This article needs to be updated.(April 2015) |


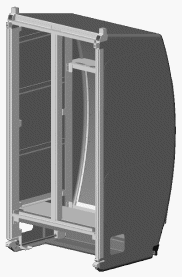
The International Standard Payload Rack (ISPR) is a steel framework container that is designed and been adopted by the International Space Station (ISS) program to support efficient integration and interchangeability of space payload hardware, such as machines and experiments. A typical rack contains 37 ISPR slots for science payloads, which are interchangeable to accommodate different components or payloads.