Related Research Articles

A Tesla coil is an electrical resonant transformer circuit designed by inventor Nikola Tesla in 1891. It is used to produce high-voltage, low-current, high-frequency alternating-current electricity. Tesla experimented with a number of different configurations consisting of two, or sometimes three, coupled resonant electric circuits.

Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) is the ability of electrical equipment and systems to function acceptably in their electromagnetic environment, by limiting the unintentional generation, propagation and reception of electromagnetic energy which may cause unwanted effects such as electromagnetic interference (EMI) or even physical damage to operational equipment. The goal of EMC is the correct operation of different equipment in a common electromagnetic environment. It is also the name given to the associated branch of electrical engineering.
A nuclear electromagnetic pulse is a burst of electromagnetic radiation created by a nuclear explosion. The resulting rapidly varying electric and magnetic fields may couple with electrical and electronic systems to produce damaging current and voltage surges. The specific characteristics of a particular nuclear EMP event vary according to a number of factors, the most important of which is the altitude of the detonation.
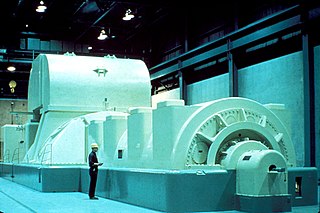
In electricity generation, a generator is a device that converts motion-based power or fuel-based power into electric power for use in an external circuit. Sources of mechanical energy include steam turbines, gas turbines, water turbines, internal combustion engines, wind turbines and even hand cranks. The first electromagnetic generator, the Faraday disk, was invented in 1831 by British scientist Michael Faraday. Generators provide nearly all the power for electrical grids.

A Faraday cage or Faraday shield is an enclosure used to block electromagnetic fields. A Faraday shield may be formed by a continuous covering of conductive material, or in the case of a Faraday cage, by a mesh of such materials. Faraday cages are named after scientist Michael Faraday, who invented them in 1836.

A spark gap consists of an arrangement of two conducting electrodes separated by a gap usually filled with a gas such as air, designed to allow an electric spark to pass between the conductors. When the potential difference between the conductors exceeds the breakdown voltage of the gas within the gap, a spark forms, ionizing the gas and drastically reducing its electrical resistance. An electric current then flows until the path of ionized gas is broken or the current reduces below a minimum value called the "holding current". This usually happens when the voltage drops, but in some cases occurs when the heated gas rises, stretching out and then breaking the filament of ionized gas. Usually, the action of ionizing the gas is violent and disruptive, often leading to sound, light, and heat.

A pulse-forming network (PFN) is an electric circuit that accumulates electrical energy over a comparatively long time, and then releases the stored energy in the form of a relatively square pulse of comparatively brief duration for various pulsed power applications. In a PFN, energy storage components such as capacitors, inductors or transmission lines are charged by means of a high-voltage power source, then rapidly discharged into a load through a high-voltage switch, such as a spark gap or hydrogen thyratron. Repetition rates range from single pulses to about 104 per second. PFNs are used to produce uniform electrical pulses of short duration to power devices such as klystron or magnetron tube oscillators in radar sets, pulsed lasers, particle accelerators, flashtubes, and high-voltage utility test equipment.

Electromagnetic interference (EMI), also called radio-frequency interference (RFI) when in the radio frequency spectrum, is a disturbance generated by an external source that affects an electrical circuit by electromagnetic induction, electrostatic coupling, or conduction. The disturbance may degrade the performance of the circuit or even stop it from functioning. In the case of a data path, these effects can range from an increase in error rate to a total loss of the data. Both man-made and natural sources generate changing electrical currents and voltages that can cause EMI: ignition systems, cellular network of mobile phones, lightning, solar flares, and auroras. EMI frequently affects AM radios. It can also affect mobile phones, FM radios, and televisions, as well as observations for radio astronomy and atmospheric science.

A Marx generator is an electrical circuit first described by Erwin Otto Marx in 1924. Its purpose is to generate a high-voltage pulse from a low-voltage DC supply. Marx generators are used in high-energy physics experiments, as well as to simulate the effects of lightning on power-line gear and aviation equipment. A bank of 36 Marx generators is used by Sandia National Laboratories to generate X-rays in their Z Machine.

