A Usenet newsgroup is a repository usually within the Usenet system, for messages posted from users in different locations using the Internet. They are discussion groups and are not devoted to publishing news. Newsgroups are technically distinct from, but functionally similar to, discussion forums on the World Wide Web. Newsreader software is used to read the content of newsgroups. Before the adoption of the World Wide Web, Usenet newsgroups were among the most popular Internet services.
rn is a Usenet newsreader written by Larry Wall and originally released in 1984. It was one of the first newsreaders to take full advantage of a character-addressable CRT terminal. Previous newsreaders, such as readnews, were mostly line-oriented and designed for use on the printing terminals which were common on the early Unix minicomputers where the Usenet software and network originated. Later variants of the original rn program included rrn, trn, and strn.
DNIX is a discontinued Unix-like real-time operating system from the Swedish company Dataindustrier AB (DIAB). A version named ABCenix was developed for the ABC 1600 computer from Luxor. Daisy Systems also had a system named Daisy DNIX on some of their computer-aided design (CAD) workstations. It was unrelated to DIAB's product.

A news server is a collection of software used to handle Usenet articles. It may also refer to a computer itself which is primarily or solely used for handling Usenet. Access to Usenet is only available through news server providers.
C News is a news server package, written by Geoff Collyer, assisted by Henry Spencer, at the University of Toronto as a replacement for B News. It was presented at the Winter 1987 USENIX conference in Washington, D.C.
The Network News Transfer Protocol (NNTP) is an application protocol used for transporting Usenet news articles (netnews) between news servers, and for reading/posting articles by the end user client applications. Brian Kantor of the University of California, San Diego, and Phil Lapsley of the University of California, Berkeley, wrote RFC 977, the specification for the Network News Transfer Protocol, in March 1986. Other contributors included Stan O. Barber from the Baylor College of Medicine and Erik Fair of Apple Computer.
UUCP is a suite of computer programs and protocols allowing remote execution of commands and transfer of files, email and netnews between computers.

NetWare is a discontinued computer network operating system developed by Novell, Inc. It initially used cooperative multitasking to run various services on a personal computer, using the IPX network protocol. The final update release was version 6.5SP8 in May 2009, and it has since been replaced by Open Enterprise Server.
On Usenet, the Usenet Death Penalty (UDP) is a final penalty that may be issued against Internet service providers or single users who produce too much spam or fail to adhere to Usenet standards. It is named after the death penalty, as it causes the banned user or provider to be unable to use Usenet, essentially "killing" their service. Messages that fall under the jurisdiction of a Usenet Death Penalty will be cancelled. Cancelled messages are deleted from Usenet servers and not allowed to propagate. This causes users on the affected ISP to be unable to post to Usenet, and it puts pressure on the ISP to change their policies. Notable cases include actions taken against UUNET, CompuServe, Excite@Home, and Google Groups.
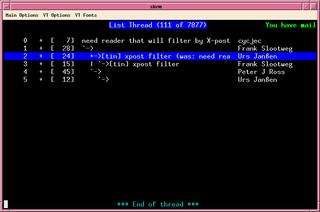
tin is an open-source, text-based, threaded newsreader, used to read and post messages on Usenet, the worldwide distributed discussion system.

A newsreader is a software application that reads articles on Usenet distributed throughout newsgroups. Newsreaders act as clients which connect to a news server, via the Network News Transfer Protocol (NNTP), to download articles and post new articles. In addition to text-based articles, Usenet is also used to distribute binary files, generally in dedicated "binaries" newsgroups.
wildmat is a pattern matching library developed by Rich Salz. Based on the wildcard syntax already used in the Bourne shell, wildmat provides a uniform mechanism for matching patterns across applications with simpler syntax than that typically offered by regular expressions. Patterns are implicitly anchored at the beginning and end of each string when testing for a match.

Internet Systems Consortium, Inc., also known as ISC, is an American non-profit corporation that supports the infrastructure of the universal, self-organizing Internet by developing and maintaining core production-quality software, protocols, and operations. ISC has developed several key Internet technologies that enable the global Internet, including: BIND, ISC DHCP and Kea. Other software projects no longer in active development include OpenReg and ISC AFTR.
NOV, or News Overview, is a widely deployed indexing method for Usenet articles, also found in some Internet email implementations. Written in 1992 by Geoff Collyer, NOV replaced a variety of incompatible indexing schemes used in different client programs, each typically requiring custom modifications to each news server before they could be used. In modern NNTP implementations, NOV is exposed as the XOVER and related commands.
An offline reader is computer software that downloads e-mail, newsgroup posts or web pages, making them available when the computer is offline: not connected to a server. Offline readers are useful for portable computers and dial-up access.

Virtuoso Universal Server is a middleware and database engine hybrid that combines the functionality of a traditional relational database management system (RDBMS), object–relational database (ORDBMS), virtual database, RDF, XML, free-text, web application server and file server functionality in a single system. Rather than have dedicated servers for each of the aforementioned functionality realms, Virtuoso is a "universal server"; it enables a single multithreaded server process that implements multiple protocols. The free and open source edition of Virtuoso Universal Server is also known as OpenLink Virtuoso. The software has been developed by OpenLink Software with Kingsley Uyi Idehen and Orri Erling as the chief software architects.
Control messages are a special kind of Usenet post that are used to control news servers. They differ from ordinary posts by a header field named Control. The body of the field contains control name and arguments.

Usenet, USENET, or, "in full", User's Network, is a worldwide distributed discussion system available on computers. It was developed from the general-purpose Unix-to-Unix Copy (UUCP) dial-up network architecture. Tom Truscott and Jim Ellis conceived the idea in 1979, and it was established in 1980. Users read and post messages to one or more topic categories, known as newsgroups. Usenet resembles a bulletin board system (BBS) in many respects and is the precursor to the Internet forums that have become widely used. Discussions are threaded, as with web forums and BBSes, though posts are stored on the server sequentially.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to software:







