Related Research Articles

Utility cycling encompasses any cycling done simply as a means of transport rather than as a sport or leisure activity. It is the original and most common type of cycling in the world. Cycling mobility is one of the various types of private transport and a major part of individual mobility.

Transport for West Midlands (TfWM) is the public body responsible for co-ordinating transport services in the West Midlands metropolitan county in England. It is an executive body of the West Midlands Combined Authority (WMCA), with bus franchising and highway management powers similar to Transport for London. TfWM's policies and strategy are set by the Transport Delivery Committee of the WMCA.

Intermodal passenger transport, also called mixed-mode commuting, involves using two or more modes of transportation in a journey. Mixed-mode commuting is often used to combine the strengths of various transportation options. A major goal of modern intermodal passenger transport is to reduce dependence on the automobile as the major mode of ground transportation and increase use of public transport. To assist the traveller, various intermodal journey planners such as Rome2rio and Google Transit have been devised to help travellers plan and schedule their journey.

The Société de transport de Montréal is a public transport agency that operates transit bus and rapid transit services in the urban agglomeration of Montreal, Quebec, Canada. Established in 1861 as the "Montreal City Passenger Railway Company", it has grown to comprise four subway lines with a total of 68 stations, as well as 212 bus routes and 23 night routes. The STM was created in 2002 to replace the Société de transport de la communauté urbaine de Montréal. The STM operates the most heavily used urban mass transit system in Canada, and one of the most heavily used rapid transit systems in North America. As of 2019, the average daily ridership is 2,297,600 passengers: 977,400 by bus, 1,306,500 by rapid transit and 13,700 by paratransit service.

The Transport Direct Programme was a division of the UK Department for Transport (DfT) to develop standards, data and better information technology systems to support public transport. It developed and operates the Transport Direct Portal which is a public facing multi-modal journey planner. It also supports the creation and management of comprehensive databases of all public transport movements in the United Kingdom with Traveline. During 2010 two key datasets were released as Open Data and published on www.data.gov.uk.
Translink is the public transit agency for Queensland, and is part of the Department of Transport and Main Roads. Translink was first introduced by the Queensland Government in June 2003 to orchestrate bus, ferry, rail and light rail services. They works with Brisbane Airtrain, Transport for Brisbane, RiverCity Ferries, Queensland Rail and other operators to provide services. Translink operates an integrated ticketing system across Queensland and the go card system to allow the use of one ticket on multiple services in South-East Queensland.
The Transport Protocol Experts Group (TPEG) is a data protocol suite for traffic and travel related information. TPEG can be carried over different transmission media (bearers), such as digital broadcast or cellular networks. TPEG applications include, among others, information on road conditions, weather, fuel prices, parking or delays of public transport.

A passenger information system, or passenger information display system, is an automated system for supplying users of public transport with information about the nature and the state of a public transport service through visual, voice or other media. It is also known as a customer information system or an operational information system. Among the information provided by such systems, a distinction can be drawn between:
In computing, Microsoft's Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 introduced in 2007/2008 a new networking stack named Next Generation TCP/IP stack, to improve on the previous stack in several ways. The stack includes native implementation of IPv6, as well as a complete overhaul of IPv4. The new TCP/IP stack uses a new method to store configuration settings that enables more dynamic control and does not require a computer restart after a change in settings. The new stack, implemented as a dual-stack model, depends on a strong host-model and features an infrastructure to enable more modular components that one can dynamically insert and remove.
A penalty fare, standard fare, or fixed penalty notice is a special, usually higher, fare charged because a passenger using public transport did not comply with the normal ticket purchasing rules. It should not be confused with an unpaid fares notice.

The OV-chipkaart is a contactless smart card system used for all public transport in the Netherlands. First introduced in the Rotterdam Metro in April 2005, it has subsequently been rolled out to other areas and travel modes. It fully replaced the national strippenkaart system for buses, trams, and metro trains in 2011, and the paper ticket system for rail travel in July 2014.
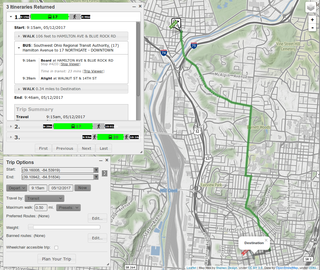
A journey planner, trip planner, or route planner is a specialized search engine used to find an optimal means of travelling between two or more given locations, sometimes using more than one transport mode. Searches may be optimized on different criteria, for example fastest, shortest, fewest changes, cheapest. They may be constrained, for example, to leave or arrive at a certain time, to avoid certain waypoints, etc. A single journey may use a sequence of several modes of transport, meaning the system may know about public transport services as well as transport networks for private transportation. Trip planning or journey planning is sometimes distinguished from route planning, which is typically thought of as using private modes of transportation such as cycling, driving, or walking, normally using a single mode at a time. Trip or journey planning, in contrast, would make use of at least one public transport mode which operates according to published schedules; given that public transport services only depart at specific times, an algorithm must therefore not only find a path to a destination, but seek to optimize it so as to minimize the waiting time incurred for each leg. In European Standards such as Transmodel, trip planning is used specifically to describe the planning of a route for a passenger, to avoid confusion with the completely separate process of planning the operational journeys to be made by public transport vehicles on which such trips are made.

