
Computer-aided design (CAD) is the use of computers to aid in the creation, modification, analysis, or optimization of a design. This software is used to increase the productivity of the designer, improve the quality of design, improve communications through documentation, and to create a database for manufacturing. Designs made through CAD software help protect products and inventions when used in patent applications. CAD output is often in the form of electronic files for print, machining, or other manufacturing operations. The terms computer-aided drafting (CAD) and computer-aided design and drafting (CADD) are also used.
A domain-specific language (DSL) is a computer language specialized to a particular application domain. This is in contrast to a general-purpose language (GPL), which is broadly applicable across domains. There are a wide variety of DSLs, ranging from widely used languages for common domains, such as HTML for web pages, down to languages used by only one or a few pieces of software, such as MUSH soft code. DSLs can be further subdivided by the kind of language, and include domain-specific markup languages, domain-specific modeling languages, and domain-specific programming languages. Special-purpose computer languages have always existed in the computer age, but the term "domain-specific language" has become more popular due to the rise of domain-specific modeling. Simpler DSLs, particularly ones used by a single application, are sometimes informally called mini-languages.

On-board diagnostics (OBD) is a term referring to a vehicle's self-diagnostic and reporting capability. In the United States, this self-diagnostic is a requirement to comply with Federal Emissions standards to detect failures that may increase the vehicle tailpipe emissions to more than 150% of the standard to which it was originally certified.
Building regulations in the United Kingdom are statutory instruments or statutory regulations that seek to ensure that the policies set out in the relevant legislation are carried out. Building regulations approval is required for most building work in the UK.
Domestic housing in the United Kingdom presents a possible opportunity for achieving the 20% overall cut in UK greenhouse gas emissions targeted by the Government for 2010. However, the process of achieving that drop is proving problematic given the very wide range of age and condition of the UK housing stock.

Autodesk Revit is a building information modelling software for architects, structural engineers, mechanical, electrical, and plumbing (MEP) engineers, design for contractors. The original software was developed by Charles River Software, founded in 1997, renamed Revit Technology Corporation in 2000, and acquired by Autodesk in 2002. The software allows users to design a building and structure and its components in 3D, annotate the model with 2D drafting elements, and access building information from the building model's database. Revit is 4D building information modeling application capable with tools to plan and track various stages in the building's lifecycle, from concept to construction and later maintenance and/or demolition.
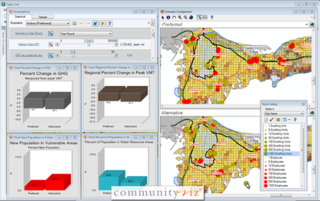
CommunityViz is the name of a group of extensions to ArcGIS Geographic Information System software. CommunityViz is an analysis tool used for, among other applications, urban planning, land use planning, geodesign, transportation planning and resource management applications. It also provides options for 3D visualization in the Scenario 3D and Scenario 360 plugins. CommunityViz also allows users to export and view their work in ArcGIS Online, Google Earth and other KML/KMZ viewers such as ArcGIS Explorer. The software was originally produced by the Orton Family Foundation and in 2005 was handed off to Placeways LLC. In 2017, the software was purchased by City Explained, Inc. where its development continues.

3D computer graphics, sometimes called CGI, 3-D-CGI or three-dimensional computer graphics, are graphics that use a three-dimensional representation of geometric data that is stored in the computer for the purposes of performing calculations and rendering digital images, usually 2D images but sometimes 3D images. The resulting images may be stored for viewing later or displayed in real time.
BasisTech is a software company specializing in applying artificial intelligence techniques to understanding documents and unstructured data written in different languages. It has headquarters in Somerville, Massachusetts with a subsidiary office in Tokyo. Its legal name is BasisTech LLC.

