Related Research Articles

Automation describes a wide range of technologies that reduce human intervention in processes, mainly by predetermining decision criteria, subprocess relationships, and related actions, as well as embodying those predeterminations in machines. Automation has been achieved by various means including mechanical, hydraulic, pneumatic, electrical, electronic devices, and computers, usually in combination. Complicated systems, such as modern factories, airplanes, and ships typically use combinations of all of these techniques. The benefit of automation includes labor savings, reducing waste, savings in electricity costs, savings in material costs, and improvements to quality, accuracy, and precision.

A self-driving car, also known as a autonomous car (AC), driverless car, robotaxi, robotic car or robo-car, is a car that is capable of operating with reduced or no human input. Self-driving cars are responsible for all driving activities, such as perceiving the environment, monitoring important systems, and controlling the vehicle, which includes navigating from origin to destination.

Logistics automation is the application of computer software or automated machinery to logistics operations in order to improve its efficiency. Typically this refers to operations within a warehouse or distribution center, with broader tasks undertaken by supply chain engineering systems and enterprise resource planning systems.
In software testing, test automation is the use of software separate from the software being tested to control the execution of tests and the comparison of actual outcomes with predicted outcomes. Test automation can automate some repetitive but necessary tasks in a formalized testing process already in place, or perform additional testing that would be difficult to do manually. Test automation is critical for continuous delivery and continuous testing.
Post-scarcity is a theoretical economic situation in which most goods can be produced in great abundance with minimal human labor, so that they become available to all very cheaply or even freely.
Systems management is enterprise-wide administration of distributed systems including computer systems. Systems management is strongly influenced by network management initiatives in telecommunications. The application performance management (APM) technologies are now a subset of Systems management. Maximum productivity can be achieved more efficiently through event correlation, system automation and predictive analysis which is now all part of APM.

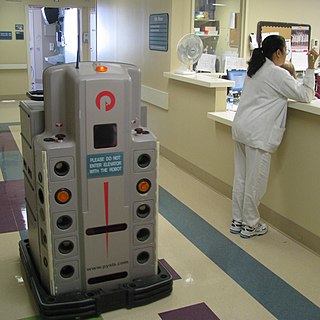
An automated guided vehicle (AGV), different from an autonomous mobile robot (AMR), is a portable robot that follows along marked long lines or wires on the floor, or uses radio waves, vision cameras, magnets, or lasers for navigation. They are most often used in industrial applications to transport heavy materials around a large industrial building, such as a factory or warehouse. Application of the automatic guided vehicle broadened during the late 20th century.

An automated storage and retrieval system consists of a variety of computer-controlled systems for automatically placing and retrieving loads from defined storage locations. Automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS) are typically used in applications where:

Vehicular automation is the use of technology to assist or replace the operator of a vehicle such as a car, truck, aircraft, rocket, military vehicle, or boat. Assisted vehicles are semi-autonomous, whereas vehicles that can travel without a human operator are autonomous. The degree of autonomy may be subject to various constraints such as conditions. Autonomy is enabled by advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) of varying capacity.

Laboratory automation is a multi-disciplinary strategy to research, develop, optimize and capitalize on technologies in the laboratory that enable new and improved processes. Laboratory automation professionals are academic, commercial and government researchers, scientists and engineers who conduct research and develop new technologies to increase productivity, elevate experimental data quality, reduce lab process cycle times, or enable experimentation that otherwise would be impossible.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to automation:
Enterprise forms automation is a company-wide computer system or set of systems for managing, distributing, completing, and processing paper-based forms, applications, surveys, contracts, and other documents. It plays a vital role in the concept of a paperless office.
Pharmacy automation involves the mechanical processes of handling and distributing medications. Any pharmacy task may be involved, including counting small objects ; measuring and mixing powders and liquids for compounding; tracking and updating customer information in databases ; and inventory management. This article focuses on the changes that have taken place in the local, or community pharmacy since the 1960s.
Open Automated Demand Response (OpenADR) is a research and standards development effort for energy management led by North American research labs and companies. The typical use is to send information and signals to cause electrical power-using devices to be turned off during periods of high demand.
HP Cloud Service Automation is cloud management software from Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE) that is used by companies and government agencies to automate the management of cloud-based IT-as-a-service, from order, to provision, and retirement. HP Cloud Service Automation orchestrates the provisioning and deployment of complex IT services such as of databases, middleware, and packaged applications. The software speeds deployment of application-based services across hybrid cloud delivery platforms and traditional IT environments.
An automated restaurant or robotic restaurant is a restaurant that uses robots to do tasks such as delivering food and drink to the tables and/or cooking the food.
Technological unemployment is the loss of jobs caused by technological change. It is a key type of structural unemployment. Technological change typically includes the introduction of labour-saving "mechanical-muscle" machines or more efficient "mechanical-mind" processes (automation), and humans' role in these processes are minimized. Just as horses were gradually made obsolete as transport by the automobile and as labourer by the tractor, humans' jobs have also been affected throughout modern history. Historical examples include artisan weavers reduced to poverty after the introduction of mechanized looms. Thousands of man-years of work was performed in a matter of hours by the bombe codebreaking machine during World War II. A contemporary example of technological unemployment is the displacement of retail cashiers by self-service tills and cashierless stores.
Automation bias is the propensity for humans to favor suggestions from automated decision-making systems and to ignore contradictory information made without automation, even if it is correct. Automation bias stems from the social psychology literature that found a bias in human-human interaction that showed that people assign more positive evaluations to decisions made by humans than to a neutral object. The same type of positivity bias has been found for human-automation interaction, where the automated decisions are rated more positively than neutral. This has become a growing problem for decision making as intensive care units, nuclear power plants, and aircraft cockpits have increasingly integrated computerized system monitors and decision aids to mostly factor out possible human error. Errors of automation bias tend to occur when decision-making is dependent on computers or other automated aids and the human is in an observatory role but able to make decisions. Examples of automation bias range from urgent matters like flying a plane on automatic pilot to such mundane matters as the use of spell-checking programs.
Marketing automation refers to software platforms and technologies designed for marketing departments and organizations automate repetitive tasks and consolidate multi-channel interactions, tracking and web analytics, lead scoring, campaign management and reporting into one system. It often integrates with customer relationship management (CRM) and customer data platform (CDP) software.

Aaron John Bastani is a British political commentator, journalist and author. He co-founded the left-wing media organisation Novara Media in 2011 and regularly hosts and contributes to its Novara Live live news show on YouTube. Bastani popularised the term "Fully Automated Luxury Communism", which describes a post-capitalist society in which automation greatly reduces the amount of labour humans need to do. He authored the book Fully Automated Luxury Communism on the subject in 2019. He ideologically identifies as a socialist.
References
- ↑ Feder, Barnaby J. (27 February 1986). "Technology; Standardizing Automation". The New York Times. Retrieved 13 January 2025.