Related Research Articles

An antibody (Ab) is the secreted form of a B cell receptor; the term immunoglobulin (Ig) can refer to either the membrane-bound form or the secreted form of the B cell receptor, but they are, broadly speaking, the same protein, and so the terms are often treated as synonymous. Antibodies are large, Y-shaped proteins belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily which are used by the immune system to identify and neutralize antigens such as bacteria and viruses, including those that cause disease. Antibodies can recognize virtually any size antigen with diverse chemical compositions from molecules. Each antibody recognizes one or more specific antigens. Antigen literally means "antibody generator", as it is the presence of an antigen that drives the formation of an antigen-specific antibody. Each tip of the "Y" of an antibody contains a paratope that specifically binds to one particular epitope on an antigen, allowing the two molecules to bind together with precision. Using this mechanism, antibodies can effectively "tag" a microbe or an infected cell for attack by other parts of the immune system, or can neutralize it directly.

B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are a type of white blood cell of the lymphocyte subtype. They function in the humoral immunity component of the adaptive immune system. B cells produce antibody molecules which may be either secreted or inserted into the plasma membrane where they serve as a part of B-cell receptors. When a naïve or memory B cell is activated by an antigen, it proliferates and differentiates into an antibody-secreting effector cell, known as a plasmablast or plasma cell. In addition, B cells present antigens and secrete cytokines. In mammals, including marsupials B cells mature in the bone marrow, which is at the core of most bones. In birds, B cells mature in the bursa of Fabricius, a lymphoid organ where they were first discovered by Chang and Glick, which is why the B stands for bursa and not bone marrow, as commonly believed.

A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include T cells, B cells, and innate lymphoid cells, of which natural killer cells are an important subtype. They are the main type of cell found in lymph, which prompted the name "lymphocyte". Lymphocytes make up between 18% and 42% of circulating white blood cells.
Humoral immunity is the aspect of immunity that is mediated by macromolecules – including secreted antibodies, complement proteins, and certain antimicrobial peptides – located in extracellular fluids. Humoral immunity is named so because it involves substances found in the humors, or body fluids. It contrasts with cell-mediated immunity. Humoral immunity is also referred to as antibody-mediated immunity.

Plasma cells, also called plasma B cells or effector B cells, are white blood cells that originate in the lymphoid organs as B cells and secrete large quantities of proteins called antibodies in response to being presented specific substances called antigens. These antibodies are transported from the plasma cells by the blood plasma and the lymphatic system to the site of the target antigen, where they initiate its neutralization or destruction. B cells differentiate into plasma cells that produce antibody molecules closely modeled after the receptors of the precursor B cell.

In immunology, a memory B cell (MBC) is a type of B lymphocyte that forms part of the adaptive immune system. These cells develop within germinal centers of the secondary lymphoid organs. Memory B cells circulate in the blood stream in a quiescent state, sometimes for decades. Their function is to memorize the characteristics of the antigen that activated their parent B cell during initial infection such that if the memory B cell later encounters the same antigen, it triggers an accelerated and robust secondary immune response. Memory B cells have B cell receptors (BCRs) on their cell membrane, identical to the one on their parent cell, that allow them to recognize antigen and mount a specific antibody response.

A lymphoblast is a modified naive lymphocyte with altered cell morphology. It occurs when the lymphocyte is activated by an antigen and increased in volume by nucleus and cytoplasm growth as well as new mRNA and protein synthesis. The lymphoblast then starts dividing two to four times every 24 hours for three to five days, with a single lymphoblast making approximately 1000 clones of its original naive lymphocyte, with each clone sharing the originally unique antigen specificity. Finally the dividing cells differentiate into effector cells, known as plasma cells, cytotoxic T cells, and helper T cells.

The adaptive immune system, also known as the acquired immune system, or specific immune system is a subsystem of the immune system that is composed of specialized, systemic cells and processes that eliminate pathogens or prevent their growth. The acquired immune system is one of the two main immunity strategies found in vertebrates.
Antigen processing, or the cytosolic pathway, is an immunological process that prepares antigens for presentation to special cells of the immune system called T lymphocytes. It is considered to be a stage of antigen presentation pathways. This process involves two distinct pathways for processing of antigens from an organism's own (self) proteins or intracellular pathogens, or from phagocytosed pathogens ; subsequent presentation of these antigens on class I or class II major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules is dependent on which pathway is used. Both MHC class I and II are required to bind antigens before they are stably expressed on a cell surface. MHC I antigen presentation typically involves the endogenous pathway of antigen processing, and MHC II antigen presentation involves the exogenous pathway of antigen processing. Cross-presentation involves parts of the exogenous and the endogenous pathways but ultimately involves the latter portion of the endogenous pathway.

The T-cell receptor (TCR) is a protein complex found on the surface of T cells, or T lymphocytes, that is responsible for recognizing fragments of antigen as peptides bound to major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules. The binding between TCR and antigen peptides is of relatively low affinity and is degenerate: that is, many TCRs recognize the same antigen peptide and many antigen peptides are recognized by the same TCR.
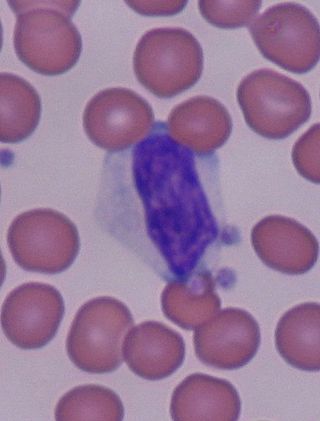
In immunology, reactive lymphocytes, variant lymphocytes, atypical lymphocytes, Downey cells or Türk cells are cytotoxic (CD8+) lymphocytes that become large as a result of antigen stimulation. Typically, they can be more than 30 μm in diameter with varying size and shape.