Energy performance certificates (EPCs) are a rating scheme to summarise the energy efficiency of buildings. The building is given a rating between A - G (Inefficient). The EPC will also include tips about the most cost-effective ways to improve the home energy rating. Energy performance certificates are used in many countries.
Business process management (BPM) is the discipline in which people use various methods to discover, model, analyze, measure, improve, optimize, and automate business processes. Any combination of methods used to manage a company's business processes is BPM. Processes can be structured and repeatable or unstructured and variable. Though not required, enabling technologies are often used with BPM.
VP/MS is a family of software components developed by CSC that support product development and product lifecycle management. Insurance companies use VP/MS to manage the rules, clauses, formulas and calculations associated with savings and both life and non-life insurance products. With VP/MS all calculations and queries for purposes such as quotes and administration are supported by a central repository of product definitions.
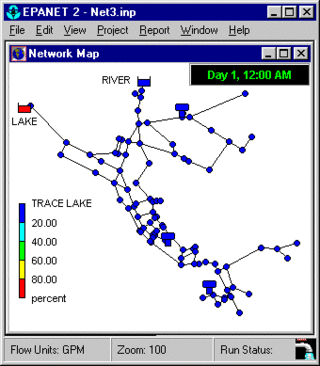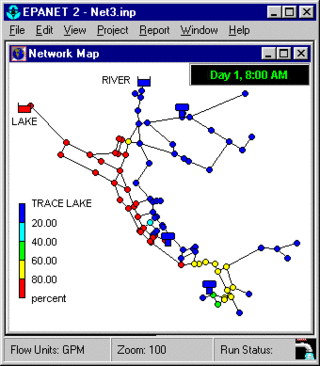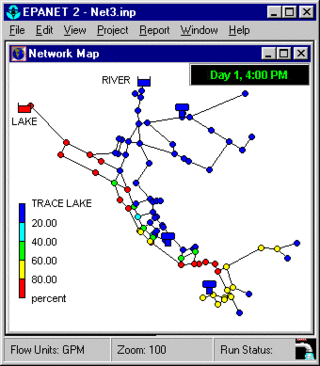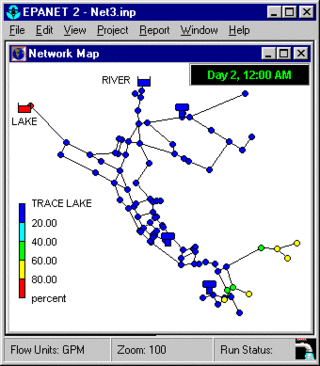
EPANET is a public domain, water distribution system modeling software package developed by the United States Environmental Protection Agency's (EPA) Water Supply and Water Resources Division. It performs extended-period simulation of hydraulic and water-quality behavior within pressurized pipe networks and is designed to be "a research tool that improves our understanding of the movement and fate of drinking-water constituents within distribution systems". EPANET first appeared in 1993.
Quantemol Ltd is based in University College London initiated by Professor Jonathan Tennyson FRS and Dr. Daniel Brown in 2004. The company initially developed a unique software tool, Quantemol-N, which provides full accessibility to the highly sophisticated UK molecular R-matrix codes, used to model electron polyatomic molecule interactions. Since then Quantemol has widened to further types of simulation, with plasmas and industrial plasma tools, in Quantemol-VT in 2013 and launched in 2016 a sustainable database Quantemol-DB, representing the chemical and radiative transport properties of a wide range of plasmas.
In Europe, the seasonal efficiency of refrigeration equipment, chillers and air conditioners is often rated by the European seasonal energy efficiency ratio (ESEER) which is controlled (among others) by the Eurovent Certification Company. A similar standard in the United States is the integrated energy efficiency ratio (IEER).

Digital Geometric Kernel, is a software development framework and a set of components for enabling 3D/CAD functionality in Windows applications, developed by DInsight.
The House Energy Rating (HER) or House Energy Rating Scheme (HERS) are worldwide standard measures of comparison by which one can evaluate the energy efficiency of a new or an existing building. The comparison is generally done for energy requirements for heating and cooling of indoor space. The energy is the main criterion considered by any international building energy rating scheme but there are some other important factors such as production of greenhouse gases emission, indoor environment quality, cost efficiency and thermal comfort, which are considered by some schemes. Basically, the energy rating of a residential building provides detailed information on the energy consumption and the relative energy efficiency of the building. Hence, HERs inform consumers about the relative energy efficiency of homes and encourage them to use this information in making their house purchase decision.

Building performance simulation (BPS) is the replication of aspects of building performance using a computer-based, mathematical model created on the basis of fundamental physical principles and sound engineering practice. The objective of building performance simulation is the quantification of aspects of building performance which are relevant to the design, construction, operation and control of buildings. Building performance simulation has various sub-domains; most prominent are thermal simulation, lighting simulation, acoustical simulation and air flow simulation. Most building performance simulation is based on the use of bespoke simulation software. Building performance simulation itself is a field within the wider realm of scientific computing.
A performance gap is a disparity that is found between the energy use predicted and carbon emissions in the design stage of buildings and the energy use of those buildings in operation. Research in the UK suggests that actual carbon emissions from new homes can be 2.5 times the design estimates, on average. For non-domestic buildings, the gap is even higher - actual carbon emissions as much as 3.8 times the design estimates, on average.








