Inter-network processors are special-purpose processors which aid in the interconnection of telecommunications networks. Most commonly used inter-network processors are switches, bridges, hubs, routers and gateways.

A network processor is an integrated circuit which has a feature set specifically targeted at the networking application domain.

A telecommunications network is a collection of terminal nodes in which links are connected so as to enable telecommunication between the terminals. The transmission links connect the nodes together. The nodes use circuit switching, message switching or packet switching to pass the signal through the correct links and nodes to reach the correct destination terminal. Each terminal in the network usually has a unique address so messages or connections can be routed to the correct recipients. The collection of addresses in the network is called the address space. Examples of telecommunications networks are:
Switches act as interfaces for communication between telecommunications circuits in a networked environment. In addition, most modern switches have integrated network managing capabilities and may operate on numerous layers of the OSI reference model. Switches usually come as managed or unmanaged. The managed switches commonly have no management interface and/or configuration options, while their counterparts offer interfaces for modification of switch operation.
Network management is the process of administering and managing computer networks. Services provided by this discipline include fault analysis, performance management, provisioning of networks and maintaining the quality of service. Software that enables network administrators to perform their functions is called network management software.
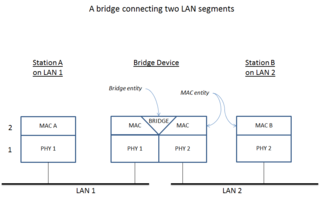
A bridge can connect numerous local area networks for the purpose of collaboration and/or exchange of information. However, the local area networks must be using the same sets of communication rules or protocols for a bridge interconnection to be successful. In slight contrast, routers are considered intelligent communications processors, which do the same thing as bridges do, namely connect two or more networks, but they allow specification of different protocols to be required factors in the interconnection process rather than the entire protocol suite. Routers are generally optimized for Ethernet LAN interfaces and are likely not to contain any other types of physical interfaces.

A local area network (LAN) is a computer network that interconnects computers within a limited area such as a residence, school, laboratory, university campus or office building. By contrast, a wide area network (WAN) not only covers a larger geographic distance, but also generally involves leased telecommunication circuits.

A router is a networking device that forwards data packets between computer networks. Routers perform the traffic directing functions on the Internet. Data sent through the internet, such as a web page or email, is in the form of data packets. A packet is typically forwarded from one router to another router through the networks that constitute an internetwork until it reaches its destination node.

Ethernet is a family of computer networking technologies commonly used in local area networks (LAN), metropolitan area networks (MAN) and wide area networks (WAN). It was commercially introduced in 1980 and first standardized in 1983 as IEEE 802.3, and has since retained a good deal of backward compatibility and been refined to support higher bit rates and longer link distances. Over time, Ethernet has largely replaced competing wired LAN technologies such as Token Ring, FDDI and ARCNET.
Hubs are communications processors which allow for port-switching, similarly to switches. Both of these processors support automatic port-switching in order to provide shared resources access to the users of a particular networked environment. However, hubs do not manage traffic so every packet that enters any port is in output on every other port, resulting in packet collisions that interrupt the flow of traffic.
When networks do not use the same protocols for the purpose of communication, they can be connected via gateways, using protocol conversion processes. In addition, gateways require congruent or at least mutually acceptable administrative procedures between the interconnecting networks. The duties of a gateway are usually much more complex than those of switches or routers.