Hemiparesis, also called unilateral paresis, is the weakness of one entire side of the body. Hemiplegia, in its most severe form, is the complete paralysis of one entire side of the body. Either hemiparesis or hemiplegia can result from a variety of medical causes, including congenital conditions, trauma, tumors, traumatic brain injury and stroke.

A spirometer is an apparatus for measuring the volume of air inspired and expired by the lungs. A spirometer measures ventilation, the movement of air into and out of the lungs. The spirogram will identify two different types of abnormal ventilation patterns, obstructive and restrictive. There are various types of spirometers that use a number of different methods for measurement.
A physical disability is a limitation on a person's physical functioning, mobility, dexterity or stamina. Other physical disabilities include impairments which limit other facets of daily living, such as respiratory disorders, blindness, epilepsy and sleep disorders.
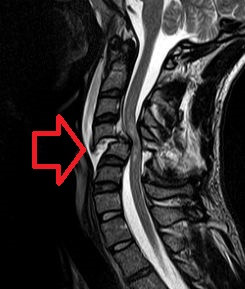
A spinal cord injury (SCI) is damage to the spinal cord that causes temporary or permanent changes in its function. It is a destructive neurological and pathological state that causes major motor, sensory and autonomic dysfunctions.
Closed-head injury is a type of traumatic brain injury in which the skull and dura mater remain intact. Closed-head injuries are the leading cause of death in children under 4 years old and the most common cause of physical disability and cognitive impairment in young people. Overall, closed-head injuries and other forms of mild traumatic brain injury account for about 75% of the estimated 1.7 million brain injuries that occur annually in the United States. Brain injuries such as closed-head injuries may result in lifelong physical, cognitive, or psychological impairment and, thus, are of utmost concern with regards to public health.
People with disabilities in the United States are a significant minority group, making up a fifth of the overall population and over half of Americans older than eighty. There is a complex history underlying the U.S. and its relationship with its disabled population, with great progress being made in the last century to improve the livelihood of disabled citizens through legislation providing protections and benefits. Most notably, the Americans with Disabilities Act is a comprehensive anti-discrimination policy that works to protect Americans with disabilities in public settings and the workplace.

A retrolisthesis is a posterior displacement of one vertebral body with respect to the subjacent vertebra to a degree less than a luxation (dislocation). Retrolistheses are most easily diagnosed on lateral x-ray views of the spine. Views where care has been taken to expose for a true lateral view without any rotation offer the best diagnostic quality.
A pain scale measures a patient's pain intensity or other features. Pain scales are a common communication tool in medical contexts, and are used in a variety of medical settings. Pain scales are a necessity to assist with better assessment of pain and patient screening. Pain measurements help determine the severity, type, and duration of the pain, and are used to make an accurate diagnosis, determine a treatment plan, and evaluate the effectiveness of treatment. Pain scales are based on trust, cartoons (behavioral), or imaginary data, and are available for neonates, infants, children, adolescents, adults, seniors, and persons whose communication is impaired. Pain assessments are often regarded as "the 5th vital sign".
An independent medical examination (IME) is a medical evaluation performed on a patient by a medical professional who was not previously involved in the treatment of that patient, to evaluate the patient's course of prior treatment and current condition. IMEs are conducted by doctors, psychologists, and other licensed healthcare professionals in essentially all medical disciplines, depending on the purpose of the exam and the claimed injuries.
Disability Insurance, often called DI or disability income insurance, or income protection, is a form of insurance that insures the beneficiary's earned income against the risk that a disability creates a barrier for completion of core work functions. For example, the worker may be unable to maintain composure in the case of psychological disorders or sustain an injury, illness or condition that causes physical impairment or incapacity to work. DI encompasses paid sick leave, short-term disability benefits (STD), and long-term disability benefits (LTD). The same concept is instantiated in some countries as income protection insurance.
Joint stability refers to the resistance offered by various musculoskeletal tissues that surround a skeletal joint. Several subsystems ensure the stability of a joint. These are the passive, active and neural subsystems. It is believed that one or more of the subsystems must have failed if joint instability occurs, usually a torn or overstretched ligament. Instability of joints can cause unhealthy ranges of movement in your joints, which can result in the joints fracturing.
The Kurtzke Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) is a method of quantifying disability in multiple sclerosis. The scale has been developed by John F. Kurtzke. The EDSS is based on a neurological examination by a clinician. However, a number of versions have been developed which enable patient self-administration.

Musculoskeletal injury refers to damage of muscular or skeletal systems, which is usually due to a strenuous activity and includes damage to skeletal muscles, bones, tendons, joints, ligaments, and other affected soft tissues. In one study, roughly 25% of approximately 6300 adults received a musculoskeletal injury of some sort within 12 months—of which 83% were activity-related. Musculoskeletal injury spans into a large variety of medical specialties including orthopedic surgery, sports medicine, emergency medicine and rheumatology.

In general, quality of life is the perceived quality of an individual's daily life, that is, an assessment of their well-being or lack thereof. This includes all emotional, social and physical aspects of the individual's life. In health care, health-related quality of life (HRQoL) is an assessment of how the individual's well-being may be affected over time by a disease, disability or disorder.

The United States has compensated military veterans for service-related injuries since the Revolutionary War, with the current indemnity model established near the end of World War I. The Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) began to provide disability benefits for post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in the 1980s after the diagnosis became part of official psychiatric nosology.
Stephen Thomas Wegener is an American rehabilitation psychologist specializing in the psychology of pain management. His work seeks to improve function and reduce disability for persons with chronic illness and impairments, including occupational injuries, rheumatic disease, spinal cord injury or limb loss. He also develops cognitive-behavioral therapy and self-management to prevent or mitigate pain associated with disability, and examines psychological variables that can affect positive outcomes.
A psychological injury is the psychological or psychiatric consequence of a traumatic event or physical injury. Such an injury might result from events such as abusive behavior, whistleblower retaliation, bullying, kidnapping, rape, motor vehicular collision or other negligent action. It may cause impairments, disorders, and disabilities perhaps as an exacerbation of a pre-existing condition.
The Disability Rating Scale (DRS) was developed as a way to track a traumatic brain injury (TBI) patient from 'Coma to Community'. The scale was used to rate the effects of injury and decide how long recovery might take. The rating gives insight into the cognitive impairment of the individual with the TBI.
Wheelchair sport classification is a system designed to allow fair competition between people of different disabilities, and minimize the impact of a person's specific disability on the outcome of a competition. Wheelchair sports is associated with spinal cord injuries, and includes a number of different types of disabilities including paraplegia, quadriplegia, muscular dystrophy, post-polio syndrome and spina bifida. The disability must meet minimal body function impairment requirements. Wheelchair sport and sport for people with spinal cord injuries is often based on the location of lesions on the spinal cord and their association with physical disability and functionality.
Age-related mobility disability is a self-reported inability to walk due to impairments, limited mobility, dexterity or stamina. It has been found mostly in older adults with decreased strength in lower extremities.





