Related Research Articles

Sildenafil, sold under the brand name Viagra among others, is a medication used to treat erectile dysfunction and pulmonary arterial hypertension. It is also sometimes used off-label for the treatment of certain symptoms in secondary Raynaud's phenomenon. It is unclear if it is effective for treating sexual dysfunction in females. It can be taken orally, intravenously, or through the sublingual route. Onset when taken orally is typically within twenty minutes and lasts for about two hours.

Pfizer Inc. is an American multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology corporation headquartered at The Spiral in Manhattan, New York City. The company was established in 1849, in New York by two German entrepreneurs, Charles Pfizer (1824–1906) and his cousin Charles F. Erhart (1821–1891).
Robert Koffler Jarvik is an American scientist, researcher, and entrepreneur known for his role in developing the Jarvik-7 artificial heart.
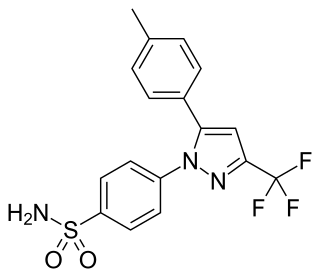
Celecoxib, sold under the brand name Celebrex among others, is a COX-2 inhibitor and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). It is used to treat the pain and inflammation in osteoarthritis, acute pain in adults, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, painful menstruation, and juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. It may also be used to decrease the risk of colorectal adenomas in people with familial adenomatous polyposis. It is taken by mouth. Benefits are typically seen within an hour.

Parke-Davis is a subsidiary of the pharmaceutical company Pfizer. Although Parke, Davis & Co. is no longer an independent corporation, it was once America's oldest and largest drug maker, and played an important role in medical history. In 1970 Parke-Davis was acquired by Warner–Lambert, which in turn was acquired by Pfizer in 2000.
G.D. Searle, LLC is a wholly owned subsidiary of Pfizer. It is currently a trademark company and subsidiary of Pfizer, operating in more than 43 countries. It also operates as a distribution trademark for various pharmaceuticals that were developed by G. D. Searle & Company. Searle is most notable for having developed the first female birth control pill, and the artificial sweetener NutraSweet. Searle also developed the drug Lomotil, an antidiarrheal medication. One notable alumnus of Searle is Donald Rumsfeld, the Secretary of Defense for George W. Bush in the 2000s. Prior to its 1985 merger with Monsanto, Searle was a company mainly focusing on life sciences, specifically pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and animal health.

Karl Christian Friedrich Pfizer, known as Charles Pfizer, was a German-American businessman and chemist who co-founded the Pfizer pharmaceutical company with his cousin, Charles F. Erhart, in 1849, as Chas. Pfizer & Co. Inc.

King Pharmaceuticals, Inc. is a pharmaceutical company, a wholly owned subsidiary of Pfizer based in Bristol, Tennessee. Before being acquired by Pfizer, it was the world's 39th largest pharmaceutical company. On October 12, 2010, King was acquired by Pfizer for $14.25 per share. King produced a wide range of pharmaceuticals, including Altace for heart attack prevention, Levoxyl for hypothyroidism, Sonata, a sleeping aid, and Skelaxin, a muscle relaxant. King Pharmaceuticals operated manufacturing facilities in Bristol, Tennessee; Rochester, Michigan; St. Louis, Missouri; St. Petersburg, Florida; and Middleton, Wisconsin. They employed approximately 2,700 people including a sales force of over 1,000 individuals.

The Upjohn Company was an American pharmaceutical manufacturing firm in Hastings, Michigan, by Dr. William E. Upjohn, a 1875 graduate of the University of Michigan medical school. The company was originally formed to make friable pills, specifically designed to be easily digested. These pills could be "reduced to a powder under the thumb", which is how they were initially marketed.

Latrepirdine is an antihistamine drug which has been used clinically in Russia since 1983.
Events from the year 1849 in the United States.
Warner–Lambert was an American pharmaceutical company.

Wyeth Pharmaceuticals Inc. was a pharmaceutical company until it was purchased by Pfizer in 2009. The company was founded in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, in 1860 as John Wyeth and Brother. Its headquarters moved to Collegeville, Pennsylvania, and Madison, New Jersey, before its headquarters were consolidated with Pfizer's in New York City after the 2009 merger.
The Pfizer Award in Enzyme Chemistry, formerly known as the Paul-Lewis Award in Enzyme Chemistry was established in 1945. Consisting of a gold medal and honorarium, its purpose is to stimulate fundamental research in enzyme chemistry by scientists not over forty years of age. The award is administered by the Division of Biological Chemistry of the American Chemical Society and sponsored by Pfizer. The award was terminated in 2022.
Nestlé-Wyeth Nutrition provides food products to meet the needs of infants, young children and adults. Through scientific research, they claim to help nourish children when breastfeeding is not an option. Wyeth Nutrition started in 1915 when Henry Grestberger manufactured the first formula patterned after breast milk called SMA. Wyeth Pharmaceuticals, formerly Wyeth-Ayerst Laboratories, is the original company founded by the Wyeth brothers, originally known as John Wyeth and Brother. They focused on the research, development, and marketing of prescription drugs. The pharmaceuticals division was further subdivided into five subdivisions: Wyeth Research, Prescription Products, Biotech, Vaccines, and Nutritionals. Wyeth's research and development director Robert Ruffolo was quoted in The New York Times about the firm's efforts to develop new drugs.

Operation Warp Speed (OWS) was a public–private partnership initiated by the United States government to facilitate and accelerate the development, manufacturing, and distribution of COVID-19 vaccines, therapeutics, and diagnostics. The first news report of Operation Warp Speed was on April 29, 2020, and the program was officially announced on May 15, 2020. It was headed by Moncef Slaoui from May 2020 to January 2021 and by David A. Kessler from January to February 2021. At the end of February 2021, Operation Warp Speed was transferred into the responsibilities of the White House COVID-19 Response Team.
The Pfizer–BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine, sold under the brand name Comirnaty, is an mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccine developed by the German biotechnology company BioNTech. For its development, BioNTech collaborated with the American company Pfizer to carry out clinical trials, logistics, and manufacturing. It is authorized for use in humans to provide protection against COVID-19, caused by infection with the SARS-CoV-2 virus. The vaccine is given by intramuscular injection. It is composed of nucleoside-modified mRNA (modRNA) that encodes a mutated form of the full-length spike protein of SARS-CoV-2, which is encapsulated in lipid nanoparticles. Initial guidance recommended a two-dose regimen, given 21 days apart; this interval was subsequently extended to up to 42 days in the United States, and up to four months in Canada.

The COVID-19 vaccination campaign in Albania is a mass immunization campaign that was put in place by the Albanian authorities in order to respond to the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. It started on 11 January 2021.

COVID-19 vaccination in Norway is an ongoing immunization campaign against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the virus that causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), in response to the ongoing pandemic in the country. As of 21 June 2022 80.5% of the population have been vaccinated with the first dose, 75.1% with the second dose and 55.9% with at least one additional dose. As of 09 March 2023, a total of 14,443,131 vaccine doses has been distributed in Norway.
References
- ↑ Roberts, William; Roberts, William Clifford (2000). Facts and Ideas from Anywhere. Wiley-Blackwell. p. 103. ISBN 978-0-87993-463-7 . Retrieved 26 September 2010.