
Computer science is the study of processes that interact with data and that can be represented as data in the form of programs. It enables the use of algorithms to manipulate, store, and communicate digital information. A computer scientist studies the theory of computation and the practice of designing software systems.
Computational linguistics is an interdisciplinary field concerned with the statistical or rule-based modeling of natural language from a computational perspective, as well as the study of appropriate computational approaches to linguistic questions.
In artificial intelligence, genetic programming (GP) is a technique whereby computer programs are encoded as a set of genes that are then modified (evolved) using an evolutionary algorithm – it is an application of genetic algorithms where the space of solutions consists of computer programs. The results are computer programs that are able to perform well in a predefined task. The methods used to encode a computer program in an artificial chromosome and to evaluate its fitness with respect to the predefined task are central in the GP technique and still the subject of active research.
Computational biology involves the development and application of data-analytical and theoretical methods, mathematical modeling and computational simulation techniques to the study of biological, ecological, behavioral, and social systems. The field is broadly defined and includes foundations in biology, applied mathematics, statistics, biochemistry, chemistry, biophysics, molecular biology, genetics, genomics, computer science and evolution.
Computational geometry is a branch of computer science devoted to the study of algorithms which can be stated in terms of geometry. Some purely geometrical problems arise out of the study of computational geometric algorithms, and such problems are also considered to be part of computational geometry. While modern computational geometry is a recent development, it is one of the oldest fields of computing with history stretching back to antiquity.
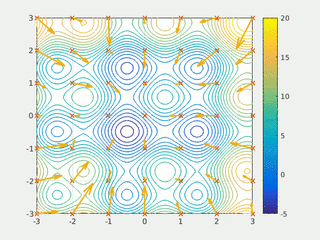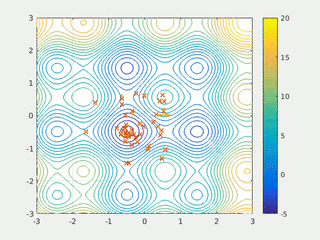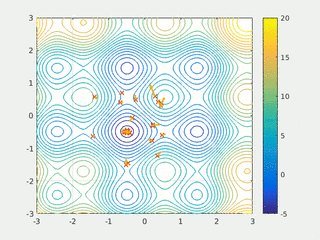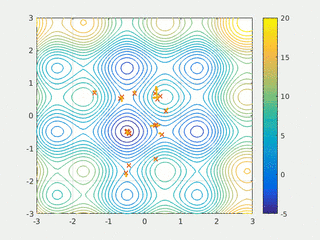
In computational science, particle swarm optimization (PSO) is a computational method that optimizes a problem by iteratively trying to improve a candidate solution with regard to a given measure of quality. It solves a problem by having a population of candidate solutions, here dubbed particles, and moving these particles around in the search-space according to simple mathematical formulae over the particle's position and velocity. Each particle's movement is influenced by its local best known position, but is also guided toward the best known positions in the search-space, which are updated as better positions are found by other particles. This is expected to move the swarm toward the best solutions.
Bio-inspired computing, short for biologically inspired computing, is a field of study that loosely knits together subfields related to the topics of connectionism, social behaviour and emergence. It is often closely related to the field of artificial intelligence, as many of its pursuits can be linked to machine learning. It relies heavily on the fields of biology, computer science and mathematics. Briefly put, it is the use of computers to model the living phenomena, and simultaneously the study of life to improve the usage of computers. Biologically inspired computing is a major subset of natural computation.

In computer science, computational learning theory is a subfield of artificial intelligence devoted to studying the design and analysis of machine learning algorithms.
Managerial economics deals with the application of the economic concepts, theories, tools, and methodologies to solve practical problems in a business. It helps the manager in decision making and acts as a link between practice and theory". It is sometimes referred to as business economics and is a branch of economics that applies microeconomic analysis to decision methods of businesses or other management units.
The expression computational intelligence (CI) usually refers to the ability of a computer to learn a specific task from data or experimental observation. Even though it is commonly considered a synonym of soft computing, there is still no commonly accepted definition of computational intelligence.
In artificial intelligence, artificial immune systems (AIS) are a class of computationally intelligent, rule-based machine learning systems inspired by the principles and processes of the vertebrate immune system. The algorithms are typically modeled after the immune system's characteristics of learning and memory for use in problem-solving.

The Computer Journal is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering computer science and information systems. It is published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Computer Society. It was established in 1958. Several breakthroughs in computer science were first reported in the journal, including the Quicksort algorithm proposed by C. A. R. Hoare. The authors of the best paper in each volume receive the Wilkes Award and Medal granted by the British Computer Society.
IEEE Intelligent Systems is a bimonthly peer-reviewed academic journal published by the IEEE Computer Society and sponsored by the Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence, British Computer Society, and European Coordinating Committee for Artificial Intelligence. The journal was established in 1986 as the quarterly IEEE Expert, changed to a bimonthly in 1990, changed its name to IEEE Intelligent Systems & Their Applications in 1997. It obtained its current name in 2001. The editor-in-chief is Daniel Zeng. According to the Journal Citation Reports, the journal has a 2013 impact factor of 1.920.

Computational statistics, or statistical computing, is the interface between statistics and computer science. It is the area of computational science specific to the mathematical science of statistics. This area is also developing rapidly, leading to calls that a broader concept of computing should be taught as part of general statistical education.
In 1995, professor Massimo Grattarola of the Biophysics and Electrical Engineering Department (DIBE) at the University of Genoa, in Genoa, Italy, created an undergraduate and graduate program named neurobioengineering. The program was designed to amalgamate anthropomorphic robotics, artificial intelligence, bioelectronics, electrical engineering, molecular biology, physics, and medicine, into a single program with the aim of developing advanced bio-compatible neuro-prosthetic implants for a variety applications.
The IEEE Computational Intelligence Society is a professional society of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) focussing on "the theory, design, application, and development of biologically and linguistically motivated computational paradigms emphasizing neural networks, connectionist systems, genetic algorithms, evolutionary programming, fuzzy systems, and hybrid intelligent systems in which these paradigms are contained".

New Mathematics and Natural Computation is an interdisciplinary journal founded in 2005 and is now published by World Scientific. It covers mathematical uncertainty and its applications to computational, biological and social sciences, with a specific focus on relatively unexplored areas in mathematical uncertainty, such as fuzzy sets and fuzzy logic.
The European Society for Fuzzy Logic and Technology (EUSFLAT) is a scientific association with the aims to disseminate and promote fuzzy logic and related subjects and to provide a platform for exchange between scientists and engineers working in these fields. The society is both open for academic and industrial members.
Gary Bryce Fogel is an American biologist and computer scientist. He is the Chief Executive Officer of Natural Selection, Inc. He is most known for his applications of computational intelligence and machine learning to bioinformatics, computational biology, and industrial optimization.







