
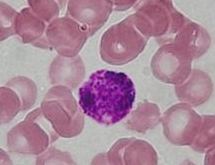
Basophilic is a technical term used by pathologists. It describes the appearance of cells, tissues and cellular structures as seen through the microscope after a histological section has been stained with a basic dye. The most common such dye is haematoxylin.
The name basophilic refers to the characteristic of these structures to be stained very well by basic dyes. This can be explained by their charges. Basic dyes are cationic, i.e. contain positive charges, and thus they stain anionic structures (i.e. structures containing negative charges), such as the phosphate backbone of DNA in the cell nucleus and ribosomes. [1]
"Basophils" are cells that "love" (from greek "-phil") basic dyes, for example haematoxylin, azure and methylene blue. Specifically, this term refers to:
An abnormal increase in basophil granulocytes is therefore also described as basophilia. [2]
The opposite of basophilic structures are acidophilic structures, also called eosinophilic. These structures contain many positive charges and are thus strongly stained by anionic dyes like eosin. A typical combination of basophilic and eosinophilic dyes is the H&E stain, which visualizes basophilic structures in blue and eosinophilic structures in red. [1]