
False Pass is a city on Unimak Island, in the Aleutians East Borough of southwestern Alaska, United States. The population was 35 at the 2010 census, down from 64 in 2000. The 2018 estimate is 49.

Unimak Island is the largest island in the Aleutian Islands chain of the U.S. state of Alaska.

Southwest Alaska is a region of the U.S. state of Alaska. The area is not exactly defined by any governmental administrative region(s); nor does it always have a clear geographic boundary.
Korovin Island is one of the Shumagin Islands in the Gulf of Alaska south of the Alaska Peninsula in the Aleutians East Borough of Alaska, United States. The island lies northeast of Popof Island and across the Unga Strait from the mainland peninsula. To its southeast are Andronica Island, and further southeast, Nagai Island. Korovin island has a land area of 67.85 km² and is uninhabited by humans.

Cape Muzon is a cape located in the Alexander Archipelago of the U.S. state of Alaska. It is the southernmost point of Dall Island and the headland marking the northwestern extremity of the Dixon Entrance. The boundary line separating Alaska from Canada runs very close to Cape Muzon, although according to the Alaska Boundary Treaty Cape Muzon is defined precisely as the western end of the so-called A-B Line, part of the Canada–United States border.

Cordova Bay is a bay in the Alexander Archipelago of southeast Alaska. It opens onto Dixon Entrance to the south, between Cape Muzon on Dall Island and Point Marsh. The name Puerto Cordova y Cordova was given by the Spanish explorer Lieutenant Don Jacinto Caamaño in 1792, in honor of Admiral Luis de Córdova y Córdova. The name was published by George Vancouver in 1798.
Ikatan is an unincorporated community in the Aleutians East Borough of the U.S. state of Alaska. Named after Ikatan Peninsula, it is located on Unimak Island. The name was published by the United States Geological Survey on a 1949 map, and entered into the Geographic Names Information System on February 5, 1999.
Fritz Cove is a bay on the northwestern coast of Douglas Island in the City and Borough of Juneau, Alaska, United States. Lying in Stephens Passage, it is 8 miles (13 km) northwest of the city of Juneau.
Benjamin Island is an island in the City and Borough of Juneau, Alaska, United States. It was named by Captain Lester A. Beardslee of the United States Navy in 1880. Located off the eastern shore of Favorite Channel, it is 25 miles (40 km) northwest of the city of Juneau. The name was collected by the United States Geological Survey between 1976 and 1981, and entered into the Geographic Names Information System on March 31, 1981.

Pennock Island is located in the U.S. state of Alaska near the city of Ketchikan. The island is situated within the Ketchikan Gateway Borough and is part of the Alexander Archipelago. Most of the island is public land managed by the Tongass National Forest.
Moira Sound is a branching inlet on the east side of the southern end of Prince of Wales Island in U.S. state of Alaska. It is situated within the Tongass National Forest.

Echo Bay is an embayment located off Long Island Sound in the city of New Rochelle in Westchester County, New York. It is an anchorage for small craft and is generally fully occupied during the summer. The depths at the anchorage range from 4 to 15 feet, and launches can anchor in the shallow cove on the northeast side of the harbor, entering between Harrison Islands and the rocky, grassy islet off the northwest side of Echo Island. Vessels frequently anchor between the entrance of Echo Bay and Hicks Ledge, in depths of 20 to 24 feet. On the northwest side of Echo Bay a dredged channel 100 feet wide and 15 feet deep, marked by buoys, leads to the New Rochelle Municipal Marina at Beaufort Point.

Port Clarence Bay is a waterway in the U.S. state of Alaska. It has the only harbor and safe anchorage for large vessels in Seward Peninsula. The bay is located 25 miles southeast of York. It is a large body of comparatively deep water, nearly circular in outline, and cut off from the sea by a long, low sand spit, which terminates in Point Spencer at the entrance to the bay. Along the north side of Port Clarence Bay, there is a shallow lagoon, separated from the bay by a narrow sand spit. This lagoon extends several miles west of the entrance to Port Clarence. The hamlet of Port Clarence, Alaska is situated on the bay.

Isanotski Strait is a strait connecting the northern Gulf of Alaska with the Bering Sea, in the U.S. state of Alaska. Isanax̂ is the Aleut name for present day Isanotski Strait, and means gap, hole, rent, or tear in the Aleut language which was rendered as Isanotski in transliterated Russian. The strait appears as Исанакъ in 1802 and Исаноцкый in 1844 on Russian maps.

Ikatan Bay is a waterway in the U.S. state of Alaska. The bay and Isanotski Strait separate Unimak Island from the Alaska Peninsula. They have been used by light-draft craft, intended for service on the Yukon River, in making the passage from Puget Sound ports to St. Michael.

The Fox Islands Passes are waterways in the Fox Islands area of the U.S. state of Alaska, connecting the Bering Sea with the North Pacific Ocean.

Unalaska Bay is a waterway of Unalaska Island in the U.S. state of Alaska. It is situated below the eastern slopes of Makushin Volcano. Composed of seven individual bays, Unalaska Bay opens onto the Bering Sea.
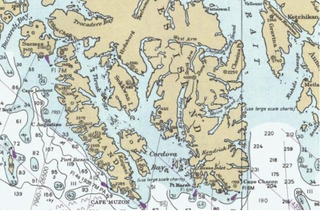
Kaigani Strait is a waterway in the U.S. state of Alaska, the southern part of the strait between Long Island and Dall Island. The Alaska Native name, as reported by Etolin is 1833, is Kalgan.
American Bay is a waterway in the U.S. state of Alaska. It is located on the east side of Dall Island, facing Long Island across Kaigani Strait.
Cholmondeley Sound is a deep bay or inlet on the southeast side of Prince of Wales Island, in the Alexander Archipelago of southeast Alaska, in Tongass National Forest and connecting to Clarence Strait. The sound's entrance lies between Chasina Point and Skin Island. It is about 20 miles (32 km) west of Ketchikan, Alaska. Cholmondeley Sound has several bays and inlets within it, including Kitkun Bay, Dora Bay, Brennan Bay, and Sunny Cove. At its western end Cholmondeley Sound splits into two fjord-like inlets: West Arm Chomondeley Sound, about 7.5 miles (12.1 km) long,, and South Arm Cholmondeley Sound, about 8 miles (13 km) long. The full length from the entrance of the sound to the head of West Arm is about 16 miles (26 km).