The Transport Direct Portal was a distributed Internet-based multi-modal journey planner providing information for travel in England, Wales and Scotland. It was managed by Transport Direct, a division of the Department for Transport. It was launched in 2004 and was operated by a consortium led by Atos and later enhanced to include a cycle journey planning function. The closure of the portal was announced in September 2014 "Closure of the Transport Direct website"(PDF). Archived from the original(PDF) on 12 September 2014. and the portal closed on 30 September 2014.
The go card is an electronic smartcard ticketing system developed by Cubic Corporation, which is currently used on the TransLink public transport network in South East Queensland. To use the go card, users hold the card less than 10 cm away from the reader to "touch on" before starting a journey, and must do the same to "touch off" the service at the end of the journey. The cost of each journey is deducted from the go card balance.
The Greater Manchester Transport Innovation Fund was a failed bid by the Greater Manchester Passenger Transport Authority (GMPTA) and Association of Greater Manchester Authorities (AGMA) to secure £1.5 billion from the Transport Innovation Fund (TIF), a major public transport funding mechanism in England, for the metropolitan county of Greater Manchester. There would have been an additional £1.2 billion borrowed and paid back through a mixture of public transport revenues and weekday, peak-time only Greater Manchester congestion charge.

Metro Trains Melbourne, often known simply as Metro, is the operator of services on the electrified suburban passenger rail network in Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. Metro Melbourne is the largest suburban rail network in Australia with 17 lines, 219 stations and 405 km (252 mi) of railways and second busiest network in Australia. It is owned by Public Transport Victoria who sublet the infrastructure and rolling stock of Metro Trains Melbourne to a joint venture between Hong Kong-based MTR Corporation (60%), John Holland Group (20%) and UGL Rail (20%). The three constituent companies are also partners in the Metro Trains Sydney joint venture, which has operated the Sydney Metro network since 2019.

Public transport is a system of transport for passengers by group travel systems available for use by the general public unlike private transport, typically managed on a schedule, operated on established routes, and that charge a posted fee for each trip. There is no rigid definition; the Encyclopædia Britannica specifies that public transportation is within urban areas, and air travel is often not thought of when discussing public transport—dictionaries use wording like "buses, trains, etc." Examples of public transport include city buses, trolleybuses, trams and passenger trains, rapid transit and ferries. Public transport between cities is dominated by airlines, coaches, and intercity rail. High-speed rail networks are being developed in many parts of the world.

Communications-based train control (CBTC) is a railway signaling system that uses telecommunications between the train and track equipment for traffic management and infrastructure control. CBTC allows a train's position to be known more accurately than with traditional signaling systems. This makes railway traffic management safer and more efficient. Metros are able to reduce headways while maintaining or even improving safety.

Opal is a contactless fare collection system for public transport services in the greater Sydney area and most other urban areas of New South Wales, Australia. Operation of the Opal system is managed by the New South Wales Government's transport authority, Transport for NSW. First launched in late 2012, Opal is valid on Transport for NSW's metro, train, bus, ferry and light rail services that operate in Sydney and the neighbouring Central Coast, Hunter Region, Blue Mountains, Illawarra and Southern Highlands areas. Opal equipment was designed from the start to support a variety of cards, but launched with the captive Opal cards.
Third-party logistics is an organization's long term committment of outsourcing its distribution services to third-party logistics businesses.
References
- ↑ Fang, Ke; Zimmerman, Samuel L.. 2015. Public transport service optimization and system integration. China transport topics; no. 14. Washington, DC: World Bank Group.
- ↑ What is successful transport integration? Professor Phil Charles. Transport Futures Institute. February 22, 2014. http://www.transport-futures.com/what-is-successful-transport-integration/ accessed 6/11/2017
- ↑ Great Britain: Parliament: House of Commons: Transport Committee. Evidence. pp. 149-155. Reg Harman. Integrated Transport: The future of light rail and modern trams in Britain. https://books.google.com/books?id=cVfnWO9pC8oC&pg=PA150