Related Research Articles

Cetuximab, sold under the brand name Erbitux, is an epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitor medication used for the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer and head and neck cancer. Cetuximab is a chimeric (mouse/human) monoclonal antibody given by intravenous infusion.
Cancer immunotherapy (immuno-oncotherapy) is the stimulation of the immune system to treat cancer, improving the immune system's natural ability to fight the disease. It is an application of the fundamental research of cancer immunology (immuno-oncology) and a growing subspecialty of oncology.
Receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-Β ligand (RANKL), also known as tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 11 (TNFSF11), TNF-related activation-induced cytokine (TRANCE), osteoprotegerin ligand (OPGL), and osteoclast differentiation factor (ODF), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TNFSF11 gene.
Panitumumab, sold under the brand name Vectibix, is a fully human monoclonal antibody specific to the epidermal growth factor receptor.
Ipilimumab, sold under the brand name Yervoy, is a monoclonal antibody medication that works to activate the immune system by targeting CTLA-4, a protein receptor that downregulates the immune system.
Matuzumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody for the treatment of cancer. It binds to the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) with high affinity. The mouse monoclonal antibody (mAb425) from which matuzumab was developed at the Wistar Institute in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania

Cediranib is a potent inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor tyrosine kinases.
Cixutumumab (IMC-A12) is a human monoclonal antibody for the treatment of solid tumors.
Ramucirumab is a fully human monoclonal antibody (IgG1) developed for the treatment of solid tumors. This drug was developed by ImClone Systems Inc. It was isolated from a native phage display library from Dyax.
Tigatuzumab (CS-1008) is a monoclonal antibody for the treatment of cancer. As of October 2009, a clinical trial for the treatment of pancreatic cancer, Phase II trials for colorectal cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, and ovarian cancer have been completed.
An inflammatory cytokine or proinflammatory cytokine is a type of signaling molecule that is secreted from immune cells like helper T cells (Th) and macrophages, and certain other cell types that promote inflammation. They include interleukin-1 (IL-1), IL-6, IL-12, and IL-18, tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), interferon gamma (IFNγ), and granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF) and play an important role in mediating the innate immune response. Inflammatory cytokines are predominantly produced by and involved in the upregulation of inflammatory reactions.
Immunotransplant is a maneuver used to make vaccines more powerful. It refers to the process of infusing vaccine-primed T lymphocytes into lymphodepleted recipients for the purpose of enhancing the proliferation and function of those T cells and increasing immune protection induced by that vaccine.
Carlumab is a discontinued human recombinant monoclonal antibody that targets human CC chemokine ligand 2 (CCL2)/monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP1). Carlumab was under development for use in the treatment of oncology and immune indications and was studied for application in systemic sclerosis, atherosclerosis, diabetic nephropathy, liver fibrosis and type 2 diabetes.
Urelumab is a fully human, non‐ligand binding, CD137 agonist immunoglobulin‐γ 4 (IgG4) monoclonal antibody. It was developed utilizing Medarex's UltiMAb(R) technology by Bristol-Myers Squibb for the treatment of cancer and solid tumors. Urelumab promotes anti-tumor immunity, or an immune response against tumor cells, via CD137 activation. The application of Urelumab has been limited due to the fact that it can cause severe liver toxicity.
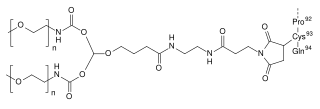
Pegdinetanib is an investigational anti-cancer drug that acts as a selective antagonist of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR-2), hindering vascularization of tumors. It is a genetically engineered peptide derivative based on the monobody technology, and is being developed by Adnexus.

Many variants of herpes simplex virus have been considered for viral therapy of cancer; the early development of these was thoroughly reviewed in the journal Cancer Gene Therapy in 2002. This page describes the most notable variants—those tested in clinical trials: G207, HSV1716, NV1020 and Talimogene laherparepvec. These attenuated versions are constructed by deleting viral genes required for infecting or replicating inside normal cells but not cancer cells, such as ICP34.5, ICP6/UL39, and ICP47.
Cytokine-induced killer cells (CIK) cells are a group of immune effector cells featuring a mixed T- and natural killer (NK) cell-like phenotype. They are generated by ex vivo incubation of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) or cord blood mononuclear cells with interferon-gamma (IFN-γ), anti-CD3 antibody, recombinant human interleukin (IL)-1 and recombinant human interleukin (IL)-2.
Eftilagimod alpha is a large-molecule cancer drug being developed by the clinical-stage biotechnology company Immutep. Efti is a soluble version of the immune checkpoint molecule LAG-3. It is an APC Activator used to increase an immune response to tumors, and is administered by subcutaneous injection. Efti has three intended clinical settings:
MM-151 is an oligoclonal mixture of fully human monoclonal antibodies, which binds multiple parts of the EGFR molecule It has started clinical trials in patients with RAS wild-type colorectal cancers (CRCs) that were resistant to other anti-EGFR therapies. It is intended to overcome the problem of cancers becoming resistant to monoclonal antibody therapies.
Abituzumab is a humanized IgG2 monoclonal antibody (mAb) targeted at CD51 currently in development by Merck KGaA Darmstadt, Germany in an attempt to prevent bone lesion metastases in castration-resistant prostate cancer.
References
- ↑ Douillard P, Thiele M, Schinagl A, Halama N, Jaeger D, Yazji S, Scheiflinger F, Kerschbaumer R (2015). "Abstract A153: Imalumab, a first-in-class anti-oxidized macrophage migration inhibitory factor (OxMIF) antibody penetrates tumor tissues and shows antitumor activity in patients". Therapeutic Agents: Biological. Vol. 14. pp. A153. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.TARG-15-A153.
{{cite book}}:|journal=ignored (help) - 1 2 Clinical trial number NCT02448810 for "Phase 2a Study of BAX69 and 5-FU/Leucovorin or Panitumumab Versus Standard of Care in Subjects With Metastatic Colorectal Cancer" at ClinicalTrials.gov
- ↑ Clinical trial number NCT01765790 for "Phase 1 Study of Anti-Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor (Anti-MIF) Antibody in Solid Tumor" at ClinicalTrials.gov
- 1 2 "Imalumab". AdisInsight. Springer Nature Switzerland AG.