Related Research Articles

Revolver is the seventh studio album by the English rock band the Beatles. It was released on 5 August 1966, accompanied by the double A-side single "Eleanor Rigby" / "Yellow Submarine". The album was the Beatles' final recording project before their retirement as live performers and marked the group's most overt use of studio technology to date, building on the advances of their late 1965 release Rubber Soul. It has since become regarded as one of the greatest and most innovative albums in the history of popular music, with recognition centred on its range of musical styles, diverse sounds and lyrical content.

"Strawberry Fields Forever" is a song by the English rock band the Beatles, written by John Lennon and credited to Lennon–McCartney. It was released on 13 February 1967 as a double A-side single with "Penny Lane". It represented a departure from the group's previous singles and a novel listening experience for the contemporary pop audience. While the song initially divided and confused music critics and the group's fans, it proved highly influential on the emerging psychedelic genre. Its accompanying promotional film is similarly recognised as a pioneering work in the medium of music video.

The Swinging Sixties was a youth-driven cultural revolution that took place in the United Kingdom during the mid-to-late 1960s, emphasising modernity and fun-loving hedonism, with Swinging London denoted as its centre. It saw a flourishing in art, music and fashion, and was symbolised by the city's "pop and fashion exports", such as the Beatles, as the multimedia leaders of the British Invasion of musical acts; the mod and psychedelic subcultures; Mary Quant's miniskirt designs; popular fashion models such as Twiggy and Jean Shrimpton; the iconic status of popular shopping areas such as London's King's Road, Kensington and Carnaby Street; the political activism of the anti-nuclear movement; and the sexual liberation movement.

Flower power was a slogan used during the late 1960s and early 1970s as a symbol of passive resistance and nonviolence. It is rooted in the opposition movement to the Vietnam War. The expression was coined by the American Beat poet Allen Ginsberg in 1965 as a means to transform war protests into peaceful affirmative spectacles. Hippies embraced the symbolism by dressing in clothing with embroidered flowers and vibrant colors, wearing flowers in their hair, and distributing flowers to the public, becoming known as flower children. The term later became generalized as a modern reference to the hippie movement and the so-called counterculture of drugs, psychedelic music, psychedelic art and social permissiveness.

"All You Need Is Love" is a song by the English rock band the Beatles that was released as a non-album single in July 1967, with "Baby, You're a Rich Man" as its B-side. It was written by John Lennon and credited to the Lennon–McCartney partnership. The song was Britain's contribution to Our World, the first live global television link, for which the band were filmed performing it at EMI Studios in London on 25 June. The programme was broadcast via satellite and seen by an audience of over 400 million in 25 countries. Lennon's lyrics were deliberately simplistic, to allow for broad appeal to the show's international audience, and captured the utopian ideals associated with the Summer of Love. The single topped sales charts in Britain, the United States and many other countries, and became an anthem for the counterculture's embrace of flower power philosophy.

Tonite Lets All Make Love in London is a soundtrack album released on LP in 1968, for the 1967 documentary film of the same name, made by Peter Whitehead about the "swinging London" scene of the sixties. The film consists of a series of psychedelic performances and interviews and features live performance by Pink Floyd, together with footage of John Lennon, Yoko Ono, Mick Jagger, Vanessa Redgrave, Lee Marvin, Julie Christie, Allen Ginsberg, Eric Burdon, Michael Caine and many others attending one of the band's concerts.

John Victor Lindsay "Hoppy" Hopkins was a British photographer, journalist, researcher and political activist, and "one of the best-known underground figures of 'Swinging London' " in the late 1960s.

"Tomorrow Never Knows" is a song by the English rock band the Beatles, written primarily by John Lennon and credited to Lennon–McCartney. It was released in August 1966 as the final track on their album Revolver, although it was the first song recorded for the LP. The song marked a radical departure for the Beatles, as the band fully embraced the potential of the recording studio without consideration for reproducing the results in concert.

"The Fool on the Hill" is a song by the English rock band the Beatles from their 1967 EP and album Magical Mystery Tour. It was written and sung by Paul McCartney and credited to the Lennon–McCartney partnership. The lyrics describe the titular "fool", a solitary figure who is not understood by others, but is actually wise. McCartney said the idea for the song was inspired by the Dutch design collective the Fool, who derived their name from the tarot card of the same name, and possibly by Maharishi Mahesh Yogi.

"Lovely Rita" is a song by the English rock band the Beatles from their 1967 album Sgt. Pepper's Lonely Hearts Club Band. It was written mainly by Paul McCartney and credited to Lennon–McCartney. It is about a meter maid and the narrator's affection for her.
"Hey Bulldog" is a song by the English rock band the Beatles released on their 1969 soundtrack album Yellow Submarine. Credited to Lennon–McCartney, but written primarily by John Lennon, it was finished in the recording studio by both Lennon and Paul McCartney. The song was recorded during the filming of the "Lady Madonna" promotional film, and, with "Lady Madonna", is one of the few Beatles songs based on a piano riff.
"Baby, You're a Rich Man" is a song by the English rock band the Beatles that was released as the B-side of their "All You Need Is Love" single in July 1967. It originated from an unfinished song by John Lennon, titled "One of the Beautiful People", to which Paul McCartney added a chorus. It is one of the best-known pop songs to make use of a clavioline, a monophonic keyboard instrument that was a forerunner to the synthesizer. Lennon played the clavioline on its oboe setting, creating a sound that suggests an Indian shehnai. The song was recorded and mixed at Olympic Sound Studios in London, making it the first of the Beatles' EMI recordings to be entirely created outside EMI Studios.

