In a chemical reaction, chemical equilibrium is the state in which both the reactants and products are present in concentrations which have no further tendency to change with time, so that there is no observable change in the properties of the system. This state results when the forward reaction proceeds at the same rate as the reverse reaction. The reaction rates of the forward and backward reactions are generally not zero, but they are equal. Thus, there are no net changes in the concentrations of the reactants and products. Such a state is known as dynamic equilibrium.
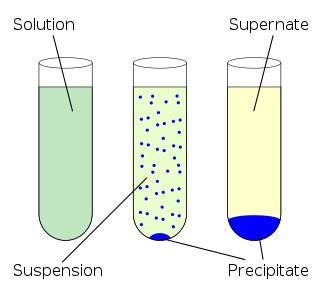
In chemistry, solubility is the ability of a substance, the solute, to form a solution with another substance, the solvent. Insolubility is the opposite property, the inability of the solute to form such a solution.
In electrochemistry, the Nernst equation is a chemical thermodynamical relationship that permits the calculation of the reduction potential of a reaction from the standard electrode potential, absolute temperature, the number of electrons involved in the redox reaction, and activities of the chemical species undergoing reduction and oxidation respectively. It was named after Walther Nernst, a German physical chemist who formulated the equation.

Drug design, often referred to as rational drug design or simply rational design, is the inventive process of finding new medications based on the knowledge of a biological target. The drug is most commonly an organic small molecule that activates or inhibits the function of a biomolecule such as a protein, which in turn results in a therapeutic benefit to the patient. In the most basic sense, drug design involves the design of molecules that are complementary in shape and charge to the biomolecular target with which they interact and therefore will bind to it. Drug design frequently but not necessarily relies on computer modeling techniques. This type of modeling is sometimes referred to as computer-aided drug design. Finally, drug design that relies on the knowledge of the three-dimensional structure of the biomolecular target is known as structure-based drug design. In addition to small molecules, biopharmaceuticals including peptides and especially therapeutic antibodies are an increasingly important class of drugs and computational methods for improving the affinity, selectivity, and stability of these protein-based therapeutics have also been developed.
Lipophilicity is the ability of a chemical compound to dissolve in fats, oils, lipids, and non-polar solvents such as hexane or toluene. Such compounds are called lipophilic. Such non-polar solvents are themselves lipophilic, and the adage "like dissolves like" generally holds true. Thus lipophilic substances tend to dissolve in other lipophilic substances, whereas hydrophilic ("water-loving") substances tend to dissolve in water and other hydrophilic substances.
In the physical sciences, a partition coefficient (P) or distribution coefficient (D) is the ratio of concentrations of a compound in a mixture of two immiscible solvents at equilibrium. This ratio is therefore a comparison of the solubilities of the solute in these two liquids. The partition coefficient generally refers to the concentration ratio of un-ionized species of compound, whereas the distribution coefficient refers to the concentration ratio of all species of the compound.
Comproportionation or synproportionation is a chemical reaction where two reactants containing the same element but with different oxidation numbers, form a compound having an intermediate oxidation number. It is the opposite of disproportionation.
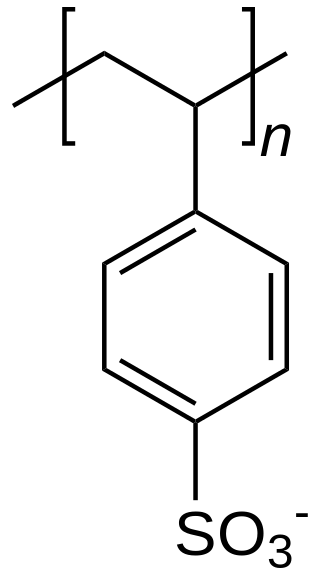
In chemistry, a counterion is the ion that accompanies an ionic species in order to maintain electric neutrality. In table salt the sodium ion is the counterion for the chloride ion and vice versa.
Redox potential is a measure of the tendency of a chemical species to acquire electrons from or lose electrons to an electrode and thereby be reduced or oxidised respectively. Redox potential is expressed in volts (V). Each species has its own intrinsic redox potential; for example, the more positive the reduction potential, the greater the species' affinity for electrons and tendency to be reduced.

