Related Research Articles

Sicily is an island in the central Mediterranean Sea, south of the Italian Peninsula in continental Europe and is one of the 20 regions of Italy. With 4.8 million inhabitants, including 1.3 million in and around the capital city of Palermo, it is the most populous island in the Mediterranean Sea. It is named after the Sicels, who inhabited the eastern part of the island during the Iron Age. Sicily has a rich and unique culture in arts, music, literature, cuisine, and architecture. Its most prominent landmark is Mount Etna, the tallest active volcano in Europe, and one of the most active in the world, currently 3,357 m (11,014 ft) high. The island has a typical Mediterranean climate. It is separated from Calabria by the Strait of Messina. It is one of the five Italian autonomous regions and is generally considered part of Southern Italy.

Palermo is a city in southern Italy, the capital of both the autonomous region of Sicily and the Metropolitan City of Palermo, the city's surrounding metropolitan province. The city is noted for its history, culture, architecture and gastronomy, playing an important role throughout much of its existence; it is over 2,700 years old. Palermo is in the northwest of the island of Sicily, by the Gulf of Palermo in the Tyrrhenian Sea.

Year 902 (CMII) was a common year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar.

Roger II or Roger the Great was King of Sicily and Africa, son of Roger I of Sicily and successor to his brother Simon. He began his rule as Count of Sicily in 1105, became Duke of Apulia and Calabria in 1127, then King of Sicily in 1130 and King of Africa in 1148.

Roger I, nicknamed “Roger Bosso” and “Grand Count Roger”, was a Norman nobleman who became the first Grand Count of Sicily from 1071 to 1101.
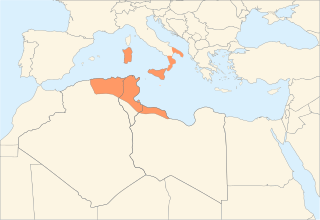
The Aghlabid dynasty was an Arab dynasty centered in Ifriqiya from 800 to 909 that conquered parts of Sicily, Southern Italy, and possibly Sardinia, nominally as vassals of the Abbasid Caliphate. The Aghlabids were from the tribe of Banu Tamim and adhered to the Mu'tazilite rationalist doctrine within Hanafi Sunni Islam, which they imposed as the state doctrine of Ifriqiya. They ruled until 909 when they were conquered by the new power of the Fatimids.

The Kalbids were a Muslim Arab dynasty which ruled the Emirate of Sicily from 948 to 1053. They were formally appointed by the Fatimids, but gained, progressively, de facto autonomous rule.

Abu Muhammad Ziyadat Allah I ibn Ibrahim ibn al-Aghlab was the Aghlabid ruler (amir) of Ifriqiya from 817 until his death in 838. His reign marked a shift towards greater control and stability for the emirs in Ifriqiya.

Abu Ishaq Ibrahim II ibn Ahmad was the Emir of Ifriqiya. He ruled from 875 until his abdication in 902. After the demise of his brother, Ibrahim was endorsed as emir where he took steps to improve safety in his domain and secured the development of commercial activities. He improved public works, such as building a vast reservoir, erecting walls as well as the development of mosques and his Raqqada palace.

The island of Sicily was under Islamic rule from the late ninth to late eleventh centuries. It became a prosperous and influential commercial power in the Mediterranean, with its capital of Palermo serving as a major cultural and political center of the Muslim world.

Misilmeri is a town and comune in the Metropolitan City of Palermo, Sicily. It is approximately 15 kilometres (9 mi) from Palermo and its name means "the resting place or the messuage of the Emir", and dates from the Muslim emirate of Sicily. The village rose around a castle founded by emir Jafar II (998–1019). In 1068 the Battle of Misilmeri was fought between the Normans and Arabs

The history of Islam in Sicily and southern Italy began with Arab colonization in Sicily, at Mazara, which was captured in 827. The subsequent rule of Sicily and Malta started in the 10th century. The Emirate of Sicily lasted from 831 until 1061, and controlled the whole island by 902. Though Sicily was the primary Muslim stronghold in Italy, some temporary footholds, the most substantial of which was the port city of Bari, were established on the mainland peninsula, especially in mainland southern Italy, though Arab raids, mainly those of Muhammad I ibn al-Aghlab, reached as far north as Naples, Rome and the northern region of Piedmont. The Arab raids were part of a larger struggle for power in Italy and Europe, with Christian Byzantine, Frankish, Norman and indigenous Italian forces also competing for control. Arabs were sometimes allied with various Christian factions against other factions.

