
Shaka kaSenzangakhona, also known as Shaka Zulu and Sigidi kaSenzangakhona, was the king of the Zulu Kingdom from 1816 to 1828. One of the most influential monarchs of the Zulu, he ordered wide-reaching reforms that reorganized the military into a formidable force.

Zulu people are a native people of Southern Africa of the Nguni. The Zulu people are the largest ethnic group and nation in South Africa, with an estimated 14.39 million people, in total of which 13.78 million people live in South Africa, mainly in the province of KwaZulu-Natal.

KwaZulu-Natal is a province of South Africa that was created in 1994 when the government merged the Zulu bantustan of KwaZulu and Natal Province.

Sea monsters are beings from folklore believed to dwell in the sea and are often imagined to be of immense size. Marine monsters can take many forms, including sea dragons, sea serpents, or tentacled beasts. They can be slimy and scaly and are often pictured threatening ships or spouting jets of water. The definition of a "monster" is subjective; further, some sea monsters may have been based on scientifically accepted creatures, such as whales and types of giant and colossal squid.

Durban is the third-most populous city in South Africa, after Johannesburg and Cape Town, and the largest city in the province of KwaZulu-Natal. Situated on the east coast of South Africa, on the Natal Bay of the Indian Ocean, Durban is largest port city in sub-saharan Africa and was formerly named Port Natal. North of the harbour and city centre lies the mouth of the Umgeni River; the flat city centre rises to the hills of the Berea on the west; and to the south, running along the coast, is the Bluff. Durban is the seat of the larger eThekwini Metropolitan Municipality, which spans an area of 2,556 km2 (987 sq mi) and had a population of 4.2 million in 2022, making the metropolitan population one of Africa's largest on the Indian Ocean. Within the city limits, Durban's population was 595,061 in 2011. The city has a humid subtropical climate, with hot, wet summers and mild, dry winters.

The Great Serpent Mound is a 1,348-feet-long (411 m), three-feet-high prehistoric effigy mound located in Peebles, Ohio. It was built on what is known as the Serpent Mound crater plateau, running along the Ohio Brush Creek in Adams County, Ohio. The mound is the largest serpent effigy known in the world.
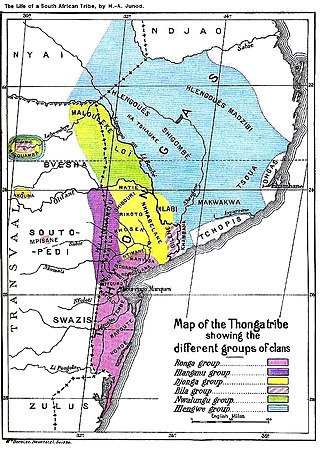
The Tsonga people are a Bantu ethnic group primarily native to Southern Mozambique and South Africa. They speak Xitsonga, a Southern Bantu language. A very small number of Tsonga people are also found in Zimbabwe and Northern Eswatini. The Tsonga people of South Africa share some history with the Tsonga people of Southern Mozambique, and have similar cultural practices, but differ in the dialects spoken.
The doctrine of the serpent seed, also known as the dual-seed or the two-seedline doctrine, is a controversial and fringe Christian religious belief which explains the biblical account of the fall of man by stating that the Serpent mated with Eve in the Garden of Eden, and the offspring of their union was Cain. This event resulted in the creation of two races of people: the wicked descendants of the Serpent who were destined for damnation, and the righteous descendants of Adam who were destined to have eternal life. The doctrine frames human history as a conflict between these two races in which the descendants of Adam will eventually triumph over the descendants of the Serpent.

Howick Falls is a waterfall in Howick, KwaZulu-Natal Province, South Africa. The waterfall is approximately 95 m in height (310 feet) and lies on the Umgeni River. The Zulu people called the falls KwaNogqaza, which means "Place of the Tall One".

