
The acetolactate synthase (ALS) enzyme is a protein found in plants and micro-organisms. ALS catalyzes the first step in the synthesis of the branched-chain amino acids.

RNA-binding motif, single-stranded-interacting protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RBMS1 gene.

The ATPC RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure found in certain cyanobacteria. It is apparently ubiquitous in Prochlorococcus marinus, and is present in many species in the genus Synechococcus. The RNA is always found within an operon encoding subunits of ATP synthase, and it is always located downstream of the gene encoding the A subunit of ATP synthase, and upstream of the C subunit gene. This location is consistent with a cis-regulatory element, but also with a non-coding RNA that is transcribed with the ATP synthase genes.

The Downstream-peptide motif refers to a conserved RNA structure identified by bioinformatics in the cyanobacterial genera Synechococcus and Prochlorococcus and one phage that infects such bacteria. It was also detected in marine samples of DNA from uncultivated bacteria, which are presumably other species of cyanobacteria.

The leu/phe-leader RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure identified by bioinformatics. These RNAs function as peptide leaders. They contain a short open reading frame (ORF) that contains many codons for leucine or phenylalanine. Normally, expression of the downstream genes is suppressed. However, when cellular concentrations of the relevant amino acid is low, ribosome stalling leads to an alternate structure that enables downstream gene expression.

The COG2908 RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. COG2908 motif RNAs are found in genomic sequences extracted from fresh water environments. They have not, as of 2018, been detected in any classified organism.
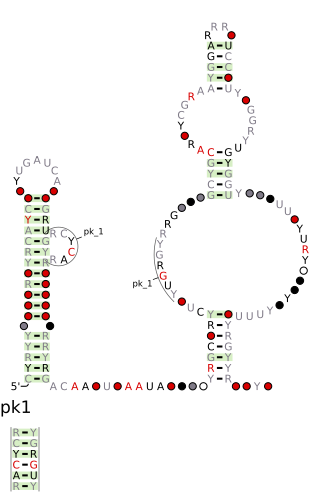
The DUF2800 RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. DUF2800 motif RNAs are found in Bacillota. DUF2800 RNAs are also predicted in the phyla Actinomycetota and Synergistota, although these RNAs are likely the result of recent horizontal gene transfer or conceivably sequence contamination.

The DUF805 RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. The motif is subdivided into the DUF805 motif and the DUF805b motif, which have similar, but distinct secondary structures. Together, these motifs are found in Bacteroidota, Chlorobiota, and Pseudomonadota.
The gltS RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. gltS motifs are found in the bacterial lineage Vibrionaceae.

The hya RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. hya motif RNAs are found in Actinomycetota.

The ilvB-OMG RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. ilvB-OMG motif RNAs are found in Gammaproteobacteria within the poorly studied OMG group (Microbiology).
The leuA-Halobacteria RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. leuA-Halobacteria motifs are found in Halobacteriaceae, a lineage of archaea.

The MDR-NUDIX RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. The MDR-NUDIX motif is found in the poorly studied phylum TM7.

The PGK RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. PGK motif RNAs are found in metagenomic sequences isolated from the gastrointestinal tract of mammals. PGK RNAs have not yet been detected in a classified organism.
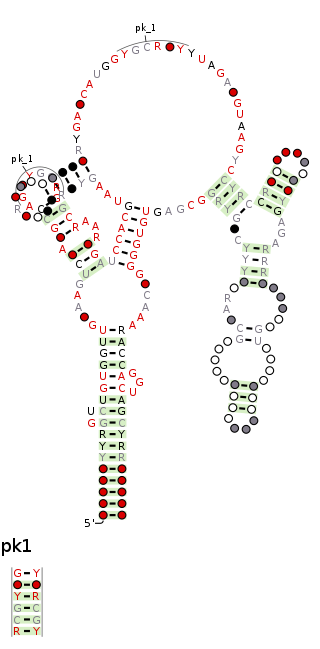
The raiA RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. raiA motif RNAs are found in Actinomycetota and Bacillota, and have many conserved features—including conserved nucleotide positions, conserved secondary structures and associated protein-coding genes—in both of these phyla. Some conserved features of the raiA RNA motif suggest that they function as cis-regulatory elements, but other aspects of the motif suggest otherwise.

The Rothia-sucC RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. Rothia-sucC motif RNAs are found in the actinobacterial genus Rothia.
The sbcC RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. The sbcC motif has, as of 2018, only been detected in metagenomic sequences, and the identities of organisms that contain these RNAs is unknown.

The ssNA-helicase RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. Although the ssNA-helicase motif was published as an RNA candidate, there is some reason to suspect that it might function as a single-stranded DNA. In terms of secondary structure, RNA and DNA are difficult to distinguish when only sequence information is available.
A Streptomyces-metKH RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. Such motifs are found in the genus Streptomyces, and are present upstream of either metK genes, which encode the S-adenosylmethionine synthetase enzyme or metH genes, which encodes the adenosylcobalamin-dependent form of methionine synthase. The RNA structures upstream of metK and metH genes are distinct from each other, but exhibit overall similar sequence and secondary structure features, suggesting that they are related to one another. Their presence upstream of protein-coding genes, and the fact that the genes perform related steps in metabolism, suggests that the RNAs function as cis-regulatory elements.

The sul1 RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. Energetically stable tetraloops often occur in this motif. sul1 motif RNAs are found in Alphaproteobacteria.
















