
Mosses are small, non-vascular flowerless plants in the taxonomic division Bryophytasensu stricto. Bryophyta may also refer to the parent group bryophytes, which comprise liverworts, mosses, and hornworts. Mosses typically form dense green clumps or mats, often in damp or shady locations. The individual plants are usually composed of simple leaves that are generally only one cell thick, attached to a stem that may be branched or unbranched and has only a limited role in conducting water and nutrients. Although some species have conducting tissues, these are generally poorly developed and structurally different from similar tissue found in vascular plants. Mosses do not have seeds and after fertilisation develop sporophytes with unbranched stalks topped with single capsules containing spores. They are typically 0.2–10 cm (0.1–3.9 in) tall, though some species are much larger. Dawsonia, the tallest moss in the world, can grow to 50 cm (20 in) in height. There are approximately 12,000 species.
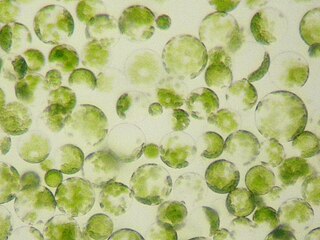
Protoplast, is a biological term coined by Hanstein in 1880 to refer to the entire cell, excluding the cell wall. Protoplasts can be generated by stripping the cell wall from plant, bacterial, or fungal cells by mechanical, chemical or enzymatic means.
Pharming, a portmanteau of farming and pharmaceutical, refers to the use of genetic engineering to insert genes that code for useful pharmaceuticals into host animals or plants that would otherwise not express those genes, thus creating a genetically modified organism (GMO). Pharming is also known as molecular farming, molecular pharming, or biopharming.

The Nottingham Arabidopsis Stock Centre (NASC) provides seed and information resources to the International Arabidopsis Genome Project and the wider research community. It is based in the School of Biosciences at the University of Nottingham's Sutton Bonington Campus, in the English county of Nottinghamshire.
Polycomb-group proteins are a family of protein complexes first discovered in fruit flies that can remodel chromatin such that epigenetic silencing of genes takes place. Polycomb-group proteins are well known for silencing Hox genes through modulation of chromatin structure during embryonic development in fruit flies. They derive their name from the fact that the first sign of a decrease in PcG function is often a homeotic transformation of posterior legs towards anterior legs, which have a characteristic comb-like set of bristles.

Physcomitrella patens is a synonym of Physcomitrium patens, the spreading earthmoss. It is a moss, a bryophyte used as a model organism for studies on plant evolution, development, and physiology.

Gene targeting is a biotechnological tool used to change the DNA sequence of an organism. It is based on the natural DNA-repair mechanism of Homology Directed Repair (HDR), including Homologous Recombination. Gene targeting can be used to make a range of sizes of DNA edits, from larger DNA edits such as inserting entire new genes into an organism, through to much smaller changes to the existing DNA such as a single base-pair change. Gene targeting relies on the presence of a repair template to introduce the user-defined edits to the DNA. The user will design the repair template to contain the desired edit, flanked by DNA sequence corresponding (homologous) to the region of DNA that the user wants to edit; hence the edit is targeted to a particular genomic region. In this way Gene Targeting is distinct from natural homology-directed repair, during which the ‘natural’ DNA repair template of the sister chromatid is used to repair broken DNA. The alteration of DNA sequence in an organism can be useful in both a research context – for example to understand the biological role of a gene – and in biotechnology, for example to alter the traits of an organism.

Genetically modified plants have been engineered for scientific research, to create new colours in plants, deliver vaccines, and to create enhanced crops. Plant genomes can be engineered by physical methods or by use of Agrobacterium for the delivery of sequences hosted in T-DNA binary vectors. Many plant cells are pluripotent, meaning that a single cell from a mature plant can be harvested and then under the right conditions form a new plant. This ability is most often taken advantage by genetic engineers through selecting cells that can successfully be transformed into an adult plant which can then be grown into multiple new plants containing transgene in every cell through a process known as tissue culture.

Freiburg Botanical Garden is a botanical garden in the Herdern district at Schänzlestraße 1, Freiburg im Breisgau, Baden-Württemberg, Germany and is associated with the University of Freiburg as the "Forschungs- und Lehrgarten der Universität Freiburg" of the Faculty of Biology. The current director of the garden is Professor Dr. Thomas Speck.

Ralf Reski is a German professor of plant biotechnology and former dean of the Faculty of Biology of the University of Freiburg. He is also affiliated to the French École supérieure de biotechnologie Strasbourg (ESBS) and Senior Fellow at the Freiburg Institute for Advanced Studies.