Basket weaving is the process of weaving or sewing pliable materials into three-dimensional artifacts, such as baskets, mats, mesh bags or even furniture. Craftspeople and artists specialized in making baskets may be known as basket makers and basket weavers. Basket weaving is also a rural craft.
Chatsworth is a large township in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa established in the 1950s to segregate the Indian population and create a buffer between the white suburbs of Durban to the north and the black townships of Durban to the south. Located in the Southern Durban basin and roughly bordered by the Umhlatuzana River in the North and Umlaas River in the South, the suburb is made up mainly of Indian/Asian and Black African people. Umhlatuzane is part of Chatsworth.

An effigy mound is a raised pile of earth built in the shape of a stylized animal, symbol, religious figure, human, or other figure. The Effigy Moundbuilder culture is primarily associated with the years 550–1200 CE during the Late Woodland Period, although radiocarbon dating has placed the origin of certain mounds as far back as 320 BCE.
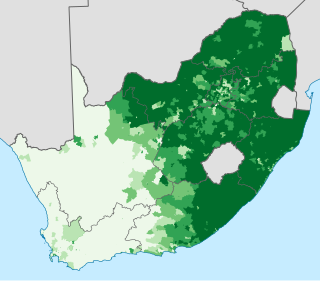
Blacks are the majority racial group in South Africa, belonging to various Bantu tribes. They are descendants of Bantu speaking people who settled in South Africa during the Bantu expansion and the Mfecane.

The Tonga people of Zambia and Zimbabwe are a Bantu ethnic group of southern Zambia and neighbouring northern Zimbabwe, and to a lesser extent, in Mozambique. They are related to the Batoka who are part of the Tokaleya people in the same area, but not to the Tonga people of Malawi. In southern Zambia they are patrons of the Kafue Twa. They differ culturally and linguistically from the Tsonga people of South Africa and southern Mozambique.

The Nguni people are a linguistic cultural group of Bantu cattle herders who migrated from central Africa into Southern Africa, made up of ethnic groups formed from iron age and proto-agrarians, with offshoots in neighboring colonially-created countries in Southern Africa. Swazi people live in both South Africa and Eswatini, while Ndebele people live in both South Africa and Zimbabwe.

Bantu religion is a system of various spiritual beliefs and practices that relate to the Bantu people of Central, East, and Southern Africa. Although Bantu peoples account for several hundred different ethnic groups, there is a high degree of homogeneity in Bantu cultures and customs, just as in Bantu languages. Many Bantu cultures traditionally believed in a supreme god whose name is a variation of Nyambe/Nzambe and ancestral veneration. The phrase "Bantu tradition" usually refers to the common, recurring themes that are found in all, or most, Bantu cultures on the continent.

The Twa, often referred to as Batwa or Mutwa (singular), are indigenous hunter-gatherer peoples of the Great Lakes Region in Central Africa, recognized as some of the earliest inhabitants of the area. Historically and academically, the term “Pygmy” has been used to describe these groups, however, it is considered derogatory, particularly by the Twa themselves. While some Batwa activists accept the term as an acknowledgement of their indigenous status, most prefer specific ethnic labels such as Bambuti, Baaka, and Bambendjelle.
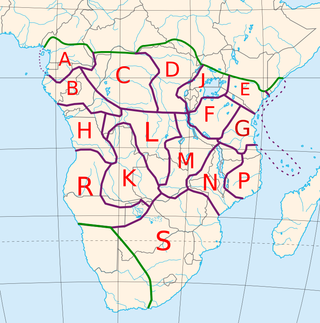
The Bantu peoples are an indigenous ethnolinguistic grouping of approximately 400 distinct native African ethnic groups who speak Bantu languages. The languages are native to countries spread over a vast area from West Africa, to Central Africa, Southeast Africa and into Southern Africa. Bantu people also inhabit southern areas of Northeast African states.
The Zulu sheep breed is native to South Africa and is predominantly raised by rural farmers in the province of KwaZulu-Natal. It serves primarily as a source of food and income to poor resource farmers. It belongs to the Nguni type of sheep together with the Pedi and the Swazi sheep.
















