Related Research Articles
Operation Husky order of battle is a listing of the significant military and air force units that were involved in the campaign for Sicily, July 10 – August 17, 1943.

The Imperial Japanese Navy land forces were a variety of land-based units of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) organized for offensive operations, the defense of Japanese naval and shore-based facilities, military policing tasks, construction and engineering, training, and shore-based anti-aircraft roles; both overseas, and in the Japanese home islands. Units ranged from dedicated military police formations, to ad-hoc groups of naval personnel pressed into service as naval infantry, to professional marines, among others. The land forces were most active during the interwar period and World War II, with IJN land forces complementing, supporting, and in some cases, operating in-place of Imperial Japanese Army units. Upon Imperial Japan’s defeat in WWII, IJN land forces were disbanded alongside the IJN proper in 1945.
The Type 97 automatic cannon is a 20-millimeter (0.79 in) Japanese anti-tank rifle that began development in the 1930s. It was used by the Imperial Japanese Army (IJA) during the Second Sino-Japanese War, the Soviet–Japanese border conflicts and the Pacific War. Improvements in armour thicknesses on tanks rendered the Type 97 obsolete by about 1942. This weapon was not related to the Type 97 heavy tank machine gun used in armored vehicles or the Type 97 aircraft machine gun used in Japanese Navy aircraft.

The Type 98 20 mm AA machine cannon was the most common light anti-aircraft gun of the Imperial Japanese Army. It entered service in 1938 and was used until the end of World War II. After World War II this gun was used by the Indonesian Army in the Indonesian National Revolution and North Vietnam in First Indochina War.
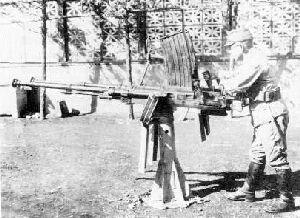
Type 4 20 mm twin AA machine cannon was an Imperial Japanese Army (IJA) anti-aircraft gun. It consisted of two Type 98 20 mm AA machine cannon. It was introduced in 1944 and approximately 500 to 616 guns were produced. It was mainly designed for use against ground targets, but was only used in an anti-aircraft role.
Teishin Shudan was a Japanese special forces/airborne unit during World War II. The unit was a division-level force, and was part of the Imperial Japanese Army Air Force (IJAAF). The Teishin units were therefore distinct from the marine parachute units of the Special Naval Landing Forces.

The 1st Tank Division, was one of four armored divisions of the Imperial Japanese Army in World War II.

The 4th Tank Division, was one of four armored divisions of the Imperial Japanese Army in World War II.

The 6th Canadian Infantry Division was an infantry division of the Canadian Army, formed in 1942 during the Second World War. It was attached to Pacific Command. The division had a brigade sent to the Aleutian Islands Campaign, particularly at Kiska, but never saw action. The 6th Division was to have been part of a proposed Commonwealth Corps, formed for a planned invasion of Japan, but was disbanded on 31 January 1946, after the surrender of Japan in August 1945.

Marine Defense Battalions were United States Marine Corps battalions charged with coastal and air defense of advanced naval bases during World War II. They maintained large anti-ship guns, anti-aircraft guns, searchlights, and small arms to repel landing forces.

The Northumberland Hussars was a Yeomanry regiment of the British Army, transferred to the Royal Artillery for the duration of the Second World War. It was disbanded as an independent Territorial Army unit in 1967, a time when the strength of the Territorial Army was greatly reduced. The regiment's name lives on in the title of the command and support squadron of the Queen's Own Yeomanry (QOY), a Formation Reconnaissance Regiment based in Newcastle upon Tyne.
The 109th Division was an infantry division of the Imperial Japanese Army. Its call sign was the Courage Division. It was formed on 24 August 1937 in Kanazawa as a square division, simultaneously with the 108th division. The nucleus for the formation was the 9th division headquarters. It was subordinated from the beginning to the Japanese Northern China Area Army.
This article details the organization of the Imperial Japanese Army.

The U.S. Army Coast Artillery Corps (CAC) was an administrative corps responsible for coastal, harbor, and anti-aircraft defense of the United States and its possessions between 1901 and 1950. The CAC also operated heavy and railway artillery during World War I.

Malta Command was an independent command of the British Army. It commanded all army units involved in the defence of Malta. Once mobilised the Command deployed its headquarters to underground hardened shelters and its combat units were deployed to fixed points in the Maltese countryside, from where they operated. This mobilised, but largely static, army garrison would be tested by aerial bombardment and naval blockade during the Second World War. Whilst Malta Command was already a functioning command structure before 1939, the Second World War would see the Command operate as a genuine war-fighting headquarters, albeit in a static defensive role.
An Anti-Aircraft Artillery Division was a type of Anti-aircraft unit of the Soviet Union's Red Army, Soviet Army, and the Soviet Air Defense Forces (PVO) during World War II and the early years of the Cold War.
The 1st Anti-Aircraft Division was an Imperial Japanese Army unit of World War II. It was responsible for the anti-aircraft guns and searchlight units assigned to defend cities in the central region of Honshu.
The IJA Amphibious Brigades were marines brigades of the Imperial Japanese Army during World War II. They were established in 1943. Although the Japanese invasion of Southeast Asia had been completed at the time of their founding, the Imperial General Headquarters (Daihon'ei) saw the need for flexible countermeasures to defend strategic islands in the Pacific Ocean from impending Allied invasion as the war situation deteriorated for the Japanese Empire.
The 25th Independent Mixed Regiment was a regiment of the Imperial Japanese Army (IJA) active during World War II. It was raised in July 1944, and deployed to Borneo in September that year. Elements of the regiment briefly saw combat against the United States Army on islands near Tawi-Tawi Island and against Australian forces during the Battle of North Borneo.
The Palembang Defense Unit was an Imperial Japanese Army formation established to protect the oil facilities at Palembang from air attack during the Japanese occupation of the Dutch East Indies. Formed in March 1943, it was initially designated the Palembang Air Defense Headquarters.
References
- Citations
- Works consulted
- Forty, George (2002). The Japanese Army Handbook 1939–1945. New York: The History Press. ISBN 0750954132.
- Ness, Leland S. (2014). Rikugun: Guide to Japanese Ground Forces, 1937–1945. Volume 1: Tactical Organization of Imperial Japanese Army & Navy Ground Forces. Solihull, United Kingdom: Helion. ISBN 9781909982000.
- War Department (1944). Handbook on Japanese Military Forces. HyperWar Project.