
Imidazoquinoline is a tricyclic organic molecule; its derivatives and compounds are often used for antiviral [1] and antiallergic [2] creams.

Imidazoquinoline is a tricyclic organic molecule; its derivatives and compounds are often used for antiviral [1] and antiallergic [2] creams.
The oxidation state, sometimes referred to as oxidation number, describes the degree of oxidation of an atom in a chemical compound. Conceptually, the oxidation state, which may be positive, negative or zero, is the hypothetical charge that an atom would have if all bonds to atoms of different elements were 100% ionic, with no covalent component. This is never exactly true for real bonds.
In the physical sciences, a partition coefficient (P) or distribution coefficient (D) is the ratio of concentrations of a compound in a mixture of two immiscible solvents at equilibrium. This ratio is therefore a comparison of the solubilities of the solute in these two liquids. The partition coefficient generally refers to the concentration ratio of un-ionized species of compound, whereas the distribution coefficient refers to the concentration ratio of all species of the compound.

Hydrangea macrophylla is a species of flowering plant in the family Hydrangeaceae, native to Japan. It is a deciduous shrub growing to 2 m (7 ft) tall by 2.5 m (8 ft) broad with large heads of pink or blue flowers in summer and autumn. Common names include bigleaf hydrangea, French hydrangea, lacecap hydrangea, mophead hydrangea, penny mac and hortensia. It is widely cultivated in many parts of the world in many climates. It is not to be confused with H. aspera 'Macrophylla'.

Ketotifen, sold under the brand name Zaditor among others, is a second-generation noncompetitive H1-antihistamine and mast cell stabilizer. It is most commonly sold as a salt with fumaric acid, ketotifen fumarate, and is available in two forms. In its ophthalmic form, it is used to treat allergic conjunctivitis. In its oral form, it is used to prevent asthma attacks or anaphylaxis, as well as various mast cell, allergic-type disorders.

The H1 receptor is a histamine receptor belonging to the family of rhodopsin-like G-protein-coupled receptors. This receptor is activated by the biogenic amine histamine. It is expressed in smooth muscles, on vascular endothelial cells, in the heart, and in the central nervous system. The H1 receptor is linked to an intracellular G-protein (Gq) that activates phospholipase C and the inositol triphosphate (IP3) signalling pathway. Antihistamines, which act on this receptor, are used as anti-allergy drugs. The crystal structure of the receptor has been determined (shown on the right) and used to discover new histamine H1 receptor ligands in structure-based virtual screening studies.

Nitroso refers to a functional group in organic chemistry which has the NO group attached to an organic moiety. As such, various nitroso groups can be categorized as C-nitroso compounds (e.g., nitrosoalkanes; R−N=O), S-nitroso compounds (nitrosothiols; RS−N=O), N-nitroso compounds (e.g., nitrosamines, R1N(−R2)−N=O), and O-nitroso compounds (alkyl nitrites; RO−N=O).

Curcuma amada, or mango ginger is a plant of the ginger family Zingiberaceae and is closely related to turmeric. The rhizomes are very similar to common ginger but lack its pungency, and instead have a raw mango flavour. They are used in making pickles in south India and chutneys in north India. The taxonomy of the species is a subject of some confusion as some authorities have considered the name C. mangga as identical while others describe it as a distinct species with C. mangga being found in southern India while C. amada is of east Indian origin. Mango-ginger is a popular spice and vegetable due to its rich flavor, which is described as sweet with subtle earthy floral and pepper overtones and similar to that of raw mango. It is a delicious addition to salads and stir fries. It is used in South Asian and Southeast Asian as well as Far East Asian cuisines.

N-Acetylaspartylglutamic acid is a peptide neurotransmitter and the third-most-prevalent neurotransmitter in the mammalian nervous system. NAAG consists of N-acetylaspartic acid (NAA) and glutamic acid coupled via a peptide bond.

Amlexanox is an anti-inflammatory antiallergic immunomodulator used to treat recurrent aphthous ulcers, and several inflammatory conditions. This drug has been discontinued in the U.S.

Polygodial is chemical compound found in dorrigo pepper, mountain pepper, horopito, canelo, paracress, water-pepper, and Dendrodoris limbata.

G protein-coupled receptor 35 also known as GPR35 is a G protein-coupled receptor which in humans is encoded by the GPR35 gene. Heightened expression of GPR35 is found in immune and gastrointestinal tissues, including the crypts of Lieberkühn.

