Related Research Articles

Boids is an artificial life program, developed by Craig Reynolds in 1986, which simulates the flocking behaviour of birds, and related group motion. His paper on this topic was published in 1987 in the proceedings of the ACM SIGGRAPH conference. The name "boid" corresponds to a shortened version of "bird-oid object", which refers to a bird-like object. Reynolds' boid model is one example of a larger general concept, for which many other variations have been developed since. The closely related work of Ichiro Aoki is noteworthy because it was published in 1982 — five years before Reynolds' boids paper.
ICRA may refer to:

A rapidly exploring random tree (RRT) is an algorithm designed to efficiently search nonconvex, high-dimensional spaces by randomly building a space-filling tree. The tree is constructed incrementally from samples drawn randomly from the search space and is inherently biased to grow towards large unsearched areas of the problem. RRTs were developed by Steven M. LaValle and James J. Kuffner Jr. They easily handle problems with obstacles and differential constraints and have been widely used in autonomous robotic motion planning.

RHex is an autonomous robot design, based on hexapod with compliant legs and one actuator per leg. A number of US universities have participated, with funding grants also coming from DARPA.
The HOAP series robots are an advanced humanoid robot platform manufactured by Fujitsu Automation in Japan. HOAP is an abbreviation for "Humanoid for Open Architecture Platform".
In robotics, Vector Field Histogram (VFH) is a real time motion planning algorithm proposed by Johann Borenstein and Yoram Koren in 1991. The VFH utilizes a statistical representation of the robot's environment through the so-called histogram grid, and therefore places great emphasis on dealing with uncertainty from sensor and modeling errors. Unlike other obstacle avoidance algorithms, VFH takes into account the dynamics and shape of the robot, and returns steering commands specific to the platform. While considered a local path planner, i.e., not designed for global path optimality, the VFH has been shown to produce near optimal paths.
Leslie Pack Kaelbling is an American roboticist and the Panasonic Professor of Computer Science and Engineering at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. She is widely recognized for adapting partially observable Markov decision processes from operations research for application in artificial intelligence and robotics. Kaelbling received the IJCAI Computers and Thought Award in 1997 for applying reinforcement learning to embedded control systems and developing programming tools for robot navigation. In 2000, she was elected as a Fellow of the Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence.
The IEEE Robotics and Automation Society is a professional society of the IEEE that supports the development and the exchange of scientific knowledge in the fields of robotics and automation, including applied and theoretical issues.
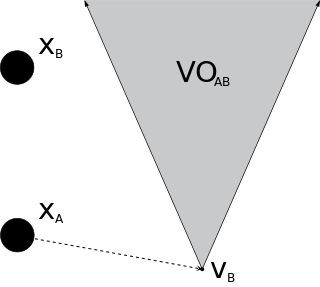
In robotics and motion planning, a velocity obstacle, commonly abbreviated VO, is the set of all velocities of a robot that will result in a collision with another robot at some moment in time, assuming that the other robot maintains its current velocity. If the robot chooses a velocity inside the velocity obstacle then the two robots will eventually collide, if it chooses a velocity outside the velocity obstacle, such a collision is guaranteed not to occur.

Any-angle path planning algorithms are pathfinding algorithms that search for a Euclidean shortest path between two points on a grid map while allowing the turns in the path to have any angle. The result is a path that cuts directly through open areas and has relatively few turns. More traditional pathfinding algorithms such as A* either lack in performance or produce jagged, indirect paths.
IROS, the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, is an annual academic conference covering advances in robotics. It is one of the premier conferences of its field with an 'A' rating from the Australian Ranking of ICT Conferences obtained in 2010 and an 'A1' rating from the Brazilian ministry of education in 2012.
University of Waterloo Nanorobotics Group (UWNRG) is an undergraduate group composed of students from several different engineering programs, including Nanotechnology, Mechatronics, Electrical, Computer, and Software Engineering, various Math and Arts programs at the University of Waterloo. Their primary goal is the design of microrobots, as well as the promotion of nanotechnology and their program. The group was founded in 2007, and their most recent accomplishment was winning the Microassembly Challenge at the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). They were the only completely undergraduate team, as well as the only Canadian team competing. UWNRG has since evolved from the robotics competition and now look into developing micro-robotics for industrial and medical applications through MAYA, and agriculture applications through Vision.
Cloud robotics is a field of robotics that attempts to invoke cloud technologies such as cloud computing, cloud storage, and other Internet technologies centered on the benefits of converged infrastructure and shared services for robotics. When connected to the cloud, robots can benefit from the powerful computation, storage, and communication resources of modern data center in the cloud, which can process and share information from various robots or agent. Humans can also delegate tasks to robots remotely through networks. Cloud computing technologies enable robot systems to be endowed with powerful capability whilst reducing costs through cloud technologies. Thus, it is possible to build lightweight, low-cost, smarter robots with an intelligent "brain" in the cloud. The "brain" consists of data center, knowledge base, task planners, deep learning, information processing, environment models, communication support, etc.
Bradley James Nelson is an American roboticist and entrepreneur. He has been the Professor of Robotics and Intelligent Systems at ETH Zurich since 2002 and is known for his research in microrobotics, nanorobotics, and medical robotics.

Dan (Danny) Halperin is an Israeli computer scientist known for his work on computational geometry and robotics. He is currently a Full Professor in the School of Computer Science at Tel Aviv University, and the CTO of Assembrix, a startup company in industrial 3D printing.

The Wingtra WingtraOne is a tail-sitting vertical take-off and landing unmanned aerial vehicle developed in Switzerland by Wingtra AG. Powered by two electric motors, it is designed primarily for use in precision agriculture and surveying roles, or for light payload delivery to rural areas.
Fog robotics can be defined as an architecture which consists of storage, networking functions, control with fog computing closer to robots.

Margarita Chli is an assistant professor and leader of the Vision for Robotics Lab at ETH Zürich in Switzerland. Chli is a leader in the field of computer vision and robotics and was on the team of researchers to develop the first fully autonomous helicopter with onboard localization and mapping. Chli is also the Vice Director of the Institute of Robotics and Intelligent Systems and an Honorary Fellow of the University of Edinburgh in the United Kingdom. Her research currently focuses on developing visual perception and intelligence in flying autonomous robotic systems.
A continuum robot is a type of robot that is characterised by infinite degrees of freedom and number of joints. These characteristics allow continuum manipulators to adjust and modify their shape at any point along their length, granting them the possibility to work in confined spaces and complex environments where standard rigid-link robots cannot operate. In particular, we can define a continuum robot as an actuatable structure whose constitutive material forms curves with continuous tangent vectors. This is a fundamental definition that allows to distinguish between continuum robots and snake-arm robots or hyper-redundant manipulators: the presence of rigid links and joints allows them to only approximately perform curves with continuous tangent vectors.

Jürgen Sturm is a German software engineer, entrepreneur and academic. He is a Senior Staff Software Engineer at Google, where he works on bringing 3D reconstruction and semantic scene understanding to mixed reality devices.