
The Lakeside and Haverthwaite Railway (L&HR) is a 3.2-mile-long (5.1 km) heritage railway in Cumbria, England.

Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 0-4-0 represents one of the simplest possible types, that with two axles and four coupled wheels, all of which are driven. The wheels on the earliest four-coupled locomotives were connected by a single gear wheel, but from 1825 the wheels were usually connected with coupling rods to form a single driven set.

The Tanfield Railway is a 4 ft 8+1⁄2 instandard gauge heritage railway in Gateshead and County Durham, England. Running on part of a former horse-drawn colliery wooden waggonway, later rope & horse, lastly rope & loco railway. It operates preserved industrial steam locomotives. The railway operates a passenger service every Sunday, plus other days, as well as occasional demonstration coal, goods and mixed trains. The line runs 3 miles (4.8 km) between a southern terminus at East Tanfield, Durham, to a northern terminus at Sunniside, Gateshead. Another station, Andrews House, is situated near the Marley Hill engine shed. A halt also serves the historic site of the Causey Arch. The railway claims it is "the world's oldest railway" because it runs on a section dating from 1725, other parts being in use since 1621.
Brush Traction was a manufacturer and maintainer of railway locomotives in Loughborough, England whose operations have now been merged into the Wabtec company's Doncaster UK operations.

The Hunslet Engine Company is a locomotive-building company, founded in 1864 in Hunslet, England. It manufactured steam locomotives for over 100 years and currently manufactures diesel shunting locomotives. The company is part of Ed Murray & Sons Ltd.

The first Locomotives of the Great Western Railway (GWR) were specified by Isambard Kingdom Brunel but Daniel Gooch was soon appointed as the railway's Locomotive Superintendent. He designed several different 7 ft 1⁄4 in broad gauge types for the growing railway, such as the Firefly and later Iron Duke Class 2-2-2s. In 1864 Gooch was succeeded by Joseph Armstrong who brought his standard gauge experience to the workshops at Swindon. To replace some of the earlier locomotives, he put broad gauge wheels on his standard gauge locomotives and from this time on all locomotives were given numbers, including the broad gauge ones that had previously carried just names.

The Hunslet Austerity 0-6-0ST is a class of steam locomotive designed by Hunslet Engine Company for shunting. The class became the standard British shunting locomotive during the Second World War, and production continued until 1964 at various locomotive manufacturers.

W. G. Bagnall was a locomotive manufacturer from Stafford, England which was founded in 1875 and operated until it was taken over in 1962 by English Electric.

Manning Wardle was a steam locomotive manufacturer based in Hunslet, Leeds, West Yorkshire, England.
Robert Stephenson and Company was a locomotive manufacturing company founded in 1823 in Forth Street, Newcastle upon Tyne in England. It was the first company in the world created specifically to build railway engines.

The NS 8800 was a series of tank engines of the Dutch railway NS for the shunting service. Of the approximately 324 British-built Hunslet Austerity C (0-6-0ST) saddle tank locomotives, many were used by the British War Department during their fight against the German army in mainland Western Europe. The NS bought 27 of them just after World War II. They had been built by the Hunslet Engine Company (12), WG Bagnall (3), Robert Stephenson & Hawthorns (RSH) (6), and Hudswell Clarke (6).

The Avonside Engine Company was a locomotive manufacturer in Avon Street, St. Philip's, Bristol, England between 1864 and 1934. However the business originated with an earlier enterprise Henry Stothert and Company.

The Baguley valve gear is a type of steam engine valve gear invented by Ernest E. Baguley, the Chief Draughtsman of the W.G. Bagnall company of locomotive manufacturers and patented in 1893. It was used by Bagnall during Baguley's time there, then by his own company of Baguley Cars Ltd.

A Giesl ejector is a suction draught system for steam locomotives that works on the same principle as a feedwater injector. This ejector was invented in 1951 by the Austrian engineer, Dr. Adolph Giesl-Gieslingen. The Giesl ejector ensures improved suction draught and a correspondingly better use of energy. The existing blastpipe in a locomotive is replaced by several, small, fan-shaped, diverging blast pipes, from which the diffuser gets its flat, long, drawn-out shape.

The W. G. Bagnall New Standard 180-6-0ST is a type of industrial steam locomotive manufactured at W. G. Bagnall's Castle Engine Works and designed by Harold Wood at W.G. Bagnall in 1951. The class was specifically designed for the Port Talbot Steelworks, and ran from 1951 to 1973 in industrial service. Two locomotives, the former Longbridge locomotives, are preserved.
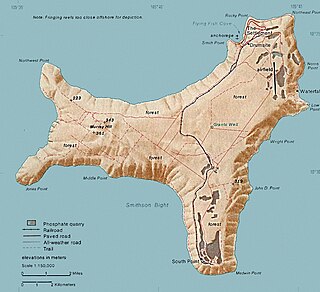
The Christmas Island Phosphate Co.'s Railway was a 19.7 km long industrial railway between Flying Fish Cove and South Point on Christmas Island. The remains of the South Point station are now heritage-listed.













