
Polyvinyl chloride (alternatively: poly(vinyl chloride), colloquial: vinyl or polyvinyl; abbreviated: PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic polymer of plastic (after polyethylene and polypropylene). About 40 million tons of PVC are produced each year.

Polyurethane refers to a class of polymers composed of organic units joined by carbamate (urethane) links. In contrast to other common polymers such as polyethylene and polystyrene, polyurethane is produced from a wide range of starting materials. This chemical variety produces polyurethanes with different chemical structures leading to many different applications. These include rigid and flexible foams, and coatings, adhesives, electrical potting compounds, and fibers such as spandex and polyurethane laminate (PUL). Foams are the largest application accounting for 67% of all polyurethane produced in 2016.

AB SKF is a Swedish bearing and seal manufacturing company founded in Gothenburg, Sweden, in 1907. The company manufactures and supplies bearings, seals, lubrication and lubrication systems, maintenance products, mechatronics products, power transmission products, condition monitoring systems and related services globally.

Polystyrene (PS) is a synthetic polymer made from monomers of the aromatic hydrocarbon styrene. Polystyrene can be solid or foamed. General-purpose polystyrene is clear, hard, and brittle. It is an inexpensive resin per unit weight. It is a poor barrier to air and water vapor and has a relatively low melting point. Polystyrene is one of the most widely used plastics, with the scale of its production being several million tonnes per year. Polystyrene is naturally transparent, but can be colored with colorants. Uses include protective packaging, containers, lids, bottles, trays, tumblers, disposable cutlery, in the making of models, and as an alternative material for phonograph records.

A thermoplastic, or thermosoftening plastic, is any plastic polymer material that becomes pliable or moldable at a certain elevated temperature and solidifies upon cooling.

Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) (chemical formula (C8H8)x·(C4H6)y·(C3H3N)z ) is a common thermoplastic polymer. Its glass transition temperature is approximately 105 °C (221 °F). ABS is amorphous and therefore has no true melting point.

In materials science, a thermosetting polymer, often called a thermoset, is a polymer that is obtained by irreversibly hardening ("curing") a soft solid or viscous liquid prepolymer (resin). Curing is induced by heat or suitable radiation and may be promoted by high pressure or mixing with a catalyst. Heat is not necessarily applied externally, and is often generated by the reaction of the resin with a curing agent. Curing results in chemical reactions that create extensive cross-linking between polymer chains to produce an infusible and insoluble polymer network.

Injection moulding is a manufacturing process for producing parts by injecting molten material into a mould, or mold. Injection moulding can be performed with a host of materials mainly including metals, glasses, elastomers, confections, and most commonly thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers. Material for the part is fed into a heated barrel, mixed, and injected into a mould cavity, where it cools and hardens to the configuration of the cavity. After a product is designed, usually by an industrial designer or an engineer, moulds are made by a mould-maker from metal, usually either steel or aluminium, and precision-machined to form the features of the desired part. Injection moulding is widely used for manufacturing a variety of parts, from the smallest components to entire body panels of cars. Advances in 3D printing technology, using photopolymers that do not melt during the injection moulding of some lower-temperature thermoplastics, can be used for some simple injection moulds.

A plasticizer is a substance that is added to a material to make it softer and more flexible, to increase its plasticity, to decrease its viscosity, and/or to decrease friction during its handling in manufacture.

ZF Sachs AG, also known as Fichtel & Sachs, was founded in Schweinfurt in 1895 and was a well-known German family business. At its last point as an independent company, the company name was Fichtel & Sachs AG.
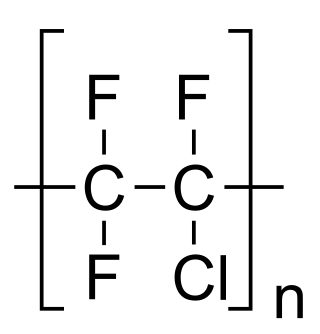
Polychlorotrifluoroethylene (PCTFE or PTFCE) is a thermoplastic chlorofluoropolymer with the molecular formula (CF2CClF)n, where n is the number of monomer units in the polymer molecule. It is similar to polytetrafluoroethene (PTFE), except that it is a homopolymer of the monomer chlorotrifluoroethylene (CTFE) instead of tetrafluoroethene. It has the lowest water vapor transmission rate of any plastic.

High-density polyethylene (HDPE) or polyethylene high-density (PEHD) is a thermoplastic polymer produced from the monomer ethylene. It is sometimes called "alkathene" or "polythene" when used for HDPE pipes. With a high strength-to-density ratio, HDPE is used in the production of plastic bottles, corrosion-resistant piping, geomembranes and plastic lumber. HDPE is commonly recycled, and has the number "2" as its resin identification code.

Fluorinated ethylene propylene (FEP) is a copolymer of hexafluoropropylene and tetrafluoroethylene. It differs from the polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) resins in that it is melt-processable using conventional injection molding and screw extrusion techniques. Fluorinated ethylene propylene was invented by DuPont and is sold under the brandname Teflon FEP. Other brandnames are Neoflon FEP from Daikin or Dyneon FEP from Dyneon/3M.
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE), sometimes referred to as thermoplastic rubbers (TPR), are a class of copolymers or a physical mix of polymers that consist of materials with both thermoplastic and elastomeric properties.
Sumitomo Electric Industries, Ltd. is a manufacturer of electric wire and optical fiber cables. Its headquarters are in Chūō-ku, Osaka, Japan. The company's shares are listed in the first section of the Tokyo, Nagoya Stock Exchanges, and the Fukuoka Stock Exchange. In the period ending March 2021, the company reported consolidated sales of US$26,5 billion.
Borealis AG is an Austrian chemical company and is the world's eighth largest producer of polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP). It is headquartered in Vienna, Austria.

NTN Corporation is one of the most prominent manufacturers of bearings in Japan, second domestically only to NSK Ltd. The company is one of the largest exporters worldwide of friction-reducing products such as constant-velocity joints.
Samvardhana Motherson International Ltd is an Indian multinational manufacturer of automotive components, based in Noida. It makes wiring harnesses, plastic components and rearview mirrors for passenger cars. The company was established in 1986 as a joint venture with the Sumitomo Group of Japan.

Geberit (Alemannic German pronunciation:[ˈɡeberɪ:t] is a Swiss multinational group specialized in manufacturing and supplying sanitary parts and related systems. It is a leader in its field in Europe with a global presence through its subsidiaries.
The Ensinger Group is a manufacturer engaged in the development and manufacture of compounds, semi-finished products, technical parts, composite materials and profiles made of engineering and high-performance plastics. The family-owned enterprise is represented in major industrial regions with manufacturing facilities or sales offices. The main office is located in Nufringen/Baden-Württemberg, Germany.
















