
A wireless network is a computer network that uses wireless data connections between network nodes. Wireless networking allows homes, telecommunications networks and business installations to avoid the costly process of introducing cables into a building, or as a connection between various equipment locations. Admin telecommunications networks are generally implemented and administered using radio communication. This implementation takes place at the physical level (layer) of the OSI model network structure.

Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) is the ability of electrical equipment and systems to function acceptably in their electromagnetic environment, by limiting the unintentional generation, propagation and reception of electromagnetic energy which may cause unwanted effects such as electromagnetic interference (EMI) or even physical damage to operational equipment. The goal of EMC is the correct operation of different equipment in a common electromagnetic environment. It is also the name given to the associated branch of electrical engineering.

Wireless communication is the transfer of information (telecommunication) between two or more points without the use of an electrical conductor, optical fiber or other continuous guided medium for the transfer. The most common wireless technologies use radio waves. With radio waves, intended distances can be short, such as a few meters for Bluetooth, or as far as millions of kilometers for deep-space radio communications. It encompasses various types of fixed, mobile, and portable applications, including two-way radios, cellular telephones, personal digital assistants (PDAs), and wireless networking. Other examples of applications of radio wireless technology include GPS units, garage door openers, wireless computer mouse, keyboards and headsets, headphones, radio receivers, satellite television, broadcast television and cordless telephones. Somewhat less common methods of achieving wireless communications involve other electromagnetic phenomena, such as light and magnetic or electric fields, or the use of sound.

Base station is – according to the International Telecommunication Union's (ITU) Radio Regulations (RR) – a "land station in the land mobile service."

Telematics is an interdisciplinary field encompassing telecommunications, vehicular technologies, electrical engineering, and computer science. Telematics can involve any of the following:

The antennas contained in mobile phones, including smartphones, emit radiofrequency (RF) radiation ; the parts of the head or body nearest to the antenna can absorb this energy and convert it to heat. Since at least the 1990s, scientists have researched whether the now-ubiquitous radiation associated with mobile phone antennas or cell phone towers is affecting human health. Mobile phone networks use various bands of RF radiation, some of which overlap with the microwave range. Other digital wireless systems, such as data communication networks, produce similar radiation.
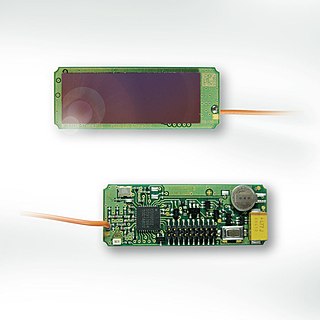
The EnOcean technology is an energy harvesting wireless technology used primarily in building automation systems, but also in other application fields such as industry, transportation, and logistics. The energy harvesting wireless modules are manufactured and marketed by the company EnOcean, headquartered in Oberhaching near Munich. The modules combine micro energy converters with ultra low power electronics and wireless communications and enable batteryless, wireless sensors, switches, and controls.
Dassault Systèmes Simulia Corp. is a computer-aided engineering (CAE) vendor. Formerly known as Abaqus Inc. and previously Hibbitt, Karlsson & Sorensen, Inc., (HKS), the company was founded in 1978 by David Hibbitt, Bengt Karlsson and Paul Sorensen, and has its headquarters in Providence, Rhode Island.
Edholm's law, proposed by and named after Phil Edholm, refers to the observation that the three categories of telecommunication, namely wireless (mobile), nomadic and wired networks (fixed), are in lockstep and gradually converging. Edholm's law also holds that data rates for these telecommunications categories increase on similar exponential curves, with the slower rates trailing the faster ones by a predictable time lag. Edholm's law predicts that the bandwidth and data rates double every 18 months, which has proven to be true since the 1970s. The trend is evident in the cases of Internet, cellular (mobile), wireless LAN and wireless personal area networks.
LDMOS is a planar double-diffused MOSFET used in amplifiers, including microwave power amplifiers, RF power amplifiers and audio power amplifiers. These transistors are often fabricated on p/p+ silicon epitaxial layers. The fabrication of LDMOS devices mostly involves various ion-implantation and subsequent annealing cycles. As an example, the drift region of this power MOSFET is fabricated using up to three ion implantation sequences in order to achieve the appropriate doping profile needed to withstand high electric fields.
MiWi is a proprietary wireless protocol supporting peer-to-peer, star network connectivity. It was designed by Microchip Technology. MiWi uses small, low-power digital radios based on the IEEE 802.15.4 standard, and is designed for low-power, cost-constrained networks, such as industrial monitoring and control, home and building automation, remote control, wireless sensors, lighting control, and automated meter reading.
AWR Corporation is an electronic design automation (EDA) software company, formerly known as Applied Wave Research, and then acquired by National Instruments
Rohde & Schwarz GmbH & Co KG is an international electronics group specializing in the fields of electronic test equipment, broadcast & media, cybersecurity, radiomonitoring and radiolocation, and radiocommunication. The company provides also products for the wireless communications, electronics industry, aerospace and defense, homeland security and critical infrastructures.

