| Type I Model 61 | |
|---|---|
| Type | Rifle grenade |
| Place of origin | Spain [1] |
| Service history | |
| Used by | Spain, Portugal |
| Wars | Portuguese Colonial War Sahrawi insurgency (1973–1976) Western Sahara conflict |
| Production history | |
| Manufacturer | Instalaza |
| Specifications | |
| Mass | 700 g (25 oz) |
| Length | 395 mm (15.6 in) |
| Diameter | 64 mm (2.5 in) |
| Filling weight | 342 g (12.1 oz) |
| Type II Model 63 | |
|---|---|
| Type | rifle grenade |
| Place of origin | Spain [1] |
| Service history | |
| Used by | Spain, Portugal |
| Production history | |
| Manufacturer | Instalaza |
| Specifications | |
| Mass | 510 g (18 oz) |
| Length | 333 mm (13.1 in) |
| Diameter | 40 mm (1.6 in) |
| Maximum firing range | 425 m (1,394 ft) |
| Filling weight | 88 g (3.1 oz) |
The Spanish munitions company Instalaza made two models of rifle grenade during the 1960s. As well as being used by the Spanish Army, the Portuguese Army also used them in the colonial wars that took place in its colonies in Africa.
The Type I could penetrate 250 mm (9.8 in) of armour, whereas the lighter Type II could penetrate 150 mm (5.9 in) of armour. [1]
Each was propelled by being mounted atop a rifle's 22 mm grenade launching adapter, and being launched by a ballistite (blank) cartridge.
The Type II was enhanced further, with a bullet trap to accept 5.56×45mm NATO.
A further development led to the Type V and is known as the FTV. [2]

A rocket-propelled grenade (RPG) is a shoulder-fired rocket weapon that launches rockets equipped with an explosive warhead. Most RPGs can be carried by an individual soldier, and are frequently used as anti-tank weapons. These warheads are affixed to a rocket motor which propels the RPG towards the target and they are stabilized in flight with fins. Some types of RPG are reloadable with new rocket-propelled grenades, while others are single-use. RPGs are generally loaded from the front.

Armour-piercing ammunition (AP) is a type of projectile designed to penetrate armour protection, most often including naval armour, body armour, and vehicle armour.

The Bazooka is a man-portable recoilless anti-tank rocket launcher weapon, widely deployed by the United States Army, especially during World War II. Also referred to as the "stovepipe", the innovative Bazooka was among the first generation of rocket-propelled anti-tank weapons used in infantry combat. Featuring a solid-propellant rocket for propulsion, it allowed for high-explosive anti-tank (HEAT) shaped charge warheads to be delivered against armored vehicles, machine gun nests, and fortified bunkers at ranges beyond that of a standard thrown grenade or mine. The universally applied nickname arose from the weapon's M1 variant's vague resemblance to the musical instrument called a bazooka invented and popularized by 1930s American comedian Bob Burns.

High-explosive anti-tank (HEAT) is the effect of a shaped charge explosive that uses the Munroe effect to penetrate heavy armor. The warhead functions by having an explosive charge collapse a metal liner inside the warhead into a high-velocity shaped charge jet; this is capable of penetrating armor steel to a depth of seven or more times the diameter of the charge. The shaped charge jet armor penetration effect is purely kinetic in nature; the round has no explosive or incendiary effect on the armor.

The Panzerfaust was a development family of single-shot man-portable anti-tank systems developed by Nazi Germany during World War II. The weapons were the first single-use light anti-tank weapons based on a pre-loaded disposable launch tube, a weapon configuration which is still used today.

An anti-tank rifle is an anti-materiel rifle designed to penetrate the armor of armored fighting vehicles, most commonly tanks, armored personnel carriers, and infantry fighting vehicles. The term is usually used for weapons that can be carried and used by one person, but is sometimes used for larger weapons. The usefulness of rifles for this purpose ran from the introduction of tanks in World War I until the Korean War. While medium and heavy tank armor became too thick to be penetrated by rigid projectiles from rifles that could be carried by a single soldier, anti-tank rifles continued to be used against other "soft" targets, though recoilless rifles and rocket-propelled grenades such as the bazooka were also introduced for infantry close-layer defense against tanks.

The M203 is a single-shot 40 mm under-barrel grenade launcher designed to attach to a rifle. It uses the same rounds as the older stand-alone M79 break-action grenade launcher, which utilizes the high-low propulsion system to keep recoil forces low. While compatible with many weapons, the M203 was originally designed and produced by the United States military for the M16 rifle and its carbine variant, the M4. The launcher can also be mounted onto a C7, a Canadian version of the M16 rifle; this requires the prior removal of the bottom handguard.

The Maschinengewehr (MG) 151 is a belt-fed autocannon for aircraft use, developed in Nazi Germany from 1934 to 1940 and produced by Waffenfabrik Mauser during World War II. It was originally produced in 15.1 mm caliber from 1940, with a 15×96mm cartridge, but due to demand for higher effect against aircraft, especially with the introduction of mine shells for the 20 mm MG-FF/M aircraft cannon, the design was rechambered to 20 mm caliber in 1941, using a newly developed 20×82mm cartridge which traded projectile velocity for explosive power. The initial 15 mm variant then became known as the MG 151/15, with the new 20 mm variant becoming the MG 151/20.

