Ichthyosis vulgaris is a skin disorder causing dry, scaly skin. It is the most common form of ichthyosis, affecting around 1 in 250 people. For this reason it is known as common ichthyosis. It is usually an autosomal dominant inherited disease, although a rare non-heritable version called acquired ichthyosis exists.

Lamellar ichthyosis, also known as ichthyosis lamellaris and nonbullous congenital ichthyosis, is a rare inherited skin disorder, affecting around 1 in 600,000 people.
Ichthyosis acquisita is a disorder clinically and histologically similar to ichthyosis vulgaris.
Keratoderma is a hornlike skin condition.

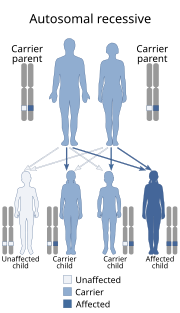
Sjögren–Larsson syndrome (SLS) is an autosomal recessive form of ichthyosis apparent at birth. Sjögren–Larsson syndrome is a rare autosomal, recessive, neurocutaneous disease. This disease can be identified by a triad of medical disorders. The first is ichthyosis, which is a buildup of skin to form a scale-like covering that causes dry skin and other problems. The second identifier is paraplegia which is characterized by leg spasms. The final identifier is intellectual delay. The gene of SLS is found on chromosome 17. In order for a child to receive SLS both parents must be carriers of the SLS gene. If they are carriers their child has a ¼ chance of getting the disease. In 1957 Sjogren and Larsson proposed that the Swedes with the disease all descended from a common ancestor 600 years ago. Today only 30–40 persons in Sweden have this disease.
Genodermatoses are inherited genetic skin conditions often grouped into three categories: chromosomal, single gene, and polygenetic.
Restrictive dermopathy is a rare, lethal autosomal recessive skin condition characterized by syndromic facies, tight skin, sparse or absent eyelashes, and secondary joint changes.

Ichthyosis bullosa of Siemens is a type of familial, autosomal dominant ichthyosis, a rare skin disorder. It is also known as bullous congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma of Siemens or ichthyosis exfoliativa. It is a genetic disorder with no known cure which is estimated to affect about 1 in 500,000 people.
Congenital Ichthyosiform Erythroderma (CIE), also known as Nonbullous congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma is a rare type of the ichthyosis family of skin diseases which occurs in 1 in 200,000 to 300,000 births.

IFAP syndrome is an extremely rare genetic syndrome. It is also known as Ichthyosis follicularis, alopecia, and photophobia syndrome or simply ichthyosis follicularis. It is extremely rare: there were only 10 known cases in 1998.
Rud syndrome is a poorly characterized disorder, probably of X-linked recessive inheritance, named after Einar Rud who described 2 patients with the case in 1927 and 1929. It was argued that all reported cases of Rud syndrome are genetically heterogeneous and significantly differ from the original case reports of Rud and that the designation Rud syndrome should be eliminated and that the patients with such diagnosis should be reassigned to other syndromes, such as Refsum disease and Sjögren-Larsson syndrome. Some consider Rud syndrome and Sjögren-Larsson syndrome the same entity and that Rud syndrome doesn't exist.

Neutral lipid storage disease is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by accumulation of triglycerides in the cytoplasm of leukocytes, muscle, liver, fibroblasts, and other tissues. It commonly occurs as one of two subtypes, cardiomyopathic neutral lipid storage disease (NLSD-M), or ichthyotic neutral lipid storage disease (NLSD-I), which are characterized primarily by cardiomyopathy and ichthyosis, respectively.
Ichthyosis hystrix is a group of rare skin disorders in the ichthyosis family of skin disorders characterized by massive hyperkeratosis with an appearance like spiny scales. This term is also used to refer to a type of epidermal nevi with extensive bilateral distribution.
Keratitis–ichthyosis–deafness syndrome presents at birth/infancy and is characterized by progressive corneal opacification, either mild generalized hyperkeratosis or discrete erythematous plaques, and neurosensory deafness.
Senter syndrome is a cutaneous condition characterized by similar skin changes and congenital hearing impairment to keratitis–ichthyosis–deafness syndrome, but is associated with glycogen storage leading to hepatomegaly, hepatic cirrhosis, growth failure and mental retardation.
Trichorrhexis invaginata is a distinctive hair shaft abnormality that may occur sporadically, either in normal hair or with other hair shaft abnormalities, or regularly as a marker for Netherton's syndrome. The primary defect appears to be abnormal keratinization of the hair shaft in the keratogenous zone, allowing for intussusception of the fully keratinized and hard distal shaft into the incompletely keratinized and soft proximal portion of the shaft.
Keratosis pilaris atropicans includes many forms of keratosis pilaris with cicatricial alopecia. Variants include keratosis pilaris atrophicans faciei, atrophoderma vermiculatum, keratosis follicularis spinulosa decalvans, and ichthyosis follicularis.
Neonatal ichthyosis–sclerosing cholangitis syndrome is a cutaneous condition caused by mutations in the Claudin 1 gene.