
The economy of Brazil is historically the largest in Latin America and the Southern Hemisphere in nominal terms. The Brazilian economy is the second largest in the Americas. It is an upper-middle income developing mixed economy. In 2024, according to International Monetary Fund (IMF), Brazil has the 8th largest gross domestic product (GDP) in the world and has the 8th largest purchasing power parity in the world. In 2024, according to Forbes, Brazil was the 7th largest country in the world by number of billionaires. According to International Monetary Fund (IMF), Brazilian nominal GDP was US$2.331 trillion, the country has a long history of being among the largest economies in the world and the GDP per capita was US$11,178 per inhabitant.

Rio de Janeiro, or simply Rio, is the capital of the state of Rio de Janeiro. It is the second-most-populous city in Brazil and the sixth-most-populous city in the Americas.

Rio de Janeiro is one of the 27 federative units of Brazil. It has the second largest economy of Brazil, with the largest being that of the state of São Paulo. The state, which has 8.2% of the Brazilian population, is responsible for 9.2% of the Brazilian GDP.

São Paulo is one of the 26 states of the Federative Republic of Brazil and is named after Saint Paul of Tarsus. It is located in the Southeast Region and is limited by the states of Minas Gerais to the north and northeast, Paraná to the south, Rio de Janeiro to the east and Mato Grosso do Sul to the west, in addition to the Atlantic Ocean to the southeast. It is divided into 645 municipalities and its total area is 248,219.481 square kilometres km², which is equivalent to 2.9% of Brazil's surface, being slightly larger than the United Kingdom. Its capital is the municipality of São Paulo.
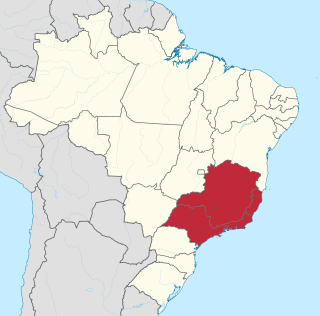
The Southeast Region of Brazil is composed of the states of Espírito Santo, Minas Gerais, Rio de Janeiro and São Paulo. It is the richest region of the country, responsible for approximately 60% of the Brazilian GDP, as São Paulo, Rio de Janeiro, and Minas Gerais are the three richest states of Brazil, the top three Brazilian states in terms of GDP. The Southeast of Brazil also has the highest GDP per capita among all Brazilian regions.

Brazilian industry has its earliest origin in workshops dating from the beginning of the 19th century. Most of the country's industrial establishments appeared in the Brazilian southeast, and, according to the Commerce, Agriculture, Factories and Navigation Joint, 77 establishments registered between 1808 and 1840 were classified as "factories" or "manufacturers". However, most, about 56 establishments, would be considered workshops by today's standards, directed toward the production of soap and tallow candles, snuff, spinning and weaving, foods, melting of iron and metals, wool and silk, amongst others. They used both slaves and free laborers.

The Federal University of the State of Rio de Janeiro is a federally funded public university located in the State of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. It has several campuses in the city of Rio de Janeiro, including two in the Urca neighborhood.
Euvaldo Lodi Institute of Rio de Janeiro is the equivalent of the Brazilian Euvaldo Lodi Institute, created by the National Confederation of Industry along with the Industry Social Service (SESI) and the National Industrial Training Service in 1969. Except it only covers Rio de Janeiro state, instead of all the Brazilian territory.
The Industry Social Service of the State of Rio de Janeiro comprehends SESI's work in Rio de Janeiro state. The institution focuses in improving work environments, quality of life and education levels of collaborators from Rio de Janeiro's enterprises. Through programs and mobile units, it carries out actions related to health, education, sports, leisure, culture, occupational health, work safety and environmental protection. These activities are aimed at workers and companies, as much as to society in general. SENAI Rio's history is parallel to the Brazilian industrial development and its designation accompanies Rio de Janeiro's changes, as when it became a capital and was renamed Guanabara state.
The creative industry in Brazil refers to various economic sectors of Brazil that depend on the talents and creativity to develop. In other words, these economic sectors generate wealth for the region through knowledge, culture and creativity, and contribute to sustainable development. The term 'creative industries' was coined by the United Kingdom in 1990 and, in 2001, was augmented by two important additions: by researcher John Howkins, who applied an entrepreneurial vision when focusing on the transformation of creativity in product; and professor Richard Florida, whose research focused on the professionals involved in the creative processes of production, and addressed the social aspects and the "potential contribution to the development" of the "creative class".
FIRJAN System is a network of private nonprofit organizations with more than ten thousand associates. Its mission is to promote business competitiveness, education and quality of life of industrial workers and the whole society, in the state of Rio de Janeiro. FIRJAN System consists of five institutions that work in an integrated manner for the growth of the industry of RJ. Together, FIRJAN, Industrial Center of Rio de Janeiro (CIRJ), Industry Social Service of the State of Rio de Janeiro, National Industrial Training Service of the State of Rio de Janeiro and Euvaldo Lodi Institute of Rio de Janeiro promote actions in economic, political and social levels to ensure a prominent position to the state on the national scenery. Today, all institutions act as service providers to enterprises and society.

Rio de Janeiro is on the far western part of a strip of Brazil's Atlantic coast, close to the Tropic of Capricorn, where the shoreline is oriented east–west. Facing largely south, the city was founded on an inlet of this stretch of the coast, Guanabara Bay, and its entrance is marked by a point of land called Sugar Loaf – a "calling card" of the city.

Paulo Roberto Nunes Guedes is a Brazilian economist and co-founder of the investment bank BTG Pactual. He is also a co-founder of the think-tank Instituto Millenium, and was the economic advisor for the campaign of President Jair Bolsonaro. Guedes served as the Minister of Economics of Brazil through the entirety of the Bolsonaro presidency, from 1 January 2019 to 1 January 2023.

Events in the year 2020 in Brazil.
Line 3 of the Rio de Janeiro Metro is a planned line which would connect Rio de Janeiro and Niterói. This is a challenge due to the fact that the line would need to cross the Guanabara Bay, presumably underwater. Niterói last had rail service of any kind in 2007 and its public transit is currently only served by buses and boats.

A long series of criminal investigations have occurred in Brazil associated with Operation Car Wash, since the first one began in March 2014. These investigations are considered offshoots of the original phased investigations.
Álvaro Coutinho Aguirre was a Brazilian agronomist, zoologist and naturalist. Aguirre created the first reserve park for wild animals in Brazil, the Sooretama Biological Reserve at the state of Espírito Santo (the first protected area created in Brazil was in 1937. He dedicated his life to the preservation of the Brazilian flora and fauna, especially the Atlantic Forest and the biggest primate of the Americas, the Muriqui. During the 1960s, he undertook many expeditions to study the life and habits of the Muriqui and its conditions at the time. The results showed a considerable reduction of the groups of the animals, due to deforestation and lack of preservation of their habitat.

Events in the year 2022 in Brazil.

The Guanabara Palace is located on Pinheiro Machado Street, in the Laranjeiras neighborhood (bairro), in the south zone of Rio de Janeiro, capital of the homonymous state. It is the official seat of the government of the State of Rio de Janeiro. The Guanabara Palace should not be confused with Laranjeiras Palace, located in the same neighborhood, which is the official residence of the Governor of the State of Rio de Janeiro.