Cryopreservation or cryoconservation is a process where biological material - cells, tissues, or organs - are frozen to preserve the material for an extended period of time. At low temperatures any cell metabolism which might cause damage to the biological material in question is effectively stopped. Cryopreservation is an effective way to transport biological samples over long distances, store samples for prolonged periods of time, and create a bank of samples for users. Molecules, referred to as cryoprotective agents (CPAs), are added to reduce the osmotic shock and physical stresses cells undergo in the freezing process. Some cryoprotective agents used in research are inspired by plants and animals in nature that have unique cold tolerance to survive harsh winters, including: trees, wood frogs, and tardigrades.The first human corpse to be frozen with the hope of future resurrection was James Bedford's, a few hours after his cancer-caused death in 1967.[15] Bedford's is the only cryonics corpse frozen before 1974 still frozen today.
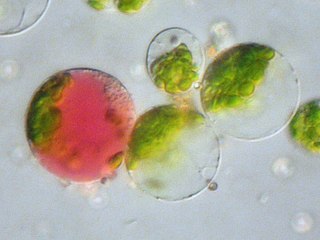
Somatic fusion, also called protoplast fusion, is a type of genetic modification in plants by which two distinct species of plants are fused together to form a new hybrid plant with the characteristics of both, a somatic hybrid. Hybrids have been produced either between different varieties of the same species or between two different species.
Dehydrin (DHN) is a multi-family of proteins present in plants that is produced in response to cold and drought stress. DHNs are hydrophilic, reliably thermostable, and disordered. They are stress proteins with a high number of charged amino acids that belong to the Group II Late Embryogenesis Abundant (LEA) family. DHNs are primarily found in the cytoplasm and nucleus but more recently, they have been found in other organelles, like mitochondria and chloroplasts.

The National Institute for Basic Biology (NIBB) is a research institute and post graduate university in Okazaki City, Aichi Prefecture, Japan. It was founded in 1977 to promote biological research in Japan in cooperation with public and private universities, and research institutes.

A knockout moss is a kind of genetically modified moss. One or more of the moss's specific genes are deleted or inactivated, for example by gene targeting or other methods. After the deletion of a gene, the knockout moss has lost the trait encoded by this gene. Thus, the function of this gene can be inferred. This scientific approach is called reverse genetics because the scientist wants to understand the function of a specific gene. In classical genetics, the scientist starts with a phenotype of interest and searches for the gene that causes this phenotype. Knockout mosses are relevant for basic research in biology as well as in biotechnology.

A moss bioreactor is a photobioreactor used for the cultivation and propagation of mosses. It is usually used in molecular farming for the production of recombinant protein using transgenic moss. In environmental science moss bioreactors are used to multiply peat mosses e.g. by the Mossclone consortium to monitor air pollution.

The Faculty of Biology is one of the eleven faculties of the University of Freiburg in Freiburg im Breisgau, Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It is part of a strong life sciences network including institutions such as the Max Planck Institute of Immunobiology and Epigenetics, the Bernstein Center Freiburg (BCF), the Center for Applied Biosciences and the Center for Biological Systems Analysis, which started operations in 2008 as offspring of the Freiburg Initiative for Systems Biology (FRISYS), funded by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF).

Reverse genetics is a method in molecular genetics that is used to help understand the function(s) of a gene by analysing the phenotypic effects caused by genetically engineering specific nucleic acid sequences within the gene. The process proceeds in the opposite direction to forward genetic screens of classical genetics. While forward genetics seeks to find the genetic basis of a phenotype or trait, reverse genetics seeks to find what phenotypes are controlled by particular genetic sequences.
Circadian Clock Associated 1 (CCA1) is a gene that is central to the circadian oscillator of angiosperms. It was first identified in Arabidopsis thaliana in 1993. CCA1 interacts with LHY and TOC1 to form the core of the oscillator system. CCA1 expression peaks at dawn. Loss of CCA1 function leads to a shortened period in the expression of many other genes.
Plant cryopreservation is a genetic resource conservation strategy that allows plant material, such as seeds, pollen, shoot tips or dormant buds to be stored indefinitely in liquid nitrogen. After thawing, these genetic resources can be regenerated into plants and used on the field. While this cryopreservation conservation strategy can be used on all plants, it is often only used under certain circumstances: 1) crops with recalcitrant seeds e.g. avocado, coconut 2) seedless crops such as cultivated banana and plantains or 3) crops that are clonally propagated such as cassava, sweet potato.
















