
The International Convention for the Regulation of Whaling (ICRW) is an international environmental agreement aimed at the "proper conservation of whale stocks and thus make possible the orderly development of the whaling industry". It governs the commercial, scientific, and aboriginal subsistence whaling practices of 88 member nations.

Whaling is the process of hunting of whales for their usable products such as meat and blubber, which can be turned into a type of oil that became increasingly important in the Industrial Revolution. It was practiced as an organized industry as early as 875 AD. By the 16th century, it had risen to be the principal industry in the coastal regions of Spain and France. The industry spread throughout the world, and became increasingly profitable in terms of trade and resources. Some regions of the world's oceans, along the animals' migration routes, had a particularly dense whale population, and became the targets for large concentrations of whaling ships, and the industry continued to grow well into the 20th century. The depletion of some whale species to near extinction led to the banning of whaling in many countries by 1969, and to a worldwide cessation of whaling as an industry in the late 1980s.

Whales are a widely distributed and diverse group of fully aquatic placental marine mammals. They are an informal grouping within the infraorder Cetacea, which usually excludes dolphins and porpoises. Whales, dolphins and porpoises belong to the order Cetartiodactyla, which consists of even-toed ungulates. Their closest living relatives are the hippopotamuses, from which they diverged about 40 million years ago. The two parvorders of whales, baleen whales (Mysticeti) and toothed whales (Odontoceti), are thought to have had their last common ancestor around 34 million years ago. Whales consist of eight extant families: Balaenopteridae, Balaenidae, Cetotheriidae, Eschrichtiidae, Monodontidae, Physeteridae, Kogiidae, and Ziphiidae.
The International Whaling Commission (IWC) is an international body established under the terms of the 1946 International Convention for the Regulation of Whaling (ICRW) to "provide for the proper conservation of whale stocks and thus make possible the orderly development of the whaling industry".

The Antarctic minke whale or southern minke whale is a species of minke whale within the suborder of baleen whales. It is the second smallest rorqual after the common minke whale and the third smallest baleen whale. Although first scientifically described in the mid-19th century, it was not recognized as a distinct species until the 1990s. Once ignored by the whaling industry due to its small size and low oil yield, the Antarctic minke was able to avoid the fate of other baleen whales and maintained a large population into the 21st century, numbering in the hundreds of thousands. Surviving to become the most abundant baleen whale in the world, it is now one of the mainstays of the industry alongside its cosmopolitan counterpart the common minke. It is primarily restricted to the Southern Hemisphere and feeds mainly on euphausiids.

The southern right whale is a baleen whale, one of three species classified as right whales belonging to the genus Eubalaena. Southern right whales inhabit oceans south of the Equator, between the latitudes of 20° and 60° south. In 2009 the global population was estimated to be approximately 13,600.

The Institute of Cetacean Research: is a non-profit organisation in Japan which claims to be a research organization specializing in the "biological and social sciences related to whales".

Japanese whaling, in terms of active hunting of whales, is estimated by the Japan Whaling Association to have begun around the 12th century. However, Japanese whaling on an industrial scale began around the 1890s when Japan started to participate in the modern whaling industry, at that time an industry in which many countries participated. Modern Japanese whaling activities have extended far outside Japanese territorial waters, including whale sanctuaries protected by other countries.

This article discusses the history of whaling from prehistoric times up to the commencement of the International Whaling Commission (IWC) moratorium on commercial whaling in 1986. Whaling has been an important subsistence and economic activity in multiple regions throughout human history. Commercial whaling dramatically reduced in importance during the 19th century due to the development of alternatives to whale oil for lighting, and the collapse in whale populations. Nevertheless, some nations continue to hunt whales even today.

The International Whaling Commission meeting in 2006 was held 16 June–20 June in St Kitts and Nevis. Pro whaling countries unsuccessfully challenged the 1982 moratorium, yet succeeded in shifting the IWC focus from whale conservation to management of commercial whaling. A full provisional meeting agenda can be seen here :Annotated Provisional Agenda (PDF) Live coverage of the Meeting is available each year here:
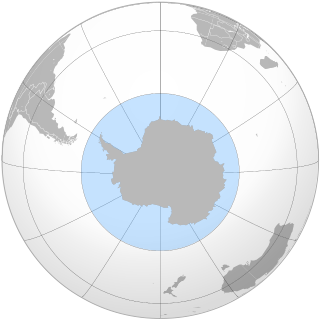
The Southern Ocean Whale Sanctuary is an area of 50 million square kilometres surrounding the continent of Antarctica where the International Whaling Commission (IWC) has banned all types of commercial whaling. To date, the IWC has designated two such sanctuaries, the other being the Indian Ocean Whale Sanctuary.

Marine conservation activism is the efforts of non-governmental organizations and individuals to bring about social and political change in the area of marine conservation. Marine conservation is properly conceived as a set of management strategies for the protection and preservation of ecosystems in oceans and seas. Activists raise public awareness and support for conservation, while pushing governments and corporations to practice sound ocean management, create conservation policy, and enforce existing laws and policy through effective regulation. There are many different kinds of organizations and agencies that work toward these common goals. They all are a part of the growing movement that is ocean conservation. These organizations fight for many causes including stopping pollution, overfishing, whaling and by-catching, and supporting marine protected areas.

The Hawaiian Islands Humpback Whale National Marine Sanctuary is one of the world's most important whale habitats, hosting thousands of humpbacks each winter.
The South Pacific Whale Sanctuary (SPWS) was a proposed region of the South Pacific Ocean in which whaling would be prohibited.

Whale Wars is a weekly American documentary-style reality television series that premiered on November 7, 2008 on the Animal Planet cable channel. The program followed Paul Watson, founder of the Sea Shepherd Conservation Society, as he and the crew aboard their various vessels attempted to stop the killing of whales by Japanese vessels (whalers) off the coast of Antarctica.
The Southern Ocean, also known as the Antarctic Ocean, comprises the southernmost waters of the World Ocean, generally taken to be south of 60° S latitude and encircling Antarctica. As such, it is regarded as the second-smallest of the five principal oceanic divisions: smaller than the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian oceans but larger than the Arctic Ocean. Over the past 30 years, the Southern Ocean has been subject to rapid climate change, which has led to changes in the marine ecosystem.

Whale conservation refers to the conservation of whales.

Anti-whaling refers to actions taken by those who seek to end whaling in various forms, whether locally or globally in the pursuit of marine conservation. Such activism is often a response to specific conflicts with pro-whaling countries and organizations that practice commercial whaling and/or research whaling, as well as with indigenous groups engaged in subsistence whaling. Some anti-whaling factions have received criticism and legal action for extreme methods including violent direct action. The term anti-whaling may also be used to describe beliefs and activities related to these actions.

The southern bottlenose whale is a species of whale, in the Ziphiid family, one of two members of the genus Hyperoodon. Seldom observed, the southern bottlenose whale is resident in Antarctic waters. The species was first described by English zoologist William Henry Flower in 1882, based on a water-worn skull from Lewis Island, in the Dampier Archipelago, Western Australia. They live in deep ocean waters over 1000 meters.
Whaling in Madagascar is currently banned on a commercial level in compliance with sanctuary regulations. Despite erratic weather conditions, there is a history of overhunting sperm whales, humpback whales, and Bryde's whales within the surrounding waters of Madagascar. In an attempt to allow native populations to recuperate from these operations, the region about Madagascar was included within the Indian Ocean Whale Sanctuary by the International Whaling Commission.
















