Related Research Articles

Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being a water world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all of Earth's water is contained in its global ocean, covering 70.8% of Earth's crust. The remaining 29.2% of Earth's crust is land, most of which is located in the form of continental landmasses within one hemisphere, Earth's land hemisphere. Most of Earth's land is somewhat humid and covered by vegetation, while large sheets of ice at Earth's polar deserts retain more water than Earth's groundwater, lakes, rivers and atmospheric water combined. Earth's crust consists of slowly moving tectonic plates, which interact to produce mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Earth has a liquid outer core that generates a magnetosphere capable of deflecting most of the destructive solar winds and cosmic radiation.

The North Atlantic Current (NAC), also known as North Atlantic Drift and North Atlantic Sea Movement, is a powerful warm western boundary current within the Atlantic Ocean that extends the Gulf Stream northeastward.

The Ordovician is a geologic period and system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years from the end of the Cambrian Period 485.4 million years ago (Ma) to the start of the Silurian Period 443.8 Mya.
The Oligocene is a geologic epoch of the Paleogene Period and extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present. As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that define the epoch are well identified but the exact dates of the start and end of the epoch are slightly uncertain. The name Oligocene was coined in 1854 by the German paleontologist Heinrich Ernst Beyrich from his studies of marine beds in Belgium and Germany. The name comes from the Ancient Greek ὀλίγος and καινός, and refers to the sparsity of extant forms of molluscs. The Oligocene is preceded by the Eocene Epoch and is followed by the Miocene Epoch. The Oligocene is the third and final epoch of the Paleogene Period.

Plate tectonics is the scientific theory that Earth's lithosphere comprises a number of large tectonic plates which have been slowly moving since about 3.4 billion years ago. The model builds on the concept of continental drift, an idea developed during the first decades of the 20th century. Plate tectonics came to be accepted by geoscientists after seafloor spreading was validated in the mid-to-late 1960s.

Oceanic trenches are prominent, long, narrow topographic depressions of the ocean floor. They are typically 50 to 100 kilometers wide and 3 to 4 km below the level of the surrounding oceanic floor, but can be thousands of kilometers in length. There are about 50,000 km (31,000 mi) of oceanic trenches worldwide, mostly around the Pacific Ocean, but also in the eastern Indian Ocean and a few other locations. The greatest ocean depth measured is in the Challenger Deep of the Mariana Trench, at a depth of 10,920 m (35,830 ft) below sea level.

The Portuguese man o' war, also known as the man-of-war, is a marine hydrozoan found in the Atlantic Ocean and the Indian Ocean. It is considered to be the same species as the Pacific man o' war or bluebottle, which is found mainly in the Pacific Ocean. The Portuguese man o' war is the only species in the genus Physalia, which in turn is the only genus in the family Physaliidae.

Continental crust is the layer of igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks that forms the geological continents and the areas of shallow seabed close to their shores, known as continental shelves. This layer is sometimes called sial because its bulk composition is richer in aluminium silicates (Al-Si) and has a lower density compared to the oceanic crust, called sima which is richer in magnesium silicate (Mg-Si) minerals. Changes in seismic wave velocities have shown that at a certain depth, there is a reasonably sharp contrast between the more felsic upper continental crust and the lower continental crust, which is more mafic in character.

The benthic zone is the ecological region at the lowest level of a body of water such as an ocean, lake, or stream, including the sediment surface and some sub-surface layers. The name comes from ancient Greek, βένθος (bénthos), meaning "the depths." Organisms living in this zone are called benthos and include microorganisms as well as larger invertebrates, such as crustaceans and polychaetes. Organisms here generally live in close relationship with the substrate and many are permanently attached to the bottom. The benthic boundary layer, which includes the bottom layer of water and the uppermost layer of sediment directly influenced by the overlying water, is an integral part of the benthic zone, as it greatly influences the biological activity that takes place there. Examples of contact soil layers include sand bottoms, rocky outcrops, coral, and bay mud.

A mid-ocean ridge (MOR) is a seafloor mountain system formed by plate tectonics. It typically has a depth of about 2,600 meters (8,500 ft) and rises about 2,000 meters (6,600 ft) above the deepest portion of an ocean basin. This feature is where seafloor spreading takes place along a divergent plate boundary. The rate of seafloor spreading determines the morphology of the crest of the mid-ocean ridge and its width in an ocean basin.
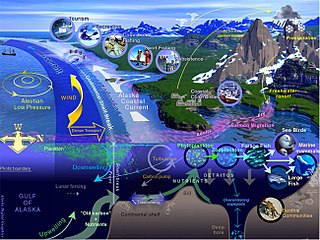
Marine life, sea life, or ocean life is the plants, animals, and other organisms that live in the salt water of seas or oceans, or the brackish water of coastal estuaries. At a fundamental level, marine life affects the nature of the planet. Marine organisms, mostly microorganisms, produce oxygen and sequester carbon. Marine life in part shape and protect shorelines, and some marine organisms even help create new land.