Multidrug and toxin extrusion protein 1 (MATE1), also known as solute carrier family 47 member 1, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC47A1 gene. SLC47A1 belongs to the MATE family of transporters that are found in bacteria, archaea and eukaryotes.

Blonanserin, sold under the brand name Lonasen, is a relatively new atypical antipsychotic commercialized by Dainippon Sumitomo Pharma in Japan and Korea for the treatment of schizophrenia. Relative to many other antipsychotics, blonanserin has an improved tolerability profile, lacking side effects such as extrapyramidal symptoms, excessive sedation, or hypotension. As with many second-generation (atypical) antipsychotics it is significantly more efficacious in the treatment of the negative symptoms of schizophrenia compared to first-generation (typical) antipsychotics such as haloperidol.
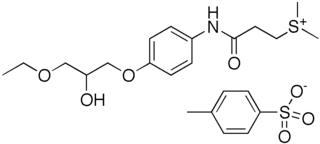
Suplatast tosilate (INN) is a Th2 cytokine inhibitor which is used as an antiallergic drug. It has been suggested and applied in the treatment of Kimura's disease a few times.
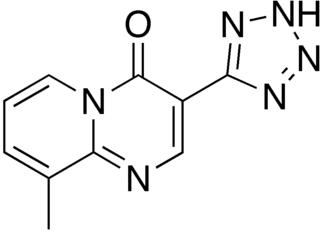
Pemirolast (INN) is a mast cell stabilizer used as an anti-allergic drug therapy. It is marketed under the tradenames Alegysal and Alamast.
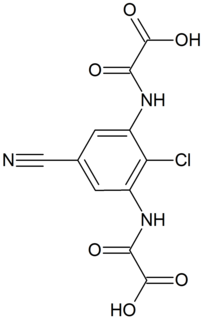
Lodoxamide is an antiallergic pharmaceutical drug. It is marketed under the tradename Alomide in the UK. Like cromoglicic acid it acts as a mast cell stabilizer. In 2014 lodoxamide and bufrolin were found to be potent agonists at the G protein-coupled receptor 35, an orphan receptor believed to play a role in inflammatory processes, pain and the development of stomach cancer.
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) block the gastric hydrogen potassium ATPase (H+/K+ ATPase) and inhibit gastric acid secretion. These drugs have emerged as the treatment of choice for acid-related diseases, including gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and peptic ulcer disease. PPIs also can bind to other types of proton pumps such as those that occur in cancer cells and are finding applications in the reduction of cancer cell acid efflux and reduction of chemotherapy drug resistance.
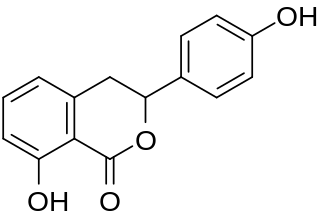
Hydrangenol is a dihydroisocoumarin. It can be found in Hydrangea macrophylla, as well as its 8-O-glucoside. (−)-Hydrangenol 4′-O-glucoside and (+)-hydrangenol 4′-O-glucoside can be found in Hydrangeae Dulcis Folium, the processed leaves of H. macrophylla var. thunbergii.
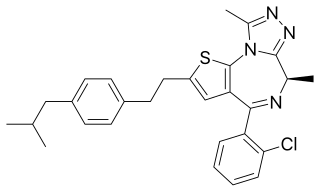
Israpafant (Y-24180) is a drug which acts as a selective antagonist for the platelet-activating factor receptor, and was originally developed for the treatment of asthma. Its chemical structure is a thienotriazolodiazepine, closely related to the sedative benzodiazepine derivative etizolam. However israpafant binds far more tightly to the platelet-activating factor receptor, with an IC50 of 0.84nM for inhibiting PAF-induced human platelet aggregation (compared to etizolam's IC50 of 998nM at this target), while it binds only weakly to benzodiazepine receptors, with a Ki of 3680nM. Israpafant has been found to inhibit the activation of eosinophil cells, and consequently delays the development of immune responses. It has also been shown to have anti-nephrotoxic properties, and to mobilize calcium transport.

Proxicromil is a detergent-like, lipophilic oral medication developed in the late 1970s that was not admitted on the market because of its possible carcinogenic effects. It suppresses allergic reactions by binding to FcεRI receptor in mast cells, thereby inhibiting production of histamines. It is absorbed through the gastrointestinal tract and is proven hepatotoxic for dogs as a result of its accumulation in the biliary canaliculus.