The Muslim conquest of Sicily began in June 827 and lasted until 902, when the last major Byzantine stronghold on the island, Taormina, fell. Isolated fortresses remained in Byzantine hands until 965, but the island was henceforth under Muslim rule until conquered in turn by the Normans in the 11th century.

The term Norman–Arab–Byzantine culture, Norman–Sicilian culture or, less inclusively, Norman–Arab culture, refers to the interaction of the Norman, Byzantine Greek, Latin, and Arab cultures following the Norman conquest of the former Emirate of Sicily and North Africa from 1061 to around 1250. The civilization resulted from numerous exchanges in the cultural and scientific fields, based on the tolerance shown by the Normans towards the Latin- and Greek-speaking Christian populations and the former Arab Muslim settlers. As a result, Sicily under the Normans became a crossroad for the interaction between the Norman and Latin Catholic, Byzantine–Orthodox, and Arab–Islamic cultures.
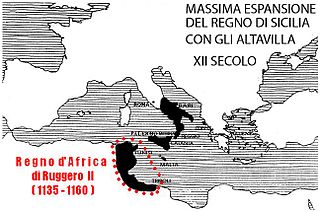
The Kingdom of Africa was an extension of the frontier zone of the Kingdom of Sicily in the former Roman province of Africa, corresponding to Tunisia and parts of Algeria and Libya today. The main primary sources for the kingdom are Arabic (Muslim); the Latin (Christian) sources are scanter.
Al-Hasan ibn Ali ibn Abi al-Husayn al-Kalbi, known in Byzantine sources as Boulchasenes and Aboulchare (Ἀβουλχαρέ), was the first Kalbid Emir of Sicily. A member of an aristocratic family within the ruling circle of the Fatimid Caliphate, he helped suppress the great revolt of Abu Yazid in 943–947 and was sent as governor of Sicily from 948 until 953, when he returned to Ifriqiya. He was succeeded in Sicily by his son Ahmad ibn al-Hasan al-Kalbi, but led several campaigns in Sicily and southern Italy against the Byzantines in 955–958, as well as the raid against Almeria that sparked a brief conflict with the Caliphate of Córdoba in 955. He died at Palermo in 964, during another campaign against the Byzantines.

The siege of Melite was the capture of the Byzantine city of Melite by an invading Aghlabid army in 870 AD. The siege was initially led by Halaf al-Hādim, a renowned engineer, but he was killed and replaced by Sawāda Ibn Muḥammad. The city withstood the siege for some weeks or months, but it ultimately fell to the invaders, and its inhabitants were massacred and the city was sacked.
Ahmad ibn Ziyadat Allah ibn Qurhub, commonly known simply as Ibn Qurhub, ruled Sicily in rebellion against the Fatimid Caliphate, from 913 to 916. He launched raids against the Byzantine Empire in southern Italy and against the shores of Fatimid Ifriqiya, but was deposed and handed over to the Fatimids, who executed him and his followers in July 916.
Salim ibn Asad ibn Abi Rashid was the governor of Sicily for the Fatimid Caliphate for twenty years, from 917 to 937.

The siege of Taormina in 902 ended the conquest of the Byzantine city of Taormina, in northeastern Sicily, by the Aghlabids. The campaign was led by the deposed Aghlabid emir, Ibrahim II, as a form of armed pilgrimage and holy war. Ibrahim's forces defeated the Byzantine garrison in a hard-fought battle in front of the city walls, and laid siege to the city. Left unsupported by the Byzantine government, Taormina capitulated on 1 August. The population was massacred or sold into slavery. The fall of this last major Byzantine stronghold signalled the completion of the Muslim conquest of Sicily, which had been ongoing since the 820s, although some minor Byzantine outposts survived until the 960s.
References
- ↑ various editors. The Cambridge Medieval History volumes 1-5. Plantagenet Publishing. Retrieved 28 March 2021.
{{cite book}}:|last1=has generic name (help) - ↑ Amari, Michele (1834). Storia dei Musulmani di Sicilia. Florence: Felice le Monnier. p. 529. Retrieved 28 March 2021.
- ↑ Ali, Ameer (2004). A Short History of the Saracens. London: Routledge. p. 586. ISBN 9781136198946 . Retrieved 28 March 2021.
- ↑ Bostom, Andrew G. (2010). The Legacy of Jihad: Islamic Holy War and the Fate of Non-Muslims. Prometheus Books. p. 603. Retrieved 28 March 2021.[ permanent dead link ]