High voltage electricity refers to electrical potential large enough to cause injury or damage. In certain industries, high voltage refers to voltage above a certain threshold. Equipment and conductors that carry high voltage warrant special safety requirements and procedures.
A magnetohydrodynamic generator is a magnetohydrodynamic converter that transforms thermal energy and kinetic energy directly into electricity. An MHD generator, like a conventional generator, relies on moving a conductor through a magnetic field to generate electric current. The MHD generator uses hot conductive ionized gas as the moving conductor. The mechanical dynamo, in contrast, uses the motion of mechanical devices to accomplish this.
Pulsed power is the science and technology of accumulating energy over a relatively long period of time and releasing it instantly, thus increasing the instantaneous power. They can be used in some applications such as food processing, water treatment, weapon, and medical applications.

In electromagnetism, an electric discharge is the release and transmission of electricity in an applied electric field through a medium such as a gas.

A homopolar generator is a DC electrical generator comprising an electrically conductive disc or cylinder rotating in a plane perpendicular to a uniform static magnetic field. A potential difference is created between the center of the disc and the rim with an electrical polarity that depends on the direction of rotation and the orientation of the field. It is also known as a unipolar generator, acyclic generator, disk dynamo, or Faraday disc. The voltage is typically low, on the order of a few volts in the case of small demonstration models, but large research generators can produce hundreds of volts, and some systems have multiple generators in series to produce an even larger voltage. They are unusual in that they can source tremendous electric current, some more than a million amperes, because the homopolar generator can be made to have very low internal resistance. Also, the homopolar generator is unique in that no other rotary electric machine can produce DC without using rectifiers or commutators.

In electrical engineering and mechanical engineering, a transient response is the response of a system to a change from an equilibrium or a steady state. The transient response is not necessarily tied to abrupt events but to any event that affects the equilibrium of the system. The impulse response and step response are transient responses to a specific input.
A linear transformer driver (LTD) within physics and energy, is an annular parallel connection of switches and capacitors. The driver is designed to deliver rapid high power pulses. The LTD was invented at the Institute of High Current Electronics (IHCE) in Tomsk, Russia. The LTD is capable of producing high current pulses, up to 1 mega amps (106 ampere), with a risetime of less than 100 ns. This is an improvement over Marx generator based pulsed power devices which require pulse compression to achieve such fast risetimes. It is being considered as a driver for z-pinch based inertial confinement fusion.
Radiofrequency MASINT is one of the six major disciplines generally accepted to make up the field of Measurement and Signature Intelligence (MASINT), with due regard that the MASINT subdisciplines may overlap, and MASINT, in turn, is complementary to more traditional intelligence collection and analysis disciplines such as SIGINT and IMINT. MASINT encompasses intelligence gathering activities that bring together disparate elements that do not fit within the definitions of Signals Intelligence (SIGINT), Imagery Intelligence (IMINT), or Human Intelligence (HUMINT).

ATLAS-I, better known as Trestle, was a unique electromagnetic pulse (EMP) generation and testing apparatus built between 1972 and 1980 during the Cold War at Sandia National Laboratories near Kirtland Air Force Base in Albuquerque, New Mexico.
An electromagnetic pulse (EMP), also referred to as a transient electromagnetic disturbance (TED), is a brief burst of electromagnetic energy. The origin of an EMP can be natural or artificial, and can occur as an electromagnetic field, as an electric field, as a magnetic field, or as a conducted electric current. The electromagnetic interference caused by an EMP can disrupt communications and damage electronic equipment. An EMP such as a lightning strike can physically damage objects such as buildings and aircraft. The management of EMP effects is a branch of electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) engineering.
The Soviet Union's K project nuclear test series was a group of five nuclear tests conducted in 1961–1962. These tests followed the 1961 Soviet nuclear tests series and preceded the 1962 Soviet nuclear tests series.
References
- 1 2 "The Soviet Lightning Machine Abandoned in a Russian Forest". Atlas Obscura. 2014-07-10. Retrieved 2017-05-12.
- ↑ "DailyTech - Pictured: Drone Survives Flyover of Russia's Largest Artificial Lightning Generator". www.dailytech.com. Archived from the original on 2017-05-05. Retrieved 2017-05-12.
- ↑ "Abandoned Marx Generator". Atlas Obscura. Retrieved 2017-05-12.
- 1 2 "Величайший «Купол» науки из Истры / Хабр". Хабр (in Russian). 2017-03-10. Retrieved 2023-09-14.
- ↑ "Instalaciones de investigación de alta tensión de la URSS: El sueño húmedo de Tesla". Rusadas (in Spanish). Retrieved 2023-09-14.
- ↑ Today, Russia (2014-07-06). "Electrifying: Giant futuristic 'Tesla Tower' in abandoned woods near Moscow (PHOTOS, VIDEO)". RT International. Retrieved 2023-09-14.