
In engineering and its various subdisciplines, acceptance testing is a test conducted to determine if the requirements of a specification or contract are met. It may involve chemical tests, physical tests, or performance tests.

The World Wide Web is an information system that enables content sharing over the Internet through user-friendly ways meant to appeal to users beyond IT specialists and hobbyists. It allows documents and other web resources to be accessed over the Internet according to specific rules of the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP).

Interoperability is a characteristic of a product or system to work with other products or systems. While the term was initially defined for information technology or systems engineering services to allow for information exchange, a broader definition takes into account social, political, and organizational factors that impact system-to-system performance.
The rational unified process (RUP) is an iterative software development process framework created by the Rational Software Corporation, a division of IBM since 2003. RUP is not a single concrete prescriptive process, but rather an adaptable process framework, intended to be tailored by the development organizations and software project teams that will select the elements of the process that are appropriate for their needs. RUP is a specific implementation of the Unified Process.
Usability can be described as the capacity of a system to provide a condition for its users to perform the tasks safely, effectively, and efficiently while enjoying the experience. In software engineering, usability is the degree to which a software can be used by specified consumers to achieve quantified objectives with effectiveness, efficiency, and satisfaction in a quantified context of use.

MediaWiki is free and open-source wiki software originally developed by Magnus Manske for use on Wikipedia on January 25, 2002, and further improved by Lee Daniel Crocker, after which development has been coordinated by the Wikimedia Foundation. It powers several wiki hosting websites across the Internet, as well as most websites hosted by the Wikimedia Foundation including Wikipedia, Wiktionary, Wikimedia Commons, Wikiquote, Meta-Wiki and Wikidata, which define a large part of the set requirements for the software. Besides its usage on Wikimedia sites, MediaWiki has been used as a knowledge management and content management system on websites such as Fandom, wikiHow and major internal installations like Intellipedia and Diplopedia.
Web development is the work involved in developing a website for the Internet or an intranet. Web development can range from developing a simple single static page of plain text to complex web applications, electronic businesses, and social network services. A more comprehensive list of tasks to which Web development commonly refers, may include Web engineering, Web design, Web content development, client liaison, client-side/server-side scripting, Web server and network security configuration, and e-commerce development.
Software prototyping is the activity of creating prototypes of software applications, i.e., incomplete versions of the software program being developed. It is an activity that can occur in software development and is comparable to prototyping as known from other fields, such as mechanical engineering or manufacturing.
Social bookmarking is an online service which allows users to add, annotate, edit, and share bookmarks of web documents. Many online bookmark management services have launched since 1996; Delicious, founded in 2003, popularized the terms "social bookmarking" and "tagging". Tagging is a significant feature of social bookmarking systems, allowing users to organize their bookmarks and develop shared vocabularies known as folksonomies.

Web 2.0 refers to websites that emphasize user-generated content, ease of use, participatory culture, and interoperability for end users.
A web framework (WF) or web application framework (WAF) is a software framework that is designed to support the development of web applications including web services, web resources, and web APIs. Web frameworks provide a standard way to build and deploy web applications on the World Wide Web. Web frameworks aim to automate the overhead associated with common activities performed in web development. For example, many web frameworks provide libraries for database access, templating frameworks, and session management, and they often promote code reuse. Although they often target development of dynamic web sites, they are also applicable to static websites.
Web scraping, web harvesting, or web data extraction is data scraping used for extracting data from websites. Web scraping software may directly access the World Wide Web using the Hypertext Transfer Protocol or a web browser. While web scraping can be done manually by a software user, the term typically refers to automated processes implemented using a bot or web crawler. It is a form of copying in which specific data is gathered and copied from the web, typically into a central local database or spreadsheet, for later retrieval or analysis.
Google Developers is Google's site for software development tools and platforms, application programming interfaces (APIs), and technical resources. The site contains documentation on using Google developer tools and APIs—including discussion groups and blogs for developers using Google's developer products.
Morfik Technology Pty Ltd. is an Australian software company that was acquired by Altium in 2010.
InetSoft Technology Corporation is a privately owned multinational computer software company that develops free and commercial web-based business intelligence applications. The company was founded in 1996, and currently has over 120 employees between its corporate headquarters in Piscataway, New Jersey, and development offices in Beijing and Xi'an, China.

AnyLogic is a multimethod simulation modeling tool developed by The AnyLogic Company. It supports agent-based, discrete event, and system dynamics simulation methodologies. AnyLogic is cross-platform simulation software that works on Windows, macOS and Linux. AnyLogic is used to simulate: markets and competition, healthcare, manufacturing, supply chains and logistics, retail, business processes, social and ecosystem dynamics, defense, project and asset management, pedestrian dynamics and road traffic, IT, and aerospace. It is considered to be among the major players in the simulation industry, especially within the domain of business processes is acknowledged to be a powerful tool.
WebDNA is a server-side scripting, interpreted language with an embedded database system, specifically designed for the World Wide Web. Its primary use is in creating database-driven dynamic web page applications. Released in 1995, the name was registered as a trademark in 1998. WebDNA is currently maintained by WebDNA Software Corporation.
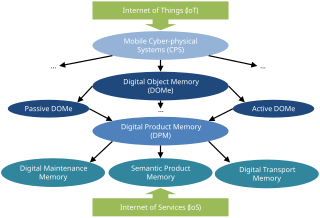
A digital object memory (DOMe) is a digital storage space intended to keep permanently all related information about a concrete physical object instance that is collected during the lifespan of this object and thus forms a basic building block for the Internet of Things (IoT) by connecting digital information with physical objects.
SafeDNS is a cybersecurity company specializing in providing cloud-based web filtering solutions and AI-powered technology. Its headquarters is in Alexandria, Virginia.

ABViewer is a software application for 2D/3D computer-aided design (CAD) developed by CADSoftTools in 2003. Its main features are viewing, editing, creating, converting, and printing CAD files. It is compatible with Windows and Linux with Wine and distributed as proprietary software. ABViewer is available in more than 30 languages.









