video images of one or both of the irises of an individual's eyes, whose complex patterns are unique, stable, and can be seen from some distance. The discriminating powers of all biometric technologies depend on the amount of entropy they are able to encode and use in matching. Iris recognition is exceptional in this regard, enabling the avoidance of "collisions" even in cross-comparisons across massive populations. Its major limitation is that image acquisition from distances greater than a meter or two, or without cooperation, can be very difficult. However, the technology is in development and iris recognition can be accomplished from even up to 10 meters away or in a live camera feed.

Near-field communication (NFC) is a set of communication protocols that enables communication between two electronic devices over a distance of 4 centimetres (1.6 in) or less. NFC offers a low-speed connection through a simple setup that can be used for the bootstrapping of capable wireless connections. Like other proximity card technologies, NFC is based on inductive coupling between two electromagnetic coils present on a NFC-enabled device such as a smartphone. NFC communicating in one or both directions uses a frequency of 13.56 MHz in the globally available unlicensed radio frequency ISM band, compliant with the ISO/IEC 18000-3 air interface standard at data rates ranging from 106 to 848 kbit/s.
Enea AB is a global information technology company with its headquarters in Kista, Sweden that provides real-time operating systems and consulting services. Enea, which is an abbreviation of Engmans Elektronik Aktiebolag, also produces the OSE operating system.

Xilinx, Inc. was an American technology and semiconductor company that primarily supplied programmable logic devices. The company is known for inventing the first commercially viable field-programmable gate array (FPGA). It also created the first fabless manufacturing model.

An electronic countermeasure (ECM) is an electrical or electronic device designed to trick or deceive radar, sonar, or other detection systems, like infrared (IR) or lasers. It may be used both offensively and defensively to deny targeting information to an enemy. The system may make many separate targets appear to the enemy, or make the real target appear to disappear or move about randomly. It is used effectively to protect aircraft from guided missiles. Most air forces use ECM to protect their aircraft from attack. It has also been deployed by military ships and recently on some advanced tanks to fool laser/IR guided missiles. It is frequently coupled with stealth advances so that the ECM systems have an easier job. Offensive ECM often takes the form of jamming. Self-protecting (defensive) ECM includes using blip enhancement and jamming of missile terminal homers.
Automatic identification and data capture (AIDC) refers to the methods of automatically identifying objects, collecting data about them, and entering them directly into computer systems, without human involvement. Technologies typically considered as part of AIDC include QR codes, bar codes, radio frequency identification (RFID), biometrics, magnetic stripes, optical character recognition (OCR), smart cards, and voice recognition. AIDC is also commonly referred to as "Automatic Identification", "Auto-ID" and "Automatic Data Capture".
Enterprise content management (ECM) extends the concept of content management by adding a timeline for each content item and, possibly, enforcing processes for its creation, approval, and distribution. Systems using ECM generally provide a secure repository for managed items, analog or digital. They also include one methods for importing content to manage new items, and several presentation methods to make items available for use. Although ECM content may be protected by digital rights management (DRM), it is not required. ECM is distinguished from general content management by its cognizance of the processes and procedures of the enterprise for which it is created.
Moog Inc. is an American-based designer and manufacturer of electric, electro-hydraulic and hydraulic motion, controls and systems for applications in aerospace, defense, industrial and medical devices. The company operates under four segments: aircraft controls, space and defense controls, industrial controls, and components. Moog is headquartered in Elma, New York, and has sales, engineering, and manufacturing facilities in twenty-six countries.

Stanford Robert Ovshinsky was an American engineer, scientist and inventor who over a span of fifty years was granted well over 400 patents, mostly in the areas of energy and information. Many of his inventions have had wide-ranging applications. Among the most prominent are: the nickel-metal hydride battery, which has been widely used in laptop computers, digital cameras, cell phones, and electric and hybrid cars; flexible thin-film solar energy laminates and panels; flat panel liquid crystal displays; rewritable CD and DVD discs; hydrogen fuel cells; and nonvolatile phase-change memory.
A three-dimensional integrated circuit is a MOS integrated circuit (IC) manufactured by stacking as many as 16 or more ICs and interconnecting them vertically using, for instance, through-silicon vias (TSVs) or Cu-Cu connections, so that they behave as a single device to achieve performance improvements at reduced power and smaller footprint than conventional two dimensional processes. The 3D IC is one of several 3D integration schemes that exploit the z-direction to achieve electrical performance benefits in microelectronics and nanoelectronics.

Intel Graphics Technology (GT) is the collective name for a series of integrated graphics processors (IGPs) produced by Intel that are manufactured on the same package or die as the central processing unit (CPU). It was first introduced in 2010 as Intel HD Graphics and renamed in 2017 as Intel UHD Graphics.
Virtex is the flagship family of FPGA products currently developed by AMD, originally Xilinx before being acquired by the former. Other current product lines include Kintex (mid-range) and Artix (low-cost), each including configurations and models optimized for different applications. In addition, AMD offers the Spartan low-cost series, which continues to be updated and is nearing production utilizing the same underlying architecture and process node as the larger 7-series devices.
Qualitrol is a condition monitoring technology company headquartered in Fairport, New York. Qualitrol manufacturers and distributes partial discharge monitoring, asset protection equipment and information products for the electrical generation, transmission and distribution industries.

The TRML is a family of air defense radars first developed by Telefunken and currently produced by Hensoldt. It is a development of the earlier TRMS.

A biometric device is a security identification and authentication device. Such devices use automated methods of verifying or recognising the identity of a living person based on a physiological or behavioral characteristic. These characteristics include fingerprints, facial images, iris and voice recognition.
References
- ↑ "Agenda of Baltic Defence Technology Exhibition of 2008". Archived from the original on 2011-05-27. Retrieved 2009-06-05.
- 1 2 Postimees 4 June 2009 22:14: Eesti müüs Läti kaitseväele raadiolainete häirimisseadmeid