"Yellow Submarine" is a song by the English rock band the Beatles from their 1966 album Revolver. It was also issued on a double A-side single, paired with "Eleanor Rigby". Written as a children's song initially by Paul McCartney with contributions from John Lennon, it was drummer Ringo Starr's vocal spot on the album. The single went to number one on charts in the United Kingdom and several other European countries, and in Australia, Canada and New Zealand. It won an Ivor Novello Award for the highest certified sales of any single written by a British songwriter and issued in the UK in 1966. In the US, the song peaked at number two on the Billboard Hot 100 chart and number one on the Cash BoxTop 100 chart.
Barry Miles is an English author known for his participation in and writing on the subjects of the 1960s London underground and counterculture. He is the author of numerous books and his work has also regularly appeared in leftist newspapers such as The Guardian. In the 1960s, he was co-owner of the Indica Gallery and helped start the independent newspaper International Times.

Aubrey "Po" Powell is a British graphic designer. He co-founded the album cover design company Hipgnosis with Storm Thorgerson in 1967. The company ran for 15 years until 1982, and created some of the most acclaimed record cover art of the 1960s, 1970s and 1980s for many of the most famous rock bands of the era including Pink Floyd, Led Zeppelin, Paul McCartney, Yes, Genesis, 10cc, Wishbone Ash, Peter Gabriel, UFO, Bad Company, Emerson, Lake & Palmer, Scorpions, Styx, Syd Barrett, and Black Sabbath. The company was nominated five times for Grammy Awards.
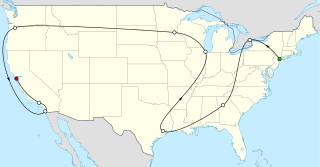
The Beatles staged their second concert tour of the United States in the late summer of 1965. At the peak of American Beatlemania, they played a mixture of outdoor stadiums and indoor arenas, with historic concerts at Shea Stadium in New York and the Hollywood Bowl. Typically of the era, the tour was a "package" presentation, with several artists on the bill. The Beatles played for just 30 minutes at each show, following sets by support acts such as Brenda Holloway and the King Curtis Band, Cannibal & the Headhunters, and Sounds Incorporated.
The International Poetry Incarnation was an event at the Royal Albert Hall in London on 11 June 1965.
This is a summary of 1967 in music in the United Kingdom.

It Was Twenty Years Ago Today is a 1987 British-made television documentary film about the 1967 Summer of Love. It premiered on 1 June 1987, twenty years after the official release date of the Beatles' album Sgt. Pepper's Lonely Hearts Club Band, and presents the album as the central factor behind the events and scenes that led to the full emergence of the 1960s counterculture.
Tonite Let’s All Make Love in London is a 1967 documentary film by Peter Whitehead. It includes sequences of “Swinging London” with accompanying contemporary pop music, concert and studio performances by musicians including the Rolling Stones and the first professional footage filmed of Pink Floyd, and several interviews. It is notable for showing footage shot inside the short-lived UFO Club, the British counter-culture night club in the basement of 31 Tottenham Court Road, and at The 14 Hour Technicolor Dream multi-artist event held in the Great Hall of the Alexandra Palace, including John Lennon. The film also shows scenes of soldiers parading in scarlet jackets and bearskins, London street scenes, a protest march, psychedelic patterns being painted on a semi-naked girl, the arrival of Playboy Bunny girls by plane, and guests including Roman Polanski and Sharon Tate, Terence Stamp, and Jim Brown arriving at the premiere of Polanski’s film Cul-de-sac.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 Metzger, Richard (4 February 2014). "London Underground: Early counterculture doc with Paul McCartney, Allen Ginsberg, Pink Floyd". Dangerous Minds. Retrieved 17 June 2018.
- 1 2 3 4 Winn, John C. (2009). That Magic Feeling: The Beatles' Recorded Legacy, Volume Two, 1966–1970. New York, NY: Three Rivers Press. p. 83. ISBN 978-0-307-45239-9.
- ↑ Riley, Tim (2011). Lennon: The Man, the Myth, the Music – The Definitive Life. London: Random House. p. 339. ISBN 978-0-7535-4020-6.
- 1 2 3 Palacios, Julian (2015). Syd Barrett & Pink Floyd: Dark Globe. Medford, NJ: Plexus. ISBN 978-0-859658829.
- 1 2 Riley 2011, pp. 338–39.
- ↑ Halpin, Michael (10 June 2017). "The Beatles, London's Counter-culture & Sgt. Pepper". Sounds Magazine. Retrieved 17 June 2018.
- ↑ Miles, Barry (2010). London Calling: A Countercultural History of London since 1945. London: Atlantic Books. ISBN 978-1-848875548.