In electrochemistry, and more generally in solution chemistry, a Pourbaix diagram, also known as a potential/pH diagram, EH–pH diagram or a pE/pH diagram, is a plot of possible thermodynamically stable phases of an aqueous electrochemical system. Boundaries (50 %/50 %) between the predominant chemical species are represented by lines. As such a Pourbaix diagram can be read much like a standard phase diagram with a different set of axes. Similarly to phase diagrams, they do not allow for reaction rate or kinetic effects. Beside potential and pH, the equilibrium concentrations are also dependent upon, e.g., temperature, pressure, and concentration. Pourbaix diagrams are commonly given at room temperature, atmospheric pressure, and molar concentrations of 10−6 and changing any of these parameters will yield a different diagram.

An amphiphile, or amphipath, is a chemical compound possessing both hydrophilic and lipophilic (fat-loving) properties. Such a compound is called amphiphilic or amphipathic. Amphiphilic compounds include surfactants. The phospholipid amphiphiles are the major structural component of cell membranes.
Ionic potential is the ratio of the electrical charge (z) to the radius (r) of an ion.
Micellar liquid chromatography (MLC) is a form of reversed phase liquid chromatography that uses an aqueous micellar solutions as the mobile phase.
Druglikeness is a qualitative concept used in drug design for how "druglike" a substance is with respect to factors like bioavailability. It is estimated from the molecular structure before the substance is even synthesized and tested. A druglike molecule has properties such as:
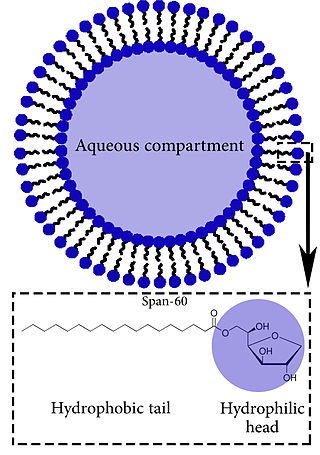
Niosomes are vesicles composed of non-ionic surfactants, incorporating cholesterol as an excipient. Niosomes are utilized for drug delivery to specific sites to achieve desired therapeutic effects. Structurally, niosomes are similar to liposomes as both consist of a lipid bilayer. However, niosomes are more stable than liposomes during formation processes and storage. Niosomes trap hydrophilic and lipophilic drugs, either in an aqueous compartment or in a vesicular membrane compartment composed of lipid material.
In electrochemistry, ITIES is an electrochemical interface that is either polarisable or polarised. An ITIES is polarisable if one can change the Galvani potential difference, or in other words the difference of inner potentials between the two adjacent phases, without noticeably changing the chemical composition of the respective phases. An ITIES system is polarised if the distribution of the different charges and redox species between the two phases determines the Galvani potential difference.
Equilibrium chemistry is concerned with systems in chemical equilibrium. The unifying principle is that the free energy of a system at equilibrium is the minimum possible, so that the slope of the free energy with respect to the reaction coordinate is zero. This principle, applied to mixtures at equilibrium provides a definition of an equilibrium constant. Applications include acid–base, host–guest, metal–complex, solubility, partition, chromatography and redox equilibria.
In aquatic toxicology, bioconcentration is the accumulation of a water-borne chemical substance in an organism exposed to the water.
The n-octanol-water partition coefficient,Kow is a partition coefficient for the two-phase system consisting of n-octanol and water. Kow is also frequently referred to by the symbol P, especially in the English literature. It is also called n-octanol-water partition ratio.
Topical drug delivery (TDD) is a route of drug administration that allows the topical formulation to be delivered across the skin upon application, hence producing a localized effect to treat skin disorders like eczema. The formulation of topical drugs can be classified into corticosteroids, antibiotics, antiseptics, and anti-fungal. The mechanism of topical delivery includes the diffusion and metabolism of drugs in the skin. Historically, topical route was the first route of medication used to deliver drugs in humans in ancient Egyptian and Babylonian in 3000 BCE. In these ancient cities, topical medications like ointments and potions were used on the skin. The delivery of topical drugs needs to pass through multiple skin layers and undergo pharmacokinetics, hence factor like dermal diseases minimize the bioavailability of the topical drugs. The wide use of topical drugs leads to the advancement in topical drug delivery. These advancements are used to enhance the delivery of topical medications to the skin by using chemical and physical agents. For chemical agents, carriers like liposomes and nanotechnologies are used to enhance the absorption of topical drugs. On the other hand, physical agents, like micro-needles is other approach for enhancement ofabsorption. Besides using carriers, other factors such as pH, lipophilicity, and drug molecule size govern the effectiveness of topical formulation.





