Related Research Articles
In telecommunication, a filled cable is a cable that has a non-hygroscopic material, usually a gel called icky-pick, inside the jacket or sheath. The nonhygroscopic material fills the spaces between the interior parts of the cable, preventing moisture from entering minor leaks in the sheath and migrating inside the cable.
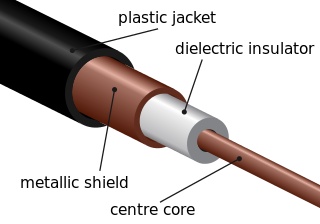
A transmission medium is a system or substance that can mediate the propagation of signals for the purposes of telecommunication. Signals are typically imposed on a wave of some kind suitable for the chosen medium. For example, data can modulate sound, and a transmission medium for sounds may be air, but solids and liquids may also act as the transmission medium. Vacuum or air constitutes a good transmission medium for electromagnetic waves such as light and radio waves. While a material substance is not required for electromagnetic waves to propagate, such waves are usually affected by the transmission media they pass through, for instance, by absorption or reflection or refraction at the interfaces between media. Technical devices can therefore be employed to transmit or guide waves. Thus, an optical fiber or a copper cable is used as transmission media.
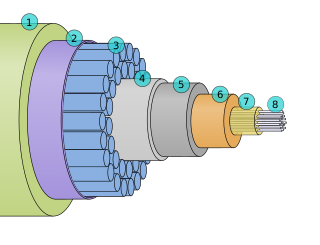
A submarine communications cable is a cable laid on the seabed between land-based stations to carry telecommunication signals across stretches of ocean and sea. The first submarine communications cables were laid beginning in the 1850s and carried telegraphy traffic, establishing the first instant telecommunications links between continents, such as the first transatlantic telegraph cable which became operational on 16 August 1858.

Telecommunications in Armenia involves the availability and use of electronic devices and services, such as the telephone, television, radio or computer, for the purpose of communication. The various telecommunications systems found and used in Armenia includes radio, television, fixed and mobile telephones, and the internet.
A mechanical splice is a junction of two or more optical fibers that are aligned and held in place by a self-contained assembly. The fibers are not permanently joined, just precisely held together so that light can pass from one to another. This impermanence is an important advantage over fusion splicing, as splice loss, the amount of power that the splice fails to transmit, can be better measured and prevented.

An optical fiber connector is a device used to link optical fibers, facilitating the efficient transmission of light signals. An optical fiber connector enables quicker connection and disconnection than splicing.

A patch cable, patch cord or patch lead is an electrical or fiber-optic cable used to connect one electronic or optical device to another for signal routing. Devices of different types are connected with patch cords.

Multi-mode optical fiber is a type of optical fiber mostly used for communication over short distances, such as within a building or on a campus. Multi-mode links can be used for data rates up to 800 Gbit/s. Multi-mode fiber has a fairly large core diameter that enables multiple light modes to be propagated and limits the maximum length of a transmission link because of modal dispersion. The standard G.651.1 defines the most widely used forms of multi-mode optical fiber.

An optical fiber, or optical fibre, is a flexible glass or plastic fiber that can transmit light from one end to the other. Such fibers find wide usage in fiber-optic communications, where they permit transmission over longer distances and at higher bandwidths than electrical cables. Fibers are used instead of metal wires because signals travel along them with less loss and are immune to electromagnetic interference. Fibers are also used for illumination and imaging, and are often wrapped in bundles so they may be used to carry light into, or images out of confined spaces, as in the case of a fiberscope. Specially designed fibers are also used for a variety of other applications, such as fiber optic sensors and fiber lasers.
Hitachi Cable, Ltd. is a Japanese electric wire and cable manufacturing company. It was formed from Hitachi Densen Works, the Hitachi Works spin-off previously known as Densen Works.

Fiber-optic communication is a method of transmitting information from one place to another by sending pulses of infrared or visible light through an optical fiber. The light is a form of carrier wave that is modulated to carry information. Fiber is preferred over electrical cabling when high bandwidth, long distance, or immunity to electromagnetic interference is required. This type of communication can transmit voice, video, and telemetry through local area networks or across long distances.
Cable compounds are materials used to prevent the ingress of moisture into telecommunication and power transmission cables. The compound used varies depending upon the type of cable; generally, they are either soft waxy compounds, soft thixotropic gels with a consistency similar to that of hair gel, or resin/polymer thickened oils. A cable with such a compound is called a filled cable. Cable compounds are formulated and manufactured to have very good electrical resistance properties to ensure good functioning of the filled cable.
An optical ground wire is a type of cable that is used in overhead power lines. Such cable combines the functions of grounding and communications. An OPGW cable contains a tubular structure with one or more optical fibers in it, surrounded by layers of steel and aluminum wire. The OPGW cable is run between the tops of high-voltage electricity pylons. The conductive part of the cable serves to bond adjacent towers to earth ground, and shields the high-voltage conductors from lightning strikes. The optical fibers within the cable can be used for high-speed transmission of data, either for the electrical utility's own purposes of protection and control of the transmission line, for the utility's own voice and data communication, or may be leased or sold to third parties to serve as a high-speed fiber interconnection between cities.

Direct-buried cable (DBC) is a kind of communications or transmissions electrical cable which is especially designed to be buried under the ground without any other cover, sheath, or duct to protect it.
Hydrogen darkening is a physical degradation of the optical properties of glass. Free hydrogen atoms are able to bind to the SiO2 silica glass compound forming hydroxyl (OH)—a chemical compound that interferes with the passage of light through the glass.

A fiber-optic cable, also known as an optical-fiber cable, is an assembly similar to an electrical cable but containing one or more optical fibers that are used to carry light. The optical fiber elements are typically individually coated with plastic layers and contained in a protective tube suitable for the environment where the cable is used. Different types of cable are used for fiber-optic communication in different applications, for example long-distance telecommunication or providing a high-speed data connection between different parts of a building.
Hairstyle products are used to change the texture and/or shape of hair.
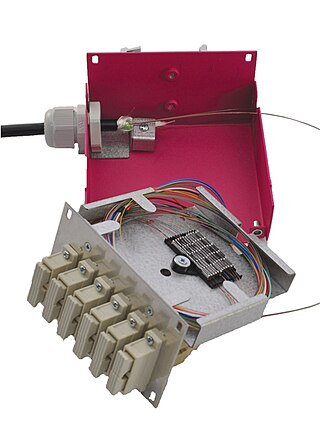
A splice box is a housing in which fiber optic cables begin or end. Fiber optics are fanned out in splice boxes that are situated at the end of fiber optic transmission paths.

Copper has been used in electrical wiring since the invention of the electromagnet and the telegraph in the 1820s. The invention of the telephone in 1876 created further demand for copper wire as an electrical conductor.
All-dielectric self-supporting (ADSS) cable is a type of optical fiber cable that is strong enough to support itself between structures without using conductive metal elements. It is used by electrical utility companies as a communications medium, installed along existing overhead transmission lines and often sharing the same support structures as the electrical conductors.
References
- ↑ Froehlich, F.E.; Kent, A. (1993). The Froehlich/Kent Encyclopedia of Telecommunications: Volume 7 - Electrical Filters: Fundamentals and System Applications to Federal Communications Commission of the United States. Encyclopedia of Telecommunicat. Taylor & Francis. ISBN 978-0-8247-2905-9 . Retrieved 2022-06-14.
- ↑ Debiec, Thomas (Jan 1, 2001). "Picking the ick out of outside plant cable" . Retrieved 2022-06-12.