This article concerns the period 239 BC – 230 BC.
Year 238 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Gracchus and Falto. The denomination 238 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Hamilcar Barca or Barcas was a Carthaginian general and statesman, leader of the Barcid family, and father of Hannibal, Hasdrubal and Mago. He was also father-in-law to Hasdrubal the Fair.

Mago Barca was a Barcid Carthaginian who played an important role in the Second Punic War, leading forces of Carthage against the Roman Republic in Iberia and northern and central Italy. Mago was the third son of Hamilcar Barca, was the brother of Hannibal and Hasdrubal, and was the brother-in-law of Hasdrubal the Fair.

Hasdrubal Barca, a latinization of ʿAzrubaʿal son of Hamilcar Barca, was a Carthaginian general in the Second Punic War. He was the brother of Hannibal and Mago Barca.

The Battle of Himera, supposedly fought on the same day as the Battle of Salamis, or at the same time as the Battle of Thermopylae, saw the Greek forces of Gelon, King of Syracuse, and Theron, tyrant of Agrigentum, defeat the Carthaginian force of Hamilcar the Magonid, ending a Carthaginian bid to restore the deposed tyrant of Himera. The alleged coincidence of this battle with the naval battle of Salamis and the resultant derailing of a Punic-Persian conspiracy aimed at destroying the Greek civilization is rejected by modern scholars. Scholars also agree that the battle led to the crippling of Carthage's power in Sicily for many decades. It was one of the most important battles of the Sicilian Wars.

The Mercenary War, also known as the Truceless War, was a mutiny by troops that were employed by Carthage at the end of the First Punic War (264–241 BC), supported by uprisings of African settlements revolting against Carthaginian control. It lasted from 241 to late 238 or early 237 BC and ended with Carthage suppressing both the mutiny and the revolt.
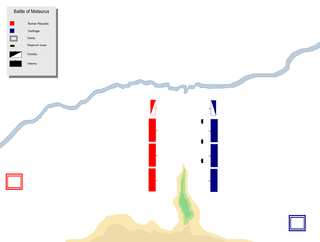
The Battle of the Metaurus was a pivotal battle in the Second Punic War between Rome and Carthage, fought in 207 BC near the Metauro River in Italy. The Carthaginians were led by Hasdrubal Barca, brother of Hannibal, who was to have brought siege equipment and reinforcements for Hannibal. The Roman armies were led by the consuls Marcus Livius, who was later nicknamed the Salinator, and Gaius Claudius Nero.

The Battle of the Saw was the culminating battle of a campaign fought between a Carthaginian army led by Hamilcar Barca and a rebel force led by Spendius in 238 BC in what is now northern Tunisia. Carthage was fighting a coalition of mutinous soldiers and rebellious African cities in the Mercenary War which had started in 241 BC. The rebels had been besieging Carthage while the Carthaginian field army under Hamilcar raided their supply lines. Under this pressure the rebels pulled back to their base at Tunis and despatched their own army to prevent Hamilcar's activities and, ideally, destroy his army.

The Sicilian Wars, or Greco-Punic Wars, were a series of conflicts fought between ancient Carthage and the Greek city-states led by Syracuse over control of Sicily and the western Mediterranean between 580 and 265 BC.

Carthaginian Iberia was a province of the larger Carthaginian Empire. The Carthaginians, conquered the Mediterranean part of Iberia and remained there until the 2nd Punic war and the Roman conquest of the peninsula.
During the siege of Tunis in October 238 BC a rebel army under Mathos was besieged by a Carthaginian force under Hamilcar Barca and Hannibal. The Carthaginian army, which had served on Sicily during the First Punic War, mutinied in late 241 BC in the wake of Carthage's defeat, starting the Mercenary War. After three years of increasingly bitter war, the Carthaginians defeated the rebel field army at the Battle of the Saw, capturing its leaders. The Carthaginians then moved to besiege the rebels' strongest remaining stronghold at Tunis.
Hamilcar's victory with Naravas took place in 240 BC in what is now north-west Tunisia. A Carthaginian army led by Hamilcar Barca defeated a rebel army led by Spendius and Autaritus, after 2,000 Numidian cavalry led by Naravas defected from the rebels to Carthage. The precise location of the battle is unknown. Carthage was fighting a coalition of mutinous soldiers and rebellious African cities in the Mercenary War which had started in 241 BC.
This section of the timeline of Hispania concerns Spanish and Portuguese history events from the Carthaginian conquests to before the barbarian invasions.

Mercenary life is recorded as a custom of Iron Age Spain, particularly in the central area of the Iberian peninsula. Departing from the native tribe and applying to serve in others was a way for economically disadvantaged youth to escape poverty and find an opportunity to use their fighting skills. Starting from 5th century BC, mercenary life would become a true social phenomenon in Hispania, with great numbers of fighters from distant lands coming to join the armies of Carthage, Rome, Sicily and even Greece, as well as other Hispanic peoples.
Gisco was a Carthaginian general who served during the closing years of the First Punic War and took a leading part in the events which sparked the Mercenary War. He was a citizen of the city state of Carthage, which was located in what is now Tunisia. His date of birth and age at death are both unknown, as are his activities prior to his rise to prominence towards the end of the First Punic War.
The Battle of Leptis Parva was fought in 238 BC between a Carthaginian army of over 30,000 commanded by Hamilcar Barca and Hanno, and approximately 20,000 mutinous Carthaginian soldiers and North African rebels under Matho in the North African province of Byzacium. The battle was the final major conflict of the Mercenary War and resulted in a decisive victory for the Carthaginians.
Spendius was a former Roman slave who led a rebel army against Carthage, in what is known as the Mercenary War. He escaped or was rescued from slavery in Campania and was recruited into the Carthaginian Army during the First Punic War at some point prior to 241 BC. Spendius's date of birth is unknown, as are most details of his activities prior to his coming to prominence as a mutineer in 241 BC. After the First Punic War, Carthage attempted to pay its soldiers less than the full amount due to them before demobilising them. Spendius faced death by torture if he were returned to Roman authority and took a dim view of the increasingly warm relationship between Carthage and Rome. He came to the fore as a member of the army most vocal in resisting Carthaginian efforts to settle the dispute. When the disagreement broke down into a full-scale mutiny in late 241 BC he was elected co-general with the African Mathos by his fellow mutineers. Mathos spread the news of the mutiny to the main African settlements under Carthaginian suzerainty and they rose in rebellion. Provisions, money and 70,000 reinforcements poured in. For four years Spendius led a rebel army against Carthage, in what is known as the Mercenary War, with mixed success.
Orissus or Orisson was a chief, leader or ruler of the Iberian Oretani.
Istolatios or Istolatius was a warlord and military chief of the Turdetans, whose activity took place during the 3rd century BC. Endowed with great prestige, he organized a large army with Turdetans and Celtiberian and Iberian troops to oppose the Carthaginian invasion of Hamilcar Barca.








