
In computing, a denial-of-service attack is a cyber-attack in which the perpetrator seeks to make a machine or network resource unavailable to its intended users by temporarily or indefinitely disrupting services of a host connected to a network. Denial of service is typically accomplished by flooding the targeted machine or resource with superfluous requests in an attempt to overload systems and prevent some or all legitimate requests from being fulfilled. The range of attacks varies widely, spanning from inundating a server with millions of requests to slow its performance, overwhelming a server with a substantial amount of invalid data, to submitting requests with an illegitimate IP address.

In computer networking, a proxy server is a server application that acts as an intermediary between a client requesting a resource and the server providing that resource. It improves privacy, security, and performance in the process.
Internet security is a branch of computer security. It encompasses the Internet, browser security, web site security, and network security as it applies to other applications or operating systems as a whole. Its objective is to establish rules and measures to use against attacks over the Internet. The Internet is an inherently insecure channel for information exchange, with high risk of intrusion or fraud, such as phishing, online viruses, trojans, ransomware and worms.

A content delivery network or content distribution network (CDN) is a geographically distributed network of proxy servers and their data centers. The goal is to provide high availability and performance ("speed") by distributing the service spatially relative to end users. CDNs came into existence in the late 1990s as a means for alleviating the performance bottlenecks of the Internet as the Internet was starting to become a mission-critical medium for people and enterprises. Since then, CDNs have grown to serve a large portion of the Internet content today, including web objects, downloadable objects, applications, live streaming media, on-demand streaming media, and social media sites.
An Internet bot, web robot, robot or simply bot, is a software application that runs automated tasks (scripts) on the Internet, usually with the intent to imitate human activity, such as messaging, on a large scale. An Internet bot plays the client role in a client–server model whereas the server role is usually played by web servers. Internet bots are able to perform simple and repetitive tasks much faster than a person could ever do. The most extensive use of bots is for web crawling, in which an automated script fetches, analyzes and files information from web servers. More than half of all web traffic is generated by bots.
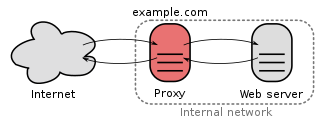
In computer networks, a reverse proxy or surrogate server is a proxy server that appears to any client to be an ordinary web server, but in reality merely acts as an intermediary that forwards the client's requests to one or more ordinary web servers. Reverse proxies help increase scalability, performance, resilience, and security, but they also carry a number of risks.

F5, Inc. is an American technology company specializing in application security, multi-cloud management, online fraud prevention, application delivery networking (ADN), application availability & performance, network security, and access & authorization.

Radware Ltd. is an American provider of cybersecurity and application delivery products for physical, cloud and software-defined data centers. Radware's corporate headquarters are located in Mahwah, New Jersey. The company also has offices in Europe, Africa and Asia Pacific regions. The company's global headquarters is in Israel. Radware is a member of the Rad Group of companies and its shares are traded on NASDAQ.
Prolexic Technologies was a US-based provider of security solutions for protecting websites, data centers, and enterprise IP applications from Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks at the network, transport, and application layers. It operated a DDoS mitigation platform and a global network of traffic scrubbing centers. Real-time monitoring and mitigation services were provided by a 24/7 security operations control center (SOCC). Prolexic indicated its DDoS mitigation services make websites, data centers and enterprise IP applications harder to take down via DDoS attacks.
Resin is a web server and Java application server developed by Caucho Technology. There are currently only two versions available: Resin (GPL), which is free for production use, and Resin Pro, designed for enterprise and production environments with a licensing fee. Resin supports the Java EE standard and features a mod_php/PHP-like engine known as Quercus.

Slowloris is a type of denial of service attack tool which allows a single machine to take down another machine's web server with minimal bandwidth and side effects on unrelated services and ports.
aiScaler Ltd. is a multinational software company founded in 2008. It develops application delivery controllers designed to allow dynamic web pages to scale content by intelligently caching frequently requested content. A number of websites in the Alexa top 1000 use aiScaler to manage their traffic.
Imperva, Inc. is an American cyber security software and services company which provides protection to enterprise data and application software. The company is headquartered in San Mateo, California.

Cloudflare, Inc. is an American company that provides content delivery network services, cloud cybersecurity, DDoS mitigation, Domain Name Service, and ICANN-accredited domain registration services. Cloudflare's headquarters are in San Francisco, California. According to The Hill, Cloudflare is used by more than 20% of the Internet for its web security services, as of 2022.
Kemp, Inc. is an American technology company that was founded in 2000 in Bethpage, New York and operates in the application delivery controller industry. The company builds load balancing products which balances user traffic between multiple application servers in a physical, virtual or cloud environment.
Security as a service (SECaaS) is a business model in which a service provider integrates their security services into a corporate infrastructure on a subscription basis more cost-effectively than most individuals or corporations can provide on their own when the total cost of ownership is considered. SECaaS is inspired by the "software as a service" model as applied to information security type services and does not require on-premises hardware, avoiding substantial capital outlays. These security services often include authentication, anti-virus, anti-malware/spyware, intrusion detection, Penetration testing, and security event management, among others.
Fireblade is an Israeli company founded in 2008. It developed the first cloud-based bot-management solution and a multi-tier SaaS security suite powered by reputational and behavioral firewalls, to protect websites against DDoS attacks, web application attacks and a variety of automated attacks, improving website health, security and performance. It offers integration with cPanel and WHM Fireblade was founded by Shay Rapaport and Erez Azaria.
Shlomo Kramer, is an Israeli information technology entrepreneur and investor. He is the co-founder of cyber-security companies Check Point and Imperva, as well as Cato Networks, a cloud-based network security provider.
NetScaler is a line of networking products owned by Cloud Software Group. The products consist of NetScaler, an application delivery controller (ADC), NetScaler AppFirewall, an application firewall, NetScaler Unified Gateway, NetScaler Application Delivery Management (ADM), and NetScaler SD-WAN, which provides software-defined wide-area networking management. NetScaler was initially developed in 1997 by Michel K Susai and acquired by Citrix Systems in 2005. Citrix consolidated all of its networking products under the NetScaler brand in 2016. On September 30, 2022, when Citrix was taken private as part of the merger with TIBCO Software, NetScaler was formed as a business unit under the Cloud Software Group.

Fastly is an American cloud computing services provider. It describes its network as an edge cloud platform, which is designed to help developers extend their core cloud infrastructure to the edge of the network, closer to users. The Fastly edge cloud platform includes their content delivery network (CDN), image optimization, video and streaming, cloud security, and load balancing services. Fastly's cloud security services include denial-of-service attack protection, bot mitigation, and a web application firewall. Fastly's web application firewall uses the Open Web Application Security Project ModSecurity Core Rule Set alongside its own ruleset.









