Inclination is the angle between a reference plane and the orbital plane.
Inclination may also refer to:
Inclination is the angle between a reference plane and the orbital plane.
Inclination may also refer to:

In mathematics, the slope or gradient of a line is a number that describes both the direction and the steepness of the line. Slope is often denoted by the letter m; there is no clear answer to the question why the letter m is used for slope, but its earliest use in English appears in O'Brien (1844) who wrote the equation of a straight line as "y = mx + b" and it can also be found in Todhunter (1888) who wrote it as "y = mx + c".
Pitch may refer to:

An inclined plane, also known as a ramp, is a flat supporting surface tilted at an angle from the vertical direction, with one end higher than the other, used as an aid for raising or lowering a load. The inclined plane is one of the six classical simple machines defined by Renaissance scientists. Inclined planes are used to move heavy loads over vertical obstacles. Examples vary from a ramp used to load goods into a truck, to a person walking up a pedestrian ramp, to an automobile or railroad train climbing a grade.

Orbital inclination measures the tilt of an object's orbit around a celestial body. It is expressed as the angle between a reference plane and the orbital plane or axis of direction of the orbiting object.

A view camera is a large-format camera in which the lens forms an inverted image on a ground-glass screen directly at the film plane. The image is viewed and then the glass screen is replaced with the film, and thus the film is exposed to exactly the same image as was seen on the screen.
A circle of latitude or line of latitude on Earth is an abstract east–west small circle connecting all locations around Earth at a given latitude coordinate line.

The grade of a physical feature, landform or constructed line refers to the tangent of the angle of that surface to the horizontal. It is a special case of the slope, where zero indicates horizontality. A larger number indicates higher or steeper degree of "tilt". Often slope is calculated as a ratio of "rise" to "run", or as a fraction in which run is the horizontal distance and rise is the vertical distance.

Beam tilt is used in radio to aim the main lobe of the vertical plane radiation pattern of an antenna below the horizontal plane.

In lunar astronomy, libration is the wagging or wavering of the Moon perceived by Earth-bound observers and caused by changes in their perspective. It permits an observer to see slightly different hemispheres of the surface at different times. It is similar in both cause and effect to the changes in the Moon's apparent size due to changes in distance. It is caused by three mechanisms detailed below, two of which cause a relatively tiny physical libration via tidal forces exerted by the Earth. Such true librations are known as well for other moons with locked rotation.

A spirit level, bubble level, or simply a level, is an instrument designed to indicate whether a surface is horizontal (level) or vertical (plumb). Different types of spirit levels may be used by carpenters, stonemasons, bricklayers, other building trades workers, surveyors, millwrights and other metalworkers, and in some photographic or videographic work.

The angle of repose, or critical angle of repose, of a granular material is the steepest angle of descent or dip relative to the horizontal plane to which the material can be piled without slumping. At this angle, the material on the slope face is on the verge of sliding. The angle of repose can range from 0° to 90°. The morphology of the material affects the angle of repose; smooth, rounded sand grains cannot be piled as steeply as can rough, interlocking sands. The angle of repose can also be affected by additions of solvents. If a small amount of water is able to bridge the gaps between particles, electrostatic attraction of the water to mineral surfaces will increase the angle of repose, and related quantities such as the soil strength.
Incline, inclined, inclining, or inclination may refer to:

An inclinometer or clinometer is an instrument used for measuring angles of slope, elevation, or depression of an object with respect to gravity's direction. It is also known as a tilt indicator, tilt sensor, tilt meter, slope alert, slope gauge, gradient meter, gradiometer, level gauge, level meter, declinometer, and pitch & roll indicator. Clinometers measure both inclines and declines using three different units of measure: degrees, percentage points, and topos. The astrolabe is an example of an inclinometer that was used for celestial navigation and location of astronomical objects from ancient times to the Renaissance.

In celestial mechanics, the longitude of the periapsis, also called longitude of the pericenter, of an orbiting body is the longitude at which the periapsis would occur if the body's orbit inclination were zero. It is usually denoted ϖ.
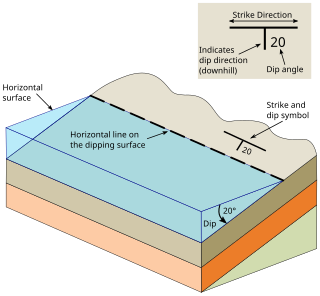
Strike and dip is a measurement convention used to describe the plane orientation or attitude of a planar geologic feature. A feature's strike is the azimuth of an imagined horizontal line across the plane, and its dip is the angle of inclination measured downward from horizontal. They are used together to measure and document a structure's characteristics for study or for use on a geologic map. A feature's orientation can also be represented by dip and dip direction, using the azimuth of the dip rather than the strike value. Linear features are similarly measured with trend and plunge, where "trend" is analogous to dip direction and "plunge" is the dip angle.

An ergonomic keyboard is a computer keyboard designed with ergonomic considerations to minimize muscle strain, fatigue, and other problems.

Tilt–shift photography is the use of camera movements that change the orientation or position of the lens with respect to the film or image sensor on cameras.
Precession refers to a specific change in the direction of the rotation axis of a rotating object, in which the second Euler angle is constant
The sliding criterion (discontinuity) is a tool to estimate easily the shear strength properties of a discontinuity in a rock mass based on visual and tactile characterization of the discontinuity. The shear strength of a discontinuity is important in, for example, tunnel, foundation, or slope engineering, but also stability of natural slopes is often governed by the shear strength along discontinuities.

A tilt detector or tilt indicator is a device which indicates whether a tilt has occurred. Tilt detectors can be used on shipments of tilt sensible items to indicate whether a potentially damaging tilt have occurred. They are also used in the field of electronics or automotive on some models to detect if a change in vehicle inclination has occurred.