The Torres Strait, also known as Zenadh Kes, is a strait between Australia and the Melanesian island of New Guinea. It is 151 km (94 mi) wide at its narrowest extent. To the south is Cape York Peninsula, the northernmost extremity of the Australian mainland. To the north is the Western Province of Papua New Guinea. It is named after the Spanish navigator Luís Vaz de Torres, who sailed through the strait in 1606.

The Torres Strait Islands are a group of at least 274 small islands in the Torres Strait, a waterway separating far northern continental Australia's Cape York Peninsula and the island of New Guinea. They span an area of 48,000 km2 (19,000 sq mi), but their total land area is 566 km2 (219 sq mi).

Torres Strait Islanders are the Indigenous Melanesian people of the Torres Strait Islands, which are part of the state of Queensland, Australia. Ethnically distinct from the Aboriginal people of the rest of Australia, they are often grouped with them as Indigenous Australians. Today there are many more Torres Strait Islander people living in mainland Australia than on the Islands.

The indigenous peoples of New Guinea in Indonesia and Papua New Guinea, commonly called Papuans, are Melanesians. There is genetic evidence for two major historical lineages in New Guinea and neighboring islands:
- a first wave from the Malay Archipelago perhaps 50,000 years ago when New Guinea and Australia were a single landmass called Sahul ...
- and, much later, a wave of Austronesian people from the north who introduced Austronesian languages and pigs about 3,500 years ago. They also left a small but significant genetic trace in many coastal Papuan peoples.

D'Entrecasteaux Islands are situated near the eastern tip of New Guinea in the Solomon Sea in Milne Bay Province of Papua New Guinea. The group spans a distance of 160 km (99 mi), has a total land area of approximately 3,100 km2 (1,197 sq mi) and is separated from the Papua New Guinea mainland by the 30 km (19 mi) wide Ward Hunt Strait in the north and the 18 km (11 mi) wide Goschen Strait in the south. D'Entrecasteaux Islands show signs of volcanism.

The Arafura Sea lies west of the Pacific Ocean, overlying the continental shelf between Australia and Western New Guinea, which is the Indonesian part of the Island of New Guinea.
The North New Guinea languages of Papua New Guinea and Indonesia form a possible linkage of Western Oceanic languages. They have been in heavy contact with Papuan languages.

Vitiaz Strait is a strait between New Britain and the Huon Peninsula, northern New Guinea.

Karkar Island is an oval-shaped volcanic island located in the Bismarck Sea, about 30 kilometres off the north coast of mainland Papua New Guinea in Madang Province, from which it is separated by the Isumrud Strait. The island is about 25 km in length and 19 km in width. In the centre is an active volcano with two nested calderas.

The Eastern Trans-Fly languages are a small independent family of Papuan languages spoken in the Oriomo Plateau to the west of the Fly River in New Guinea.

Talbot Islands are a group of Torres Strait Islands in Queensland, Australia. They lie between the Australian mainland and the island of New Guinea and a few kilometres west of Saibai Island, Torres Strait, only 4 km from the Papua New Guinea mainland at the mouth of the Mai Kussa River.

Umboi is a volcanic island between the mainland of Papua New Guinea and the island of New Britain. It is separated from New Britain by the Dampier Strait and Huon Peninsula, and New Guinea by the Vitiaz Strait. It has an elevation of 1,335 metres.

The Bird's Head Peninsula or Doberai Peninsula, is a large peninsula that makes up the northwest portion of the island of New Guinea and the major part of the province of West Papua, Indonesia. The peninsula at the opposite end of the island is called the Bird's Tail Peninsula.

Long Island is a volcanic island in Papua New Guinea. It is located north of the island of New Guinea, separated from it by the Vitiaz Strait.

Daru Island is an island in the Western Province of Papua New Guinea. It is one of the Torres Strait Islands. The eponymous town on the island is the capital of the province, and houses the vast majority of the island's population of 20,524 (2009). Daru Island is elliptical in shape, with dimensions of 5.0 by 3.7 kilometers, an area of 14.7 km², and an elevation of up to 27 m. The island is separated from the mainland in the north, specifically the mouth of Oriomo River, by the 3.5 km wide Daru Roads. The shortest distance to the larger Bristow Island in the south is 1.3 km.

Kiwai Island is the largest island in the Fly River delta, Papua New Guinea. It is one of the Torres Strait Islands. It is 59 km long along the northwest–southeast axis from Wamimuba Point in the northwest to the village of Saguane (Sanguane) in the south, and up to 9 km wide, with an average width of 5.6 km. Its area is 359 km2. Neighboring Purutu and Wabuda Islands to the north and northeast are also among the three largest islands in the Fly River delta. A language study mentioned a population of about 4500, but the census of population of 2000 showed only 2092 inhabitants.

The Mombum languages, also known as the Komolom or Muli Strait languages, are a pair of Trans–New Guinea languages, Mombum (Komolom) and Koneraw, spoken on Komolom Island just off Yos Sudarso Island, and on the southern coast of Yos Sudarso Island, respectively, on the southern coast of New Guinea. Komolom Island is at the southern end of the Muli Strait.
The Northern Adelbert or Pihom–Isumrud languages are a family of two dozen languages in the Madang stock of New Guinea. The occupy the coastal northern Adelbert Range of mountains, vs. the Southern Adelbert languages, another branch of Madang.
Papua New Guinean Australians are the citizens and residents of Australia who were born in Papua New Guinea (PNG) or have Papua New Guinean ancestry.
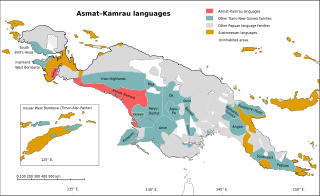
The Asmat–Muli Strait languages are a branch of the Trans–New Guinea languages spoken along the southern coast of Indonesian New Guinea, established by Timothy Usher and Edgar Suter.