| IV Corps | |
|---|---|
| Active | 1950–present |
| Country | North Korea |
| Branch | Army |
| Type | infantry |
| Part of | Korean People's Army |
| Garrison/HQ | Haeju, South Hwanghae Province |
| Engagements | Korean War |
The IV Corps is a corps of the Korean People's Army of the Democratic People's Republic of Korea. It was established after the outbreak of the Korean War in June 1950.
Rottman writes that in July 1951 it comprised the 4th and 5th Divisions, the 105th Armoured Division, and the 26th Brigade. [1] By the ceasefire of July 1953, it comprised the 4th, 5th, and 10th Divisions. [2]
In 2001, it was responsible for the southwestern part of North Korea. [3] The corps is reportedly headquartered at Haeju, South Hwanghae Province.
This is the Korean War order of battle. Subsidiary commands are listed on sub-pages. Where no date is shown for a command, assume it present at the start of the war, on June 25, 1950.

The 1st Commonwealth Division was the military unit that commanded Commonwealth land forces in the Korean War. The division was a part of the multinational British Commonwealth Forces Korea, with infantry units of the British Army, Canadian Army and Australian Army forming the bulk of the division. Additionally, the New Zealand Army supplied artillery contingents and an Indian medical unit was also attached. As with the "Korean Augmentation To the United States Army" (KATUSA) programme, numerous South Korean troops were seconded to the Commonwealth division to make up numbers under a scheme known as "KATCOM".

The Marine Raiders were special operations forces originally established by the United States Marine Corps during World War II to conduct amphibious light infantry warfare. "Edson's" Raiders of 1st Marine Raider Battalion and "Carlson's" Raiders of 2nd Marine Raider Battalion are said to have been the first United States special operations forces to form and see combat during World War II.

The 1st Marine Division is a Marine division of the United States Marine Corps headquartered at Marine Corps Base Camp Pendleton, California. It is the ground combat element of the I Marine Expeditionary Force.

The 1st Provisional Marine Brigade was a marine brigade of the United States Marine Corps (USMC) that existed periodically from 1912 to 1950. It was an ad hoc unit formed for specific operations and not considered a "permanent" USMC unit.

The 7th Marine Regiment is an infantry regiment of the United States Marine Corps based at Marine Corps Air Ground Combat Center Twentynine Palms, California. Nicknamed the "Magnificent Seventh", the regiment falls under the command of the 1st Marine Division and the I Marine Expeditionary Force.

Marine Air Control Squadron 1 (MACS-1) is a United States Marine Corps aviation command and control squadron. The squadron provides aerial surveillance, air traffic control, ground-controlled intercept, and aviation data-link connectivity for the I Marine Expeditionary Force. It was the first air warning squadron commissioned as part of the Marine Corps' new air warning program and is the second oldest aviation command and control unit in the Marine Corps. The squadron is based at Marine Corps Air Station Yuma and falls under Marine Air Control Group 38 and the 3rd Marine Aircraft Wing.
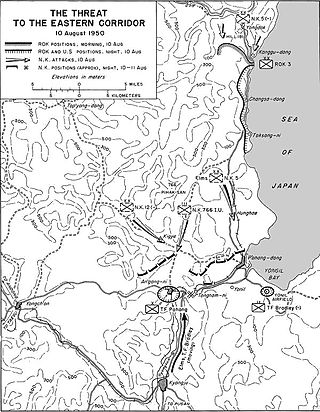
The 766th Independent Infantry Regiment was an elite light infantry unit of North Korea's Korean People's Army (KPA) that existed briefly during the Korean War. It was headquartered in Hoeryong, North Korea, and was also known as the 766th Unit. Trained extensively in amphibious warfare and unconventional warfare, the 766th Regiment was considered a commando unit. The regiment was trained to conduct assaults by sea and then to lead other North Korean units on offensive operations, to infiltrate behind enemy lines, and to disrupt enemy supplies and communications.
The 27th Infantry Division was a military formation of the Korean People's Army, as part of the II Corps.

The V Amphibious Corps (VAC) was a formation of the United States Marine Corps which was composed of the 3rd, 4th and 5th Marine Divisions in World War II. The three divisions were the amphibious landing force for the United States Fifth Fleet with two goals, removal of Japanese forces from islands so U.S. Seabees could build advance bases to project US power. In doing this VAC was notably involved in the battles for Tarawa, Saipan, and Iwo Jima. V Amphibious Corps was commanded by General Holland 'Howlin Mad' Smith followed by General Harry Schmidt.
The 60th Corps was a military formation of the People's Liberation Army. During the Korean War it formed part of the CPV/PLA III Army Group.
The 16th Marine Regiment was a composite engineer regiment of the United States Marine Corps subordinate to the 5th Marine Division. While its subordinate battalions went to the Pacific Theater as part of the 5th Marine Division, the Regimental headquarters was disbanded while still in the United States.
This is the order of battle for United Nations and North Korean forces during the Battle of Pusan Perimeter in August and September 1950 during the Korean War. The engagement brought each side to muster substantial ground, air and sea resources to fight across southeastern Korea.
Lee Kwon-mu, also known as Yi Kwon-mu or Ri Gwon-mu, was a North Korean general officer during the Korean War. He commanded a division, and later a corps, on the front line of the conflict and received North Korea's two highest military honours, the Hero of the Republic and the Order of the National Flag, First Class.
Operation Polecharge was an offensive undertaken by United Nations Command (UN) forces during the Korean War between 15–19 October 1951, following on from the successful Operation Commando which established the Jamestown Line.

This is the order of battle for Chinese People's Volunteer Army during major periods of hostilities in the Korean War. After the People's Republic of China entered the Korean War in October 1950 by designating the People's Liberation Army (PLA) North East Frontier Force as the People's Volunteer Army (PVA), the PVA spent the next two years and nine months in combat operations and five years and three months in garrison duties. Its last elements did not leave Korea until as late as 1958.
The III Corps is a corps of the Korean People's Army. It was created just before the North Korean invasion of 1950 with Lt. General Yu Kyong-su in command. During the initial North Korean invasion of the south, it was in reserve, comprising the 10th Infantry Division, the 13th Division, and the 15th Infantry Division.

The 2nd Heavy Combined Arms Brigade, originally the 2nd Tank Division, the 2nd Armored Division and the 2nd Armored Brigade, is an armored formation of the People's Liberation Army Ground Force of the People's Republic of China.
The 4th Aviation Division is a formation of the Chinese People's Liberation Army Air Force (PLAAF). Initially established in 1950, it served in Korea under Commander Fang Ziyi and Commissar Ye Songsheng, flying Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-15s. It ended its third combat tour in July 1953. It was soon redesignated the 1st Fighter Division.