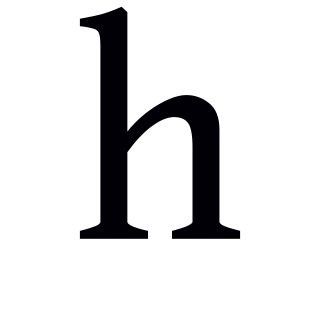Approximants are speech sounds that involve the articulators approaching each other but not narrowly enough nor with enough articulatory precision to create turbulent airflow. Therefore, approximants fall between fricatives, which do produce a turbulent airstream, and vowels, which produce no turbulence. This class is composed of sounds like and semivowels like and, as well as lateral approximants like.
An affricate is a consonant that begins as a stop and releases as a fricative, generally with the same place of articulation. It is often difficult to decide if a stop and fricative form a single phoneme or a consonant pair. English has two affricate phonemes, and, often spelled ch and j, respectively.
In phonetics and phonology, a semivowel, glide or semiconsonant is a sound that is phonetically similar to a vowel sound but functions as the syllable boundary, rather than as the nucleus of a syllable. Examples of semivowels in English are the consonants y and w in yes and west, respectively. Written in IPA, y and w are near to the vowels ee and oo in seen and moon, written in IPA. The term glide may alternatively refer to any type of transitional sound, not necessarily a semivowel.

The voiced alveolar approximant is a type of consonantal sound used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents the alveolar and postalveolar approximants is ⟨ɹ⟩, a lowercase letter r rotated 180 degrees. The equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is r\.
The voiced alveolar trill is a type of consonantal sound used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents dental, alveolar, and postalveolar trills is ⟨r⟩, and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is r. It is commonly called the rolled R, rolling R, or trilled R. Quite often, ⟨r⟩ is used in phonemic transcriptions of languages like English and German that have rhotic consonants that are not an alveolar trill. That is partly for ease of typesetting and partly because ⟨r⟩ is the letter used in the orthographies of such languages.

The voiced labiodental nasal is a type of consonantal sound. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨ɱ⟩. The IPA symbol is a lowercase letter m with a leftward hook protruding from the lower right of the letter. Occasionally it is instead transcribed as an with a dental diacritic: ⟨m̪⟩.

The voiced retroflex lateral approximant is a type of consonantal sound used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨ɭ ⟩, and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is l`.

The voiceless alveolar lateral fricative is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents voiceless dental, alveolar, and postalveolar lateral fricatives is, and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is K.
The voiced alveolar fricatives are consonantal sounds. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents these sounds depends on whether a sibilant or non-sibilant fricative is being described.
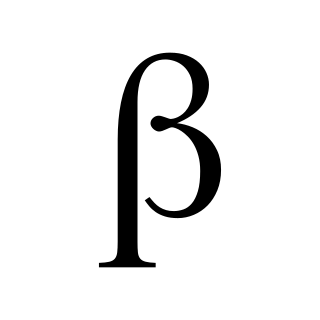
The voiced bilabial fricative is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨β⟩, and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is B. The official symbol ⟨β⟩ is the Greek letter beta.
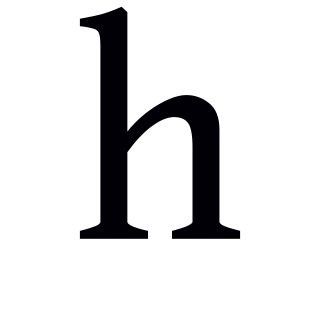
The voiceless glottal fricative, sometimes called voiceless glottal transition or the aspirate, is a type of sound used in some spoken languages that patterns like a fricative or approximant consonant phonologically, but often lacks the usual phonetic characteristics of a consonant. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨h⟩. However, has been described as a voiceless phonation because in many languages, it lacks the place and manner of articulation of a prototypical consonant, as well as the height and backness of a prototypical vowel:
[h and ɦ] have been described as voiceless or breathy voiced counterparts of the vowels that follow them [but] the shape of the vocal tract [...] is often simply that of the surrounding sounds. [...] Accordingly, in such cases it is more appropriate to regard h and ɦ as segments that have only a laryngeal specification, and are unmarked for all other features. There are other languages [such as Hebrew and Arabic] which show a more definite displacement of the formant frequencies for h, suggesting it has a [glottal] constriction associated with its production.

The voiceless labial–velar fricative is a type of consonantal sound, used in spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨xʷ⟩ or occasionally ⟨ʍ⟩. The letter ⟨ʍ⟩ was defined as a voiceless until 1979, when it was defined as a fricative with the place of articulation of the same way that is an approximant with the place of articulation of. However, the IPA Handbook treats it as both a "fricative".

The (near) open front rounded vowel, or (near) low front rounded vowel, is a type of vowel sound that has not been confirmed to be phonemic in any spoken language. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨ɶ⟩, and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is &. The letter ⟨ɶ⟩ is a small caps rendition of ⟨Œ⟩. ⟨œ⟩, the lowercase version of the ligature, is used for the open-mid front rounded vowel.

The open-mid central unrounded vowel, or low-mid central unrounded vowel, is a type of vowel sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨ɜ⟩. The IPA symbol is not the digit ⟨3⟩ or the Cyrillic small letter Ze (з). The symbol is instead a reversed Latinized variant of the lowercase epsilon, ɛ. The value was specified only in 1993; until then, ⟨ɜ⟩ was an alternative symbol for the mid central unrounded vowel.
In phonetics, nasalization is the production of a sound while the velum is lowered, so that some air escapes through the nose during the production of the sound by the mouth. Examples of archetypal nasal sounds include and.
In phonology, tenseness or tensing is, most broadly, the pronunciation of a sound with greater muscular effort or constriction than is typical. More specifically, tenseness is the pronunciation of a vowel with less centralization, longer duration, and narrower mouth width compared with another vowel. The opposite quality to tenseness is known as laxness or laxing: the pronunciation of a vowel with relatively more centralization, shorter duration, and more widening.
An obstruent is a speech sound such as, , or that is formed by obstructing airflow. Obstruents contrast with sonorants, which have no such obstruction and so resonate. All obstruents are consonants, but sonorants include vowels as well as consonants.

Peter Nielsen Ladefoged was a British linguist and phonetician. He was Professor of Phonetics at University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA), where he taught from 1962 to 1991. His book A Course in Phonetics is a common introductory text in phonetics, and The Sounds of the World's Languages is widely regarded as a standard phonetics reference. Ladefoged also wrote several books on the phonetics of African languages. Prior to UCLA, he was a lecturer at the universities of Edinburgh, Scotland and Ibadan, Nigeria (1959–60).
The voiceless bilabial nasal (stop) is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨⟩, a combination of the letter for the voiced bilabial nasal and a diacritic indicating voicelessness. The equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is m_0.

The voiceless alveolar nasal is a type of consonant in some languages. The symbols in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represent the sound are ⟨n̥⟩ and ⟨n̊⟩, combinations of the letter for the voiced alveolar nasal and a diacritic indicating voicelessness above or below the letter. The equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is n_0.