The M79 grenade launcher is a single-shot, shoulder-fired, break-action grenade launcher that fires a 40×46mm grenade, which uses what the US Army calls the High-Low Propulsion System to keep recoil forces low, and first appeared during the Vietnam War. Its distinctive report has earned it colorful nicknames, such as "Thumper", "Thump-Gun", "Bloop Tube", "Big Ed", "Elephant Gun", and "Blooper" among American soldiers as well as "Can Cannon" in reference to the grenade size; Australian units referred to it as the "Wombat Gun". The M79 can fire a wide variety of 40 mm rounds, including explosive, anti-personnel, smoke, buckshot, flechette, and illumination. While largely replaced by the M203, the M79 has remained in service in many units worldwide in niche roles.

The Type 59 main battle tank is a Chinese-produced version of the Soviet T-54A tank, an early model of the ubiquitous T-54/55 series. The first vehicles were produced in 1958 and it was accepted into service in 1959, with serial production beginning in 1963. Over 9,500 of the tanks were produced by the time production ended in 1985 with approximately 5,500 serving with the Chinese armed forces. The tank formed the backbone of the Chinese People's Liberation Army armoured units until the early 2000s, with an estimated 5,000 of the later Type 59-I and Type 59-II variants in service in 2002.
A rifle grenade is a grenade that uses a rifle-based launcher to permit a longer effective range than would be possible if the grenade were thrown by hand.
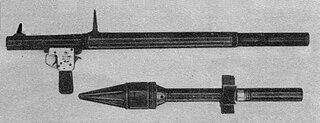
The RPG-2 is a man-portable, shoulder-fired anti-tank weapon that was designed in the Soviet Union. It was the first successful anti-tank weapon of its type, being a successor to the earlier and unsuccessful rocket-propelled grenade RPG-1.

The Pak 36 is a 3.7 cm / 37mm caliber German anti-tank gun used during the Second World War. It was the main anti-tank weapon of Wehrmacht Panzerjäger units until 1942. Developed by Rheinmetall in 1933, it was first issued to the German Army in 1936, with 9,120 being available by the beginning of the war in September 1939 and a further 5,339 produced during the war. As the predominant anti-tank gun design in the world during the late 1930s, demand was high for the Pak 36, with another 6,000 examples produced for export and the design being copied by the Soviet Union as the 45 mm anti-tank gun M1932 (19-K) and by other nations such as Japan.

The Instalaza C90 is a 90 millimetres disposable, shoulder-fired and one-man operated rocket-propelled grenade (RPG) launcher, which can be fitted with a VN38-C night vision device for full night combat capability. It is being used as an infantry-type weapon, with Instalaza also claiming it to be the, "lightest infantry weapons system in its class".
The Energa anti-tank rifle grenade is a rifle-launched anti-tank grenade that is propelled by a ballistite-filled blank cartridge. The name Energa comes from the firm in Liechtenstein that designed it, the Anstalt für die ENtwicklung von ERfindungen und Gewerblichen Anwendungen, based in Vaduz.

The PAPOP was a French project to construct a computerized infantry weapon for the FÉLIN system, capable of hitting hidden or protected targets. It would have combined a 35 mm grenade launcher with a 5.56×45mm NATO assault rifle, both in a bullpup configuration, complete with targeting aids and an unorthodox sight.
The high–low system is a design of cannon and anti-tank warfare launcher using a smaller high-pressure chamber to store propellant. It allows a much larger projectile to be launched without the heavy equipment usually needed for large caliber weapons. When the propellant is ignited, the higher pressure gases are bled out through vents at reduced pressure to a much larger low pressure chamber to push a projectile forward. The high-low system allows the weight of the weapon and its ammunition to be reduced significantly. Production cost and time are drastically lower than for standard cannon or other small-arm weapon systems firing a projectile of the same size and weight. It has a far more efficient use of the propellant, unlike earlier recoilless weapons, where most of the propellant is expended to the rear of the weapon to counter the recoil of the projectile being fired.
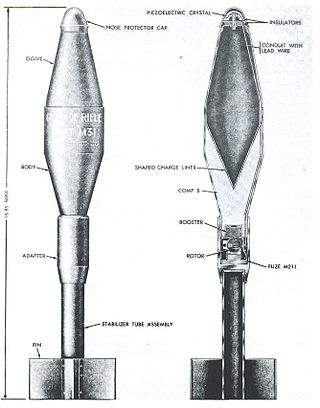
The M31 HEAT is a fin-stabilized anti-tank rifle grenade designed in the late 1950s to replace the Belgian ENERGA rifle grenade which was adopted by the US Army and US Marines as an emergency stop-gap measure during the Korean War. Like the ENERGA, it has a nose-initiated, based-detonated HEAT warhead, but unlike the ENERGA, the mechanical impact fuse system is replaced with a less complex and more reliable piezo-electric fuse system which also allows higher angles of impact, up to 65 degrees.

Man-portable anti-tank systems are traditionally portable shoulder-launched projectile systems firing heavy shell-type projectiles, typically designed to combat protected targets, such as armoured vehicles, field fortifications and at times even low-flying aircraft.

Yugoslavia manufactured two types of rifle grenade, both with the nomenclature of M60. The M60 anti-personnel rifle grenade bore a resemblance to the French M52 rifle grenade. The M60 anti-tank rifle grenade bore a resemblance to the STRIM 65, also of French origin. It could penetrate 200mm of armour.