An RF module is a (usually) small electronic device used to transmit and/or receive radio signals between two devices. In an embedded system it is often desirable to communicate with another device wirelessly. This wireless communication may be accomplished through optical communication or through radio-frequency (RF) communication. For many applications, the medium of choice is RF since it does not require line of sight. RF communications incorporate a transmitter and a receiver. They are of various types and ranges. Some can transmit up to 500 feet. RF modules are typically fabricated using RF CMOS technology.
CISC Semiconductor GmbH defines itself as “a design and consulting service company for industries developing embedded microelectronic systems with extremely short Time-To-Market cycles.” The company started in 1999, working in the semiconductor industry, but soon expanded its field towards the automotive branch and further extended business towards the radio frequency technology (RFID) sector in 2003. Since then, CISC gained significant experience and expertise in RFID, developing an own business segment and highly sensitive measurement equipment to test and verify RFID systems for different industries. Representatives of CISC Semiconductor are actively working on and contributing to worldwide standardization of future technologies like RFID, in different standardization organizations. This effort brings CISC into the position of being a leader in research and development, and thus being able to be “one step ahead of innovation”. As of 2011 CISC Semiconductor was in a globally leading standardization position for RFID testing by providing the convener of ISO/IEC JTC1 WG4/SG6 on “RFID performance and conformance test methods“, as well as GS1 EPCglobal co-chairs for performance and conformance tests.

Li-Fi is a wireless communication technology which utilizes light to transmit data and position between devices. The term was first introduced by Harald Haas during a 2011 TEDGlobal talk in Edinburgh.
One way of outlining the subject of radio science is listing the topics associated with it by authoritative bodies.
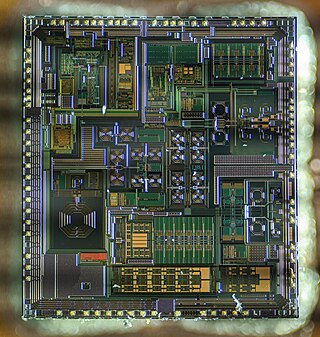
RF CMOS is a metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) integrated circuit (IC) technology that integrates radio-frequency (RF), analog and digital electronics on a mixed-signal CMOS RF circuit chip. It is widely used in modern wireless telecommunications, such as cellular networks, Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, GPS receivers, broadcasting, vehicular communication systems, and the radio transceivers in all modern mobile phones and wireless networking devices. RF CMOS technology was pioneered by Pakistani engineer Asad Ali Abidi at UCLA during the late 1980s to early 1990s, and helped bring about the wireless revolution with the introduction of digital signal processing in wireless communications. The development and design of RF CMOS devices was enabled by van der Ziel's FET RF noise model, which was published in the early 1960s and remained largely forgotten until the 1990s.
Yihong Qi is an engineer, professor, entrepreneur, and inventor. His work focuses on networking science and technology. Qi is currently an adjunct professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering at the Missouri University of Science and Technology. He is a Fellow of The Canadian Academy of Engineering and of the National Academy of Inventors. Qi's research has led to the founding of five independent companies.










