Related Research Articles

The No Child Left Behind Act of 2001 (NCLB) was a 2002 U.S. Act of Congress promoted by the presidency of George W. Bush. It reauthorized the Elementary and Secondary Education Act and included Title I provisions applying to disadvantaged students. It mandated standards-based education reform based on the premise that setting high standards and establishing measurable goals could improve individual outcomes in education. To receive federal school funding, states had to create and give assessments to all students at select grade levels.
ISAT can stand for:
The New England Common Assessment Program was a series of reading, writing, mathematics and science achievement tests, administered annually, which were developed in response to the Federal No Child Left Behind Act. Starting in 2005, school students in New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont participated in NECAP, and Maine joined the assessment program in 2009. It was a collaborative project of the New Hampshire, Rhode Island and Vermont departments of education, with assistance from the National Center for the Improvement of Educational Assessments. Measured Progress, an assessment contractor from Dover, New Hampshire, coordinates production, administration, scoring and reporting.

The National Assessment of Educational Progress (NAEP) is the largest continuing and nationally representative assessment of what U.S. students know and can do in various subjects. NAEP is a congressionally mandated project administered by the National Center for Education Statistics (NCES), within the Institute of Education Sciences (IES) of the United States Department of Education. The first national administration of NAEP occurred in 1969. The National Assessment Governing Board (NAGB) is an independent, bipartisan board that sets policy for NAEP and is responsible for developing the framework and test specifications.The National Assessment Governing Board, whose members are appointed by the U.S. Secretary of Education, includes governors, state legislators, local and state school officials, educators, business representatives, and members of the general public. Congress created the 26-member Governing Board in 1988.
The Standards of Learning (SOL) is a public school standardized testing program in the Commonwealth of Virginia. It sets forth learning and achievement expectations for core subjects for grades K-12 in Virginia's Public Schools. The standards represent what many teachers, school administrators, parents, and business and community leaders believe schools should teach and students should learn. The Virginia Department of Education, schools, and school systems routinely receive essential feedback on the effectiveness of implementation and address effective instructional strategies and best practices. The Standards of Learning is supportive of the No Child Left Behind Act, which was signed into law by then-President George W. Bush on January 8, 2002. They address student achievement in four critical areas: (1) English, (2) mathematics, (3) science, and (4) history/social studies. Students are assessed in English and mathematics in grades 3-8 and upon completion of certain high school level courses. Science and history SOL are administered in grades 4, 5, and 8 and at the end of completing high school courses in these respective subjects.
Adequate Yearly Progress (AYP) was a measurement defined by the United States federal No Child Left Behind Act that allowed the U.S. Department of Education to determine how every public school and school district in the country was performing academically according to results on standardized tests. As defined by National Council on Measurement in Education (NCME), AYP was "the amount of annual achievement growth to be expected by students in a particular school, district, or state in the U.S. federal accountability system, No Child Left Behind (NCLB)." AYP has been identified as one of the sources of controversy surrounding George W. Bush administration's Elementary and Secondary Education Act. Private schools were not required to make AYP.
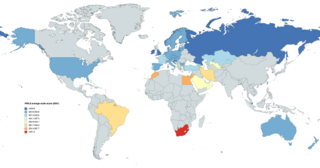
The IEA's Progress in International Reading Literacy Study (PIRLS) is an international study of reading (comprehension) achievement in 9-10 year olds. It has been conducted every five years since 2001 by the International Association for the Evaluation of Educational Achievement (IEA). It is designed to measure children's reading literacy achievement, to provide a baseline for future studies of trends in achievement, and to gather information about children's home and school experiences in learning to read.

The New Jersey Department of Education administers state and federal aid programs affecting more than 1.4 million public and non-public elementary and secondary school children in the state of New Jersey. The department is headquartered in the Judge Robert L. Carter Building in Trenton.
Accelerated Reader (AR) is an educational program created by Renaissance Learning. It is designed to monitor and manage students' independent reading practice and comprehension in both English and Spanish. The program assesses students' performance through quizzes and tests based on the books they have read. As the students read and take quizzes, they are awarded points. AR monitors students' progress and establishes personalised reading goals according to their reading levels.