David Harold Blackwell was an American statistician and mathematician who made significant contributions to game theory, probability theory, information theory, and statistics. He is one of the eponyms of the Rao–Blackwell theorem. He was the first African American inducted into the National Academy of Sciences, the first African American full professor at the University of California, Berkeley, and the seventh African American to receive a Ph.D. in mathematics. In 2012, President Obama posthumously awarded Blackwell the National Medal of Science.

Walter Heinrich Munk was an American physical oceanographer. He was one of the first scientists to bring statistical methods to the analysis of oceanographic data. Munk worked on a wide range of topics, including surface waves, geophysical implications of variations in the Earth's rotation, tides, internal waves, deep-ocean drilling into the sea floor, acoustical measurements of ocean properties, sea level rise, and climate change. His work won awards including the National Medal of Science, the Kyoto Prize, and induction to the French Legion of Honour.

Manjul Bhargava is a Canadian-American mathematician. He is the Brandon Fradd, Class of 1983, Professor of Mathematics at Princeton University, the Stieltjes Professor of Number Theory at Leiden University, and also holds Adjunct Professorships at the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research, the Indian Institute of Technology Bombay, and the University of Hyderabad. He is known primarily for his contributions to number theory.

The ocean is a body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of the Earth and contains 97% of Earth's water. The term ocean also refers to any of the large bodies of water into which the world ocean is conventionally divided. Distinct names are used to identify five different areas of the ocean: Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Antarctic/Southern, and Arctic. Seawater covers approximately 361,000,000 km2 (139,000,000 sq mi) of the planet. The ocean is the primary component of the Earth's hydrosphere, and thus essential to life on Earth. The ocean influences climate and weather patterns, the carbon cycle, and the water cycle by acting as a huge heat reservoir.

Antarctica is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of 14,200,000 km2 (5,500,000 sq mi). Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of 1.9 km (1.2 mi).

Pangaea or Pangea was a supercontinent that existed during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras. It assembled from the earlier continental units of Gondwana, Euramerica and Siberia during the Carboniferous approximately 335 million years ago, and began to break apart about 200 million years ago, at the end of the Triassic and beginning of the Jurassic. In contrast to the present Earth and its distribution of continental mass, Pangaea was centred on the equator and surrounded by the superocean Panthalassa and the Paleo-Tethys and subsequent Tethys Oceans. Pangaea is the most recent supercontinent to have existed and the first to be reconstructed by geologists.
The evolution of tectonophysics is closely linked to the history of the continental drift and plate tectonics hypotheses. The continental drift/ Airy-Heiskanen isostasy hypothesis had many flaws and scarce data. The fixist/ Pratt-Hayford isostasy, the contracting Earth and the expanding Earth concepts had many flaws as well.

Helmut Hermann W. Hofer is a German-American mathematician, one of the founders of the area of symplectic topology.

There are many effects of climate change on oceans. One of the main ones is an increase in ocean temperatures. More frequent marine heatwaves are linked to this. The rising temperature contributes to a rise in sea levels. Other effects include ocean acidification, sea ice decline, increased ocean stratification and reductions in oxygen levels. Changes to ocean currents including a weakening of the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation are another important effect. All these changes have knock-on effects which disturb marine ecosystems. The main cause of these changes is climate change due to human emissions of greenhouse gases. Carbon dioxide and methane are examples of greenhouse gases. This leads to ocean warming, because the ocean takes up most of the additional heat in the climate system. The ocean absorbs some of the extra carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. This causes the pH value of the ocean to drop. Scientists estimate that the ocean absorbs about 25% of all human-caused CO2 emissions.
References
- ↑ Maul, George A. (2019). "Intra-Americas Sea". Encyclopedia of Ocean Sciences. Elsevier. pp. 374–383. doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-409548-9.11060-7. ISBN 9780128130827.
- ↑ Escobar Briones, Elva (1962). "Chapter 7: Structure and Function in the Ecosystems of the Intra-Americas Sea (IAS)". In Robinson, Allan R.; Brink, Kenneth H. (eds.). The Global Coastal Ocean. The Sea. Vol. 14A. New York: Interscience Publishers. ISBN 0-471-63393-3. OCLC 965081.
- ↑ Intra-Americas Sea, McGraw-Hill Professional, doi: 10.1036/1097-8542.757445 , S2CID 133186654
- ↑ Amador, Jorge A. (2008). "The Intra-Americas Sea Low-level Jet". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. Wiley. 1146 (1): 153–188. Bibcode:2008NYASA1146..153A. doi:10.1196/annals.1446.012. ISSN 0077-8923. PMID 19076415. S2CID 20686793.