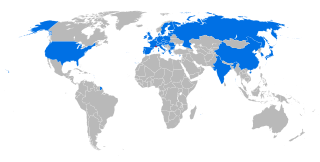
ITER is an international nuclear fusion research and engineering megaproject aimed at creating energy through a fusion process similar to that of the Sun. It is being built next to the Cadarache facility in southern France. Upon completion of construction of the main reactor and first plasma, planned for 2033–2034, ITER will be the largest of more than 100 fusion reactors built since the 1950s, with six times the plasma volume of JT-60SA in Japan, the largest tokamak operating today.

The French Alternative Energies and Atomic Energy Commission, or CEA, is a French public government-funded research organisation in the areas of energy, defense and security, information technologies and health technologies. The CEA maintains a cross-disciplinary culture of engineers and researchers, building on the synergies between fundamental and technological research.
General Atomics (GA) is an American energy and defense corporation headquartered in San Diego, California, that specializes in research and technology development. This includes physics research in support of nuclear fission and nuclear fusion energy. The company also provides research and manufacturing services for remotely operated surveillance aircraft, including the Predator drones, airborne sensors, and advanced electric, electronic, wireless, and laser technologies.

Cadarache is the largest technological research and development centre for energy in Europe. It includes the CEA research activities and ITER. CEA Cadarache is one of the 10 research centres of the French Commission of Atomic and Alternative Energies.
Ravi B. Grover is an Indian nuclear scientist and a mechanical engineer. He is the founding vice-chancellor of the Homi Bhabha National Institute, a member of the Atomic Energy Commission, chairman of the Board of Research in Nuclear Sciences, a fellow of the Indian National Academy of Engineering, and World Academy of Art and Science. He was the president of the Indian Society of Heat and Mass Transfer for the period 2010–2013. He has been awarded Padma Shri by the Government of India in the year 2014.

The Federal Ministry of Education and Research, abbreviated BMBF, is a cabinet-level ministry of Germany. It is headquartered in Bonn, with an office in Berlin. The Ministry provides funding for research projects and institutions and sets general educational policy. It also provides student loans in Germany. However, a large part of educational policy in Germany is decided at the state level, strongly limiting the influence of the ministry in educational matters.

The Kurchatov Institute is Russia's leading research and development institution in the field of nuclear energy. It is named after Igor Kurchatov and is located at 1 Kurchatov Square, Moscow.

Marcoule Nuclear Site is a nuclear facility in the Chusclan and Codolet communes, near Bagnols-sur-Cèze in the Gard department of France, which is in the tourist, wine and agricultural Côtes-du-Rhône region. The plant is around 25 km north west of Avignon, on the banks of the Rhone.

Catherine Jeanne Cesarsky is an Argentine and French astronomer, known for her research activities in astrophysics and for her leadership in astronomy and atomic energy. She is the current chairperson of the Square Kilometre Array's governing body, SKAO Council. She was the first female president of the International Astronomical Union (2006-2009) and the first female director general of the European Southern Observatory (1999-2007).
The Jules Horowitz Reactor is a materials testing reactor (MTR) cooled and moderated with water. It is under construction at Cadarache in southern France, based on the recommendations of the European Roadmap for Research Infrastructures Report, which was published by the European Strategy Forum on Research Infrastructures (ESFRI) in 2006. The reactor, which is named for the 20th-century French nuclear scientist Jules Horowitz.
Ignitor is the Italian name for a proposed tokamak device, developed by ENEA. The project was abandoned in 2022.

Fusion for Energy(F4E) is a joint undertaking of the European Atomic Energy Community (Euratom) that is responsible for the EU's contribution to the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER), the world's largest scientific partnership aiming to demonstrate fusion as a viable and sustainable source of energy. The organisation is officially named European Joint Undertaking for ITER and the Development of Fusion Energy and was created under article 45 of the Treaty establishing the European Atomic Energy Community by the decision of the Council of the European Union on 27 March 2007 for a period of 35 years.

CEA-Leti is a research institute for electronics and information technologies, based in Grenoble, France. It is one of the world's largest organizations for applied research in microelectronics and nanotechnology. It is located within the CEA Grenoble center of the French Alternative Energies and Atomic Energy Commission (CEA).
The 2011 French presidential election was held on 22 April and 6 May 2011 and marked the end of Nicolas Sarkozy's presidency. The Socialist Party candidate, François Hollande, defeated the incumbent President Sarkozy and became the first left-wing President of the Fifth Republic.

13/9/1993: National Atomic Energy Commission was renamed Vietnam Atomic Energy Institute under the Ministry of Science, Technology and Environment (According to Decree No. 59/CP dated September 13, 1993 of the Government)

The CEA Paris-Saclay center is one of nine centers belonging to the French Alternative Energies and Atomic Energy Commission (CEA). Following a reorganization in 2017, the center consists of multiple sites, including the CEA Saclay site, the Fontenay-aux-Roses site and the sites of Paris, Évry, Orsay and Caen.

The Culham Centre for Fusion Energy (CCFE) is the UK's national laboratory for fusion research. It is located at the Culham Science Centre, near Culham, Oxfordshire, and is the site of the Joint European Torus (JET), Mega Ampere Spherical Tokamak (MAST) and the now closed Small Tight Aspect Ratio Tokamak (START).

Jules Guéron was a French physical chemist and atomic scientist who played a key role in the development of atomic energy in France.

Bernard Bigot was a French academic and civil servant. He served as the Director-General of the ITER organization between 2015 and 2022. He was the president of the École normale supérieure de Lyon and director of the French Commission for Atomic Energy.

L'Institut national des sciences et techniques nucléaires, is a public higher education institution administered by the CEA under the joint authority of the Ministry of National Education, Higher Education and Research, the Ministry of the Economy, Industry and the Digital Sector and the Ministry of the Environment, Energy and Marine Affairs. It is the main centre of education for nuclear energy in France.