Shelley High School is an institution for public education in the town of Shelley, Idaho, United States. It is the city's only high school, and is nicknamed "the spud cellar" because of its unique mascot and resemblance to a potato cellar. The mascot, King Russet, is a Russet Burbank potato with a scepter and crown. The approximately 600 students, called Russets, receive two weeks of break in late September because some of them work in the local potato harvest.

Skyview High School is a four-year public secondary school in Nampa, Idaho. Opened in 1996, it is the second of three traditional high schools operated by the Nampa School District #131. Skyview is on a block schedule, with students taking 4 classes on A day and 4 classes on B day.
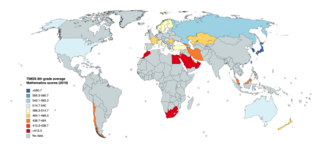
The International Association for the Evaluation of Educational Achievement (IEA)'s Trends in International Mathematics and Science Study (TIMSS) is a series of international assessments of the mathematics and science knowledge of students around the world. The participating students come from a diverse set of educational systems in terms of economic development, geographical location, and population size. In each of the participating educational systems, a minimum of 4,000 to 5,000 students is evaluated. Contextual data about the conditions in which participating students learn mathematics and science are collected from the students and their teachers, their principals, and their parents via questionnaires.

DeWitt Clinton School is a Chicago Public School on the north side of Chicago, Illinois.
Libertyville District 70 is located in Libertyville, Illinois, about 35 miles north of Chicago in the suburbs.
Lincolnshire-Prairie View School District 103 is an elementary district located in Lincolnshire Lake County, Illinois, in suburban Chicago. The school district serves approximately 1,800 students from the communities of Lincolnshire and Prairie View and portions of Buffalo Grove, Vernon Hills, Mettawa, Riverwoods, and Lake Forest. Students attend Laura B. Sprague Elementary School (K-2), Half Day Intermediate School (3-5) and Daniel Wright Junior High Schools (6-8). Students from this district usually would later attend Adlai E. Stevenson High School which is also located within Lincolnshire.
The Illinois Standards Achievement Test (ISAT) measured individual student achievement based on the Illinois Learning Standards. The results of this score were applied to the No Child Left Behind Act, to identify failing schools. The ISAT was retired as a state assessment tool. The ISAT was last administered in the 2013–2014 school year.
The Lexile Framework for Reading is an educational tool that uses a measure called a Lexile to match readers with reading resources such as books and articles. Readers and texts are assigned a Lexile score, where lower scores reflect easier readability for texts and lower reading ability for readers. Lexile scores are assigned based on individual words and sentence length, rather than qualitative analysis of the content. Thus, Lexile scores do not reflect multiple levels of textual meaning or the maturity of the content. The United States Common Core State Standards recommend the use of alternative, qualitative methods to select books for grade 6 and above. In the U.S., Lexile measures are reported annually from reading programs and assessments. According to LightSail Education, about half of U.S. students in grades 3-12 receive a Lexile measure each year. The Georgia Department of Education provides resources for using Lexile measures.

The Idaho Department of Education is an executive agency of the Idaho state education system. The department is responsible for public elementary and secondary school matters as provided by Title 33, Idaho Code, or as determined by the Idaho State Board of Education. It is headquartered in the state capital, Boise, Idaho.
ISE, formerly known as the International School Eastern Seaboard, is a private, co-educational international school founded in 1994. ISE sets amidst the rolling hills of the Burapha Golf Course in Chonburi province, Thailand, and offers an American style international curriculum, presented in English from Pre-school through Grade 12. The school also offers the International Baccalaureate (IB) program in the High School. ISE is fully accredited through The Western Association of Schools and Colleges.
References
- ↑ "ISAT Assessments". Idaho State Department of Education . Retrieved March 22, 2017.
- ↑ "Idaho State Department of Education (SDE)". SDE. Retrieved 2021-12-08.