Germinal centers or germinal centres (GCs) are transiently formed structures within B cell zone (follicles) in secondary lymphoid organs – lymph nodes, ileal Peyer's patches, and the spleen – where mature B cells are activated, proliferate, differentiate, and mutate their antibody genes during a normal immune response; most of the germinal center B cells (BGC) are removed by tingible body macrophages. There are several key differences between naive B cells and GC B cells, including level of proliferative activity, size, metabolic activity and energy production. The B cells develop dynamically after the activation of follicular B cells by T-dependent antigen. The initiation of germinal center formation involves the interaction between B and T cells in the interfollicular area of the lymph node, CD40-CD40L ligation, NF-kB signaling and expression of IRF4 and BCL6.

Monoblasts are the committed progenitor cells that differentiated from a committed macrophage or dendritic cell precursor (MDP) in the process of hematopoiesis. They are the first developmental stage in the monocyte series leading to a macrophage. Their myeloid cell fate is induced by the concentration of cytokines they are surrounded by during development. These cytokines induce the activation of transcription factors which push completion of the monoblast's myeloid cell fate. Monoblasts are normally found in bone marrow and do not appear in the normal peripheral blood. They mature into monocytes which, in turn, develop into macrophages. They then are seen as macrophages in the normal peripheral blood and many different tissues of the body. Macrophages can produce a variety of effector molecules that initiate local, systemic inflammatory responses. These monoblast differentiated cells are equipped to fight off foreign invaders using pattern recognition receptors to detect antigen as part of the innate immune response.

MHC Class II molecules are a class of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules normally found only on professional antigen-presenting cells such as dendritic cells, macrophages, some endothelial cells, thymic epithelial cells, and B cells. These cells are important in initiating immune responses.
Lymphopoiesis (lĭm'fō-poi-ē'sĭs) is the generation of lymphocytes, one of the five types of white blood cells (WBCs). It is more formally known as lymphoid hematopoiesis.
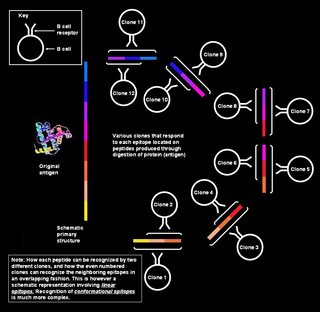
Polyclonal B cell response is a natural mode of immune response exhibited by the adaptive immune system of mammals. It ensures that a single antigen is recognized and attacked through its overlapping parts, called epitopes, by multiple clones of B cell.

B-lymphocyte antigen CD19, also known as CD19 molecule, B-Lymphocyte Surface Antigen B4, T-Cell Surface Antigen Leu-12 and CVID3 is a transmembrane protein that in humans is encoded by the gene CD19. In humans, CD19 is expressed in all B lineage cells. Contrary to some early doubts, human plasma cells do express CD19, as confirmed by others. CD19 plays two major roles in human B cells: on the one hand, it acts as an adaptor protein to recruit cytoplasmic signaling proteins to the membrane; on the other, it works within the CD19/CD21 complex to decrease the threshold for B cell receptor signaling pathways. Due to its presence on all B cells, it is a biomarker for B lymphocyte development, lymphoma diagnosis and can be utilized as a target for leukemia immunotherapies.

CD69 is a human transmembrane C-Type lectin protein encoded by the CD69 gene. It is an early activation marker that is expressed in hematopoietic stem cells, T cells, and many other cell types in the immune system. It is also implicated in T cell differentiation as well as lymphocyte retention in lymphoid organs.
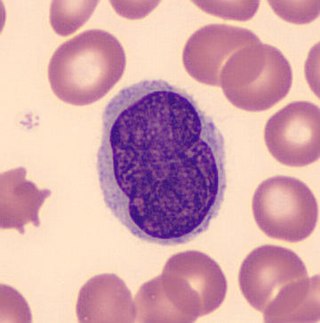
Lutzner cells were discovered by Marvin A. Lutzner, Lucien-Marie Pautrier, and Albert Sézary. These cells are described as the smaller forms of Sézary cells, or Sézary-Lutzner cells, and the two variants are recognised as being morphologically different. Aggregates of these cells in mycosis fungoides are known as a Pautrier's microabscesses. They are a form of T-lymphocytes that has been mutated This atypical form of T-lymphocytes contains T-cell receptors on the surface and is found in both the dermis and epidermis layers of the skin. Since Lutzner cells are a mutated form of T-lymphocytes, they develop in bone marrow and are transported to the thymus is order to mature. The production and maturation stages occur before the cell has developed a mutation. Lutzner cells can form cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, which is a form of skin cancer.

A centroblast generally refers to an activated B cell that is enlarged and is rapidly proliferating in the germinal center of a lymphoid follicle. They are specifically located in the dark zone of the germinal center. Centroblasts form from naive B cells being exposed to follicular dendritic cell cytokines, such as IL-6, IL-15, 8D6, and BAFF. Stimulation from helper T cells is also required for centroblast development. Interaction between CD40 ligand on an activated T helper cell and the B cell CD40 receptor induces centroblasts to express activation-induced cytidine deaminase, leading to somatic hypermutation, allowing the B cell receptor to potentially gain stronger affinity for an antigen. In the absence of FDC and helper T cell stimulation, centroblasts are unable to differentiate and will undergo CD95-mediated apoptosis.