Related Research Articles

Enhanced Data rates for GSM Evolution (EDGE), also known as 2.75G, Enhanced GPRS (EGPRS), IMT Single Carrier (IMT-SC), and Enhanced Data rates for Global Evolution, is a 2G digital mobile phone technology for data transmission. It is a subset of General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) on the GSM network and improves upon it offering speeds close to 3G technology, hence the name 2.75G.

Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) is a set of communication standards for simultaneous digital transmission of voice, video, data, and other network services over the digitalised circuits of the public switched telephone network. Work on the standard began in 1980 at Bell Labs and was formally standardized in 1988 in the CCITT "Red Book". By the time the standard was released, newer networking systems with much greater speeds were available, and ISDN saw relatively little uptake in the wider market. One estimate suggests ISDN use peaked at a worldwide total of 25 million subscribers at a time when 1.3 billion analog lines were in use. ISDN has largely been replaced with digital subscriber line (DSL) systems of much higher performance.
The Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS) is a 3G mobile cellular system for networks based on the GSM standard. Developed and maintained by the 3GPP, UMTS is a component of the International Telecommunication Union IMT-2000 standard set and compares with the CDMA2000 standard set for networks based on the competing cdmaOne technology. UMTS uses wideband code-division multiple access (W-CDMA) radio access technology to offer greater spectral efficiency and bandwidth to mobile network operators.

The T-carrier is a member of the series of carrier systems developed by AT&T Bell Laboratories for digital transmission of multiplexed telephone calls.

Time-division multiplexing (TDM) is a method of transmitting and receiving independent signals over a common signal path by means of synchronized switches at each end of the transmission line so that each signal appears on the line only a fraction of time according to agreed rules, e.g. with each transmitter working in turn. It can be used when the bit rate of the transmission medium exceeds that of the signal to be transmitted. This form of signal multiplexing was developed in telecommunications for telegraphy systems in the late 19th century but found its most common application in digital telephony in the second half of the 20th century.
Telephony is the field of technology involving the development, application, and deployment of telecommunication services for the purpose of electronic transmission of voice, fax, or data, between distant parties. The history of telephony is intimately linked to the invention and development of the telephone.
In the seven-layer OSI model of computer networking, the physical layer or layer 1 is the first and lowest layer: the layer most closely associated with the physical connection between devices. The physical layer provides an electrical, mechanical, and procedural interface to the transmission medium. The shapes and properties of the electrical connectors, the frequencies to transmit on, the line code to use and similar low-level parameters, are specified by the physical layer.
In telecommunications, common-channel signaling (CCS), or common-channel interoffice signaling (CCIS), is the transmission of control information (signaling) via a separate channel than that used for the messages, The signaling channel usually controls multiple message channels.

CDMA2000 is a family of 3G mobile technology standards for sending voice, data, and signaling data between mobile phones and cell sites. It is developed by 3GPP2 as a backwards-compatible successor to second-generation cdmaOne (IS-95) set of standards and used especially in North America and South Korea.

X.21 is an interface specification for differential communications introduced in the mid-1970s by the ITU-T. X.21 was first introduced as a means to provide a digital signaling interface for telecommunications between carriers and customers' equipment. This includes specifications for DTE/DCE physical interface elements, alignment of call control characters and error checking, elements of the call control phase for circuit switching services, and test loops.

The base station subsystem (BSS) is the section of a traditional cellular telephone network which is responsible for handling traffic and signaling between a mobile phone and the network switching subsystem. The BSS carries out transcoding of speech channels, allocation of radio channels to mobile phones, paging, transmission and reception over the air interface and many other tasks related to the radio network.

Evolution-Data Optimized is a telecommunications standard for the wireless transmission of data through radio signals, typically for broadband Internet access. EV-DO is an evolution of the CDMA2000 (IS-2000) standard which supports high data rates and can be deployed alongside a wireless carrier's voice services. It uses advanced multiplexing techniques including code-division multiple access (CDMA) as well as time-division multiplexing (TDM) to maximize throughput. It is a part of the CDMA2000 family of standards and has been adopted by many mobile phone service providers around the world particularly those previously employing CDMA networks. It is also used on the Globalstar satellite phone network.
In communications, Circuit Switched Data (CSD) is the original form of data transmission developed for the time-division multiple access (TDMA)-based mobile phone systems like Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM). After 2010 many telecommunication carriers dropped support for CSD, and CSD has been superseded by GPRS and EDGE (E-GPRS).

A business telephone system is a telephone system typically used in business environments, encompassing the range of technology from the key telephone system (KTS) to the private branch exchange (PBX).
The IP Multimedia Subsystem or IP Multimedia Core Network Subsystem (IMS) is a standardised architectural framework for delivering IP multimedia services. Historically, mobile phones have provided voice call services over a circuit-switched-style network, rather than strictly over an IP packet-switched network. Various voice over IP technologies are available on smartphones; IMS provides a standard protocol across vendors.
The media-independent interface (MII) was originally defined as a standard interface to connect a Fast Ethernet medium access control (MAC) block to a PHY chip. The MII is standardized by IEEE 802.3u and connects different types of PHYs to MACs. Being media independent means that different types of PHY devices for connecting to different media can be used without redesigning or replacing the MAC hardware. Thus any MAC may be used with any PHY, independent of the network signal transmission medium.

A Medium Attachment Unit (MAU) is a transceiver which converts signals on an Ethernet cable to and from Attachment Unit Interface (AUI) signals.
Networking hardware, also known as network equipment or computer networking devices, are electronic devices that are required for communication and interaction between devices on a computer network. Specifically, they mediate data transmission in a computer network. Units which are the last receiver or generate data are called hosts, end systems or data terminal equipment.

A digital subscriber line (DSL) modem is a device used to connect a computer or router to a telephone line which provides the digital subscriber line (DSL) service for connection to the Internet, which is often called DSL broadband. The modem connects to a single computer or router, through an Ethernet port, USB port, or is installed in a computer PCI slot.
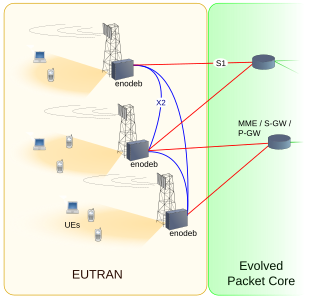
E-UTRA is the air interface of 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) Long Term Evolution (LTE) upgrade path for mobile networks. It is an acronym for Evolved UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access, also known as the Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access in early drafts of the 3GPP LTE specification. E-UTRAN is the combination of E-UTRA, user equipment (UE), and a Node B.
References
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from Federal Standard 1037C. General Services Administration. Archived from the original on 2022-01-22.
This article incorporates public domain material from Federal Standard 1037C. General Services Administration. Archived from the original on 2022-01-22.