
Samuel de Champlain was a French explorer, navigator, cartographer, draftsman, soldier, geographer, ethnologist, diplomat, and chronicler. He made between 21 and 29 trips across the Atlantic Ocean, and founded Quebec City, and New France, on 3 July 1608. An important figure in Canadian history, Champlain created the first accurate coastal map during his explorations and founded various colonial settlements.

The Wyandot people are Indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands of North America, and speakers of an Iroquoian language, Wyandot.
New France was the territory colonized by France in North America, beginning with the exploration of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Great Britain and Spain in 1763 under the Treaty of Paris.

The Algonquin people are an Indigenous people who now live in Eastern Canada. They speak the Algonquin language, which is part of the Algonquian language family. Culturally and linguistically, they are closely related to the Odawa, Potawatomi, Ojibwe, Mississaugas, and Nipissing, with whom they form the larger Anicinàpe (Anishinaabeg). Algonquins are known by many names, including Omàmiwinini and Abitibiwinni or the more generalised name of Anicinàpe.
Étienne Brûlé was the first European explorer to journey beyond the St. Lawrence River into what is now known as Canada. He spent much of his early adult life among the Hurons, and mastered their language and learned their culture. Brûlé became an interpreter and guide for Samuel de Champlain, who later sent Brûlé on a number of exploratory missions, among which he is thought to have preceded Champlain to the Great Lakes, reuniting with him upon Champlain's first arrival at Lake Huron. Among his many travels were explorations of Georgian Bay and Lake Huron, as well as the Humber and Ottawa Rivers. Champlain agreed to send Brûlé, at his own request, as an interpreter to live among the Onontchataron, an Algonquin people, in 1610. In 1629, during the Anglo-French War, he escaped after being captured by the Seneca tribe. Brûlé was killed by the Bear tribe of the Huron people, who believed he had betrayed them to the Seneca.

The Kanien'kehá:ka are in the easternmost section of the Haudenosaunee, or Iroquois Confederacy. They are an Iroquoian-speaking Indigenous people of North America, with communities in southeastern Canada and northern New York State, primarily around Lake Ontario and the St. Lawrence River. As one of the five original members of the Iroquois League, the Mohawk are known as the Keepers of the Eastern Door – the traditional guardians of the Iroquois Confederation against invasions from the east. The Mohawk are federally recognized in the United States as the Saint Regis Mohawk Tribe.

The Beaver Wars, also known as the Iroquois Wars or the French and Iroquois Wars were a series of conflicts fought intermittently during the 17th century in North America throughout the Saint Lawrence River valley in Canada and the Great Lakes region which pitted the Iroquois against the Hurons, northern Algonquians and their French allies. As a result of this conflict, the Iroquois destroyed several confederacies and tribes through warfare: the Hurons or Wendat, Erie, Neutral, Wenro, Petun, Susquehannock, Mohican and northern Algonquins whom they defeated and dispersed, some fleeing to neighbouring peoples and others assimilated, routed, or killed.

The Ottawa Valley is the valley of the Ottawa River, along the boundary between Eastern Ontario and the Outaouais, Quebec, Canada. The valley is the transition between the Saint Lawrence Lowlands and the Canadian Shield. Because of the surrounding shield, the valley is narrow at its western end and then becomes increasingly wide as it progresses eastward. The underlying geophysical structure is the Ottawa-Bonnechere Graben. Approximately 1.3 million people reside in the valley, around 80% of whom reside in Ottawa. The total area of the Ottawa Valley is 2.4 million ha. The National Capital Region area has just over 1.4 million inhabitants in both provinces.

Events from the 1600s in Canada.

