The British Isles are a group of islands in the North Atlantic off the north-western coast of continental Europe that consist of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Hebrides and over six thousand smaller isles. They have a total area of about 315,159 km2 and a combined population of almost 72 million, and include two sovereign states, the Republic of Ireland, and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. The islands of Alderney, Jersey, Guernsey, and Sark, and their neighbouring smaller islands, are sometimes also taken to be part of the British Isles, even though, as islands off the coast of France, they do not form part of the archipelago.

The Isle of Man, sometimes referred to simply as Mann, is a self-governing British Crown dependency in the Irish Sea between Great Britain and Ireland. The head of state is Queen Elizabeth II, who holds the title of Lord of Mann and is represented by a lieutenant governor. Defence is the responsibility of the United Kingdom.

The Isle of Man had become separated from Britain and Ireland by 6500 BC. It appears that colonisation took place by sea sometime during the Mesolithic era. The island has been visited by various raiders and trading peoples over the years. After being settled by people from Ireland in the first millennium, the Isle of Man was converted to Christianity and then suffered raids by Vikings from Norway. After becoming subject to Norwegian suzerainty as part of the Kingdom of Mann and the Isles, the Isle of Man later became a possession of the Scottish and then the English crowns.

The Isle of Wight is a county and the largest and second-most populous island in England. It is in the English Channel, between 2 and 5 miles off the coast of Hampshire, separated by the Solent. The island has resorts that have been holiday destinations since Victorian times, and is known for its mild climate, coastal scenery, and verdant landscape of fields, downland and chines.

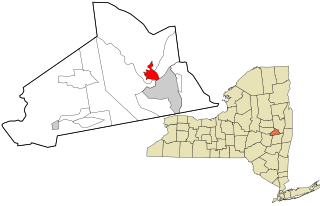
Onondaga County is a county in the U.S. state of New York. As of the 2010 census, the population was 467,026. The county seat is Syracuse.
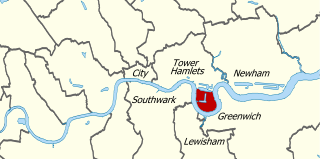
The Isle of Dogs is a district in East London and is in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets, and is a part of the East End. It is referred to as the Island, It is bounded on three sides by one of the largest meanders in the River Thames. The northern boundary has never been clearly or consistently defined but many accept it to be the (former) line of the West India South Dock. The name Isle of Dogs had no official status until 1987, with the creation of the Isle of Dogs Neighbourhood by Tower Hamlets London Borough Council.

Onondaga is a town located in Onondaga County, New York, United States. As of the 2010 U.S. Census, the town had a population of 23,103. The town is named after the native Onondaga tribe, part of the Iroquois Confederacy. Onondaga is located southwest of the city of Syracuse, which it borders.

Hiawatha was a precolonial Indian leader and co-founder of the Iroquois Confederacy. He was a leader of the Onondaga people, the Mohawk people, or both. According to some accounts, he was born an Onondaga but adopted into the Mohawks.

The Crown dependencies are three island territories off the coast of Great Britain that are self-governing possessions of the Crown: the Bailiwick of Guernsey, the Bailiwick of Jersey and the Isle of Man. They do not form part of either the United Kingdom or the British Overseas Territories. Internationally, the dependencies are considered "territories for which the United Kingdom is responsible", rather than sovereign states. As a result, they are not member states of the Commonwealth of Nations. However, they do have relationships with the Commonwealth, the European Union, and other international organisations, and are members of the British–Irish Council. They have their own teams in the Commonwealth Games. They are not part of the European Union (EU), although they are within the EU's customs area. The Isle of Man is within the EU's VAT area.
The Onondagapeople are one of the original five constituent nations of the Iroquois (Haudenosaunee) Confederacy in northeast North America. Their traditional homeland is in and around present-day Onondaga County, New York, south of Lake Ontario. They are known as Gana’dagwëni:io’geh to the other Iroquois tribes. Being centrally located, they are considered the "Keepers of the Fire" in the figurative longhouse that shelters the Five Nations. The Cayuga and Seneca have territory to their west and the Oneida and Mohawk to their east. For this reason, the League of the Iroquois historically met at the Iroquois government's capital at Onondaga, as the traditional chiefs do today.

Onondaga Community College (OCC) is a public community college that serves Onondaga County, New York, at two campuses. Part of the State University of New York (SUNY) system, OCC is one of 30 locally sponsored community colleges in New York State.

Onondaga Lake is a lake in Central New York, immediately northwest of and adjacent to Syracuse, New York. The southeastern end of the lake and the southwestern shore abut industrial areas and expressways; the northeastern shore and northwestern end border a series of parks and museums.

USS Onondaga was a river monitor built for the Union Navy during the American Civil War. The ship spent her entire active career with the James River Flotilla, covering the water approaches to Richmond, Virginia, during the last year of the Civil War. After the war, she was purchased by France.

The Battle of the Thousand Islands was an engagement fought on 16–24 August 1760, in the upper St. Lawrence River, among the Thousand Islands, along the present day Canada–United States border, by British and French forces during the closing phases of the Seven Years' War, as it is called in Canada and Europe, or the French and Indian War as it is referred to in the United States.

The Council of the Isles of Scilly is a sui generis unitary local government authority covering the Isles of Scilly off the west coast of Cornwall. It is currently made up of 16 seats, with all councillors being Independents as of 2 May 2013. The council was created in 1890 as the Isles of Scilly Rural District Council and was renamed in 1974.

The Isles of Scilly is an archipelago off the southwestern tip of Cornwall. One of the islands, St Agnes, is the most southerly point in England, being over 4 miles (6.4 km) further south than the most southerly point of the British mainland at Lizard Point.

Belle Isle Park, more commonly known simply as Belle Isle, is a 982-acre island park in the Detroit River between Michigan and Ontario. The U.S.-Canada border is in the channel south of Belle Isle such that the island is not in Canada. Owned by the city of Detroit, Belle Isle is managed as a state park by the Michigan Department of Natural Resources through a 30-year lease initiated in 2013; it was previously a city park. Belle Isle is the largest city-owned island park in the United States and is the third largest island in the Detroit River after Grosse Ile and Fighting Island. It is connected to mainland Detroit by the MacArthur Bridge.

Lower South Bay, commonly called South Bay, is a hamlet on the southwest corner of Oneida Lake, Onondaga County, New York State, United States. It is opposite North Bay, and is surrounded by many islands to the west, north and east, including Geersbeck Island, Hall Island, Glosky Island, Schroeppel Island, Denmans Island and Long Island. Lower South Bay also lies near the town of Cicero, about 2 miles west.