Related Research Articles

The gallon is a unit of volume in British imperial units and United States customary units. Three different versions are in current use:

The common ostrich, or simply ostrich, is a species of flightless bird native to certain large areas of Africa. It is one of two extant species of ostriches, the only living members of the genus Struthio in the ratite order of birds. The other is the Somali ostrich, which was recognized as a distinct species by BirdLife International in 2014 having been previously considered a distinctive subspecies of ostrich.

Volume is a measure of regions in three-dimensional space. It is often quantified numerically using SI derived units or by various imperial or US customary units. The definition of length and height (cubed) is interrelated with volume. The volume of a container is generally understood to be the capacity of the container; i.e., the amount of fluid that the container could hold, rather than the amount of space the container itself displaces. By metonymy, the term "volume" sometimes is used to refer to the corresponding region.

In recipes, quantities of ingredients may be specified by mass, by volume, or by count.

The integumentary system is the set of organs forming the outermost layer of an animal's body. It comprises the skin and its appendages, which act as a physical barrier between the external environment and the internal environment that it serves to protect and maintain the body of the animal. Mainly it is the body's outer skin.

Perspiration, also known as sweat, is the fluid secreted by sweat glands in the skin of mammals.

Oncotic pressure, or colloid osmotic-pressure, is a type of osmotic pressure induced by the plasma proteins, notably albumin, in a blood vessel's plasma that causes a pull on fluid back into the capillary.

In physiology, dehydration is a lack of total body water, with an accompanying disruption of metabolic processes. It occurs when free water loss exceeds free water intake, usually due to exercise, disease, or high environmental temperature. Mild dehydration can also be caused by immersion diuresis, which may increase risk of decompression sickness in divers.
In physiology, body water is the water content of an animal body that is contained in the tissues, the blood, the bones and elsewhere. The percentages of body water contained in various fluid compartments add up to total body water (TBW). This water makes up a significant fraction of the human body, both by weight and by volume. Ensuring the right amount of body water is part of fluid balance, an aspect of homeostasis.

A fluid ounce is a unit of volume typically used for measuring liquids. The British Imperial, the United States customary, and the United States food labeling fluid ounce are the three that are still in common use, although various definitions have been used throughout history.
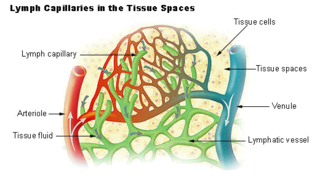
Lymph is the fluid that flows through the lymphatic system, a system composed of lymph vessels (channels) and intervening lymph nodes whose function, like the venous system, is to return fluid from the tissues to be recirculated. At the origin of the fluid-return process, interstitial fluid—the fluid between the cells in all body tissues—enters the lymph capillaries. This lymphatic fluid is then transported via progressively larger lymphatic vessels through lymph nodes, where substances are removed by tissue lymphocytes and circulating lymphocytes are added to the fluid, before emptying ultimately into the right or the left subclavian vein, where it mixes with central venous blood.

The amniotic fluid is the protective liquid contained by the amniotic sac of a gravid amniote. This fluid serves as a cushion for the growing fetus, but also serves to facilitate the exchange of nutrients, water, and biochemical products between mother and fetus.
Fluid balance is an aspect of the homeostasis of organisms in which the amount of water in the organism needs to be controlled, via osmoregulation and behavior, such that the concentrations of electrolytes in the various body fluids are kept within healthy ranges. The core principle of fluid balance is that the amount of water lost from the body must equal the amount of water taken in; for example, in humans, the output must equal the input. Euvolemia is the state of normal body fluid volume, including blood volume, interstitial fluid volume, and intracellular fluid volume; hypovolemia and hypervolemia are imbalances. Water is necessary for all life on Earth. Humans can survive for 4 to 6 weeks without food but only for a few days without water.

The cup is a cooking measure of volume, commonly associated with cooking and serving sizes. In the US, it is traditionally equal to one-half US pint (236.6 ml). Because actual drinking cups may differ greatly from the size of this unit, standard measuring cups may be used, with a metric cup being 250 millilitres.

Both the British imperial measurement system and United States customary systems of measurement derive from earlier English unit systems used prior to 1824 that were the result of a combination of the local Anglo-Saxon units inherited from Germanic tribes and Roman units.

Santorio Santorio whose real name was Santorio Santori better known in English as Sanctorius of Padua was an Italian physiologist, physician, and professor, who introduced the quantitative approach into the life sciences and is considered the father of experimental physiology. He is also known as the inventor of several medical devices. His work De Statica Medicina, written in 1614, saw many publications and influenced generations of physicians.

Transepidermal water loss is the loss of water that passes from inside a body through the epidermis to the surrounding atmosphere via diffusion and evaporation processes. TEWL in mammals is also known as insensible water loss (IWL), as it is a process over which organisms have little physiologic control and of which they are usually mostly unaware. Insensible loss of body water can threaten fluid balance; in humans, substantial dehydration sometimes occurs before a person realizes what is happening.

Iatrophysics or iatromechanics is the medical application of physics. It provides an explanation for medical practices with mechanical principles. It was a school of medicine in the seventeenth century which attempted to explain physiological phenomena in mechanical terms. Believers of iatromechanics thought that physiological phenomena of the human body followed the laws of physics. It was related to iatrochemistry in studying the human body in a systematic manner based on observations from the natural world though it had more emphasis on mathematical models rather than chemical processes.
Volume contraction is a decrease in the volume of body fluid, including the dissolved substances that maintain osmotic balance (osmolytes). The loss of the water component of body fluid is specifically termed dehydration.
The recommended daily amount of drinking water for humans varies. It depends on activity, age, health, and environment. In the United States, the Adequate Intake for total water, based on median intakes, is 4.0 litres per day for males older than 18, and 3.0 litres per day for females over 18; it assumes about 80% from drink and 20% from food. The European Food Safety Authority recommends 2.0 litres of total water per day for women and 2.5 litres per day for men.
References
- 1 2 Lote, Christopher J. (2012). Principles of renal physiology (5th ed.). New York, NY: Springer. p. 11. ISBN 978-1-4614-3785-7. OCLC 796995047.
- ↑ Brandis K. "Insensible Water Loss". anaesthesiamcq.com. Retrieved 6 August 2020.
- 1 2 Brandis, Kerry. "Fluid Physiology – 3.2 Insensible Water Loss". www.anaesthesiamcq.com.
- 1 2 "Insensible perspiration Definition and Examples – Biology Online Dictionary". Biology Articles, Tutorials & Dictionary Online. October 7, 2019.
- 1 2 Hollerbach, Teresa (June 11, 2018). "The Weighing Chair of Sanctorius Sanctorius: A Replica". NTM. 26 (2): 121–149. doi:10.1007/s00048-018-0193-z. PMC 5993855 . PMID 29761203.
- ↑ "Santorio Santorio (1561–1636): Medicina statica". Vaulted Treasures. University of Virginia, Claude Moore Health Sciences Library.