Black Robe is a 1991 historical drama film directed by Bruce Beresford, adapted by Brian Moore from his 1985 novel of the same name. Set in the 17th century, it depicts the adventures of a Jesuit missionary tasked with founding a mission in New France. To do so, he must traverse 1500 miles of harsh wilderness with the help of a group of Algonquins, facing danger from both the unfamiliar environment and rival tribes. The title refers to the nickname given to the Jesuits by the Algonquins, referring to his black cassock.
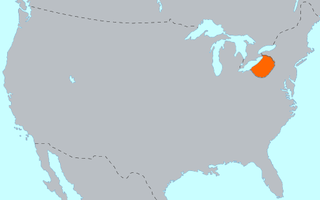
The Erie people were Indigenous people historically living on the south shore of Lake Erie. An Iroquoian group, they lived in what is now western New York, northwestern Pennsylvania, and northern Ohio before 1658. Their nation was almost exterminated in the mid-17th century by five years of prolonged warfare with the powerful neighboring Iroquois for helping the Huron in the Beaver Wars for control of the fur trade. Captured survivors were adopted or enslaved by the Iroquois.
The St. Lawrence Iroquoians were an Iroquoian Indigenous people who existed until about the late 16th century. They concentrated along the shores of the St. Lawrence River in present-day Quebec and Ontario, Canada, and in the American states of New York and northernmost Vermont. They spoke Laurentian languages, a branch of the Iroquoian family.

Guillaume Couture was a citizen of New France. During his life he was a lay missionary with the Jesuits, a survivor of torture, a member of an Iroquois council, a translator, a diplomat, a militia captain, and a lay leader among the colonists of the Pointe-Lévy in the Seigneury of Lauzon, a district of New France located on the South Side of Quebec City.

The Wabanaki Confederacy is a North American First Nations and Native American confederation of five principal Eastern Algonquian nations: the Abenaki of St. Francis, Mi'kmaq, Maleceet, Passamaquoddy (Peskotomahkati) and Penobscot.

The Battle of Long Sault occurred over a five-day period in early May 1660 during the Beaver Wars. It was fought between French colonial militia, with their Huron and Algonquin allies, against the Iroquois Confederacy.
Events from the year 1609 in Quebec.
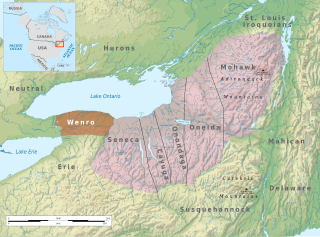
The Wenrohronon or Wenro people were an Iroquoian indigenous nation of North America, originally residing in present-day western New York, who were conquered by the Confederation of the Five Nations of the Iroquois in two decisive wars between 1638–1639 and 1643. This was likely part of the Iroquois Confederacy campaign against the Neutral people, another Iroquoian-speaking tribe, which lived across the Niagara River. This warfare was part of what was known as the Beaver Wars, as the Iroquois worked to dominate the lucrative fur trade. They used winter attacks, which were not usual among Native Americans, and their campaigns resulted in attrition of both the larger Iroquoian confederacies, as they had against the numerous Huron.
The Iroquois, also known as the Five Nations, and later as the Six Nations from 1722 onwards; alternatively referred to by the endonym Haudenosaunee are an Iroquoian-speaking confederacy of Native Americans and First Nations peoples in northeast North America. They were known by the French during the colonial years as the Iroquois League, and later as the Iroquois Confederacy, while the English simply called them the "Five Nations". The peoples of the Iroquois included the Mohawk, Oneida, Onondaga, Cayuga, and Seneca. After 1722, the Iroquoian-speaking Tuscarora people from the southeast were accepted into the confederacy, from which point it was known as the "Six Nations".

The Battle of Sorel occurred on June 19, 1610, with Samuel de Champlain supported by the Kingdom of France and his allies, the Huron, Algonquin people, and Montagnais that fought against the Mohawk people in New France at present-day Sorel-Tracy, Quebec. The forces of Champlain armed with the arquebus engaged and killed or captured nearly all of the Mohawks. The battle ended major hostilities with the Mohawks for twenty years.
Pieskaret was a famous chief of the Adirondac Indians. His tribe fought against the English forces, helping the French in the early 17th century. The Adirondacs under him drove the Iroquois Confederation out of Canada.
















