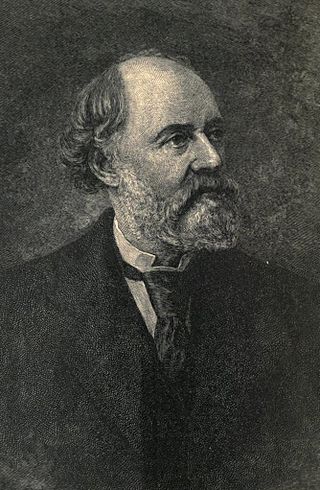East Lynne is an English sensation novel of 1861 by Ellen Wood, writing as Mrs Henry Wood. A Victorian best-seller, it is remembered chiefly for its elaborate and implausible plot, centring on infidelity and double identities. There have been numerous stage and film adaptations.

Alan Bennett is an English playwright, author, actor and screenwriter. Over his entertainment career he has received numerous awards and honours including two BAFTA Awards, four Laurence Olivier Awards, and two Tony Awards. He also earned an Academy Award nomination for his film The Madness of King George (1994). In 2005 he received the Society of London Theatre Special Award.
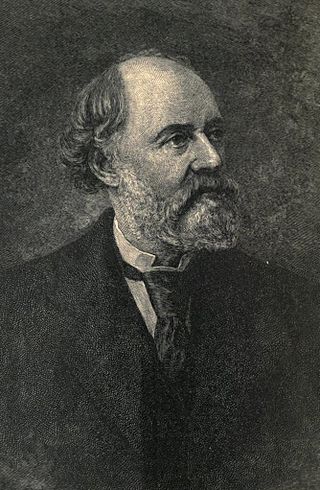
Charles Reade was a British novelist and dramatist, best known for The Cloister and the Hearth.

The Black Tulip is a historical novel and a work of Romantic poetry written by Alexandre Dumas, père, and first published in 1850.

Trilby is a novel by George du Maurier and one of the most popular novels of its time. Published serially in Harper's New Monthly Magazine from January to August 1894, it was published in book form on 8 September 1894 and sold 200,000 copies in the United States alone. Trilby is set in the 1850s in an idyllic bohemian Paris. Though Trilby features the stories of two English artists and a Scottish artist, one of the most memorable characters is Svengali, a rogue, masterful musician and hypnotist.

The Woman in Black is a 1983 gothic horror novel by English writer Susan Hill, about a mysterious spectre that haunts a small English town. A television film based on it, also called The Woman in Black, was produced in 1989, with a screenplay by Nigel Kneale. In 2012, another film adaption was released starring Daniel Radcliffe.

For the Term of His Natural Life is a story written by Marcus Clarke and published in The Australian Journal between 1870 and 1872. It was published as a novel in 1874 and is the best known novelisation of life as a convict in early Australian history. At times relying on seemingly implausible coincidences, the story follows the fortunes of Rufus Dawes, a young man transported for a murder that he did not commit. The book clearly conveys the harsh and inhumane treatment meted out to the convicts, some of whom were transported for relatively minor crimes, and graphically describes the conditions the convicts experienced. The novel was based on research by the author as well as a visit to the penal settlement of Port Arthur, Tasmania.

The Cloister and the Hearth (1861) is an historical novel by the British author Charles Reade. Set in the 15th century, it relates the travels of a young scribe and illuminator, Gerard Eliassoen, through several European countries. The Cloister and the Hearth often describes the events, people and their practices in minute detail. Its main theme is the struggle between man's obligations to family and to Church.

The Manxman is a novel by Hall Caine, first appearing as a serial in The Queen, The Lady's Newspaper and Court Chronicle between January and July 1894. Published as one volume in August 1894 by Heinemann, The Manxman ended the system of three-volume novels. A highly popular novel of its period, it was set in the Isle of Man and concerned a romantic triangle. The novel has as its central themes, the mounting consequences of sin and the saving grace of simple human goodness.

No Orchids for Miss Blandish is a 1939 crime novel by the British writer James Hadley Chase. It was a critical and commercial success upon release, though it also provoked considerable controversy due to its explicit depiction of sexuality and violence. In 1942, the novel was adapted into a stage play and in 1948 it became a British film. The novel became particularly popular with British servicemen during World War II.
It's Never Too Late to Mend is a 1937 British melodrama film directed by David MacDonald and starring Tod Slaughter, Jack Livesey and Marjorie Taylor. The plot involves a villainous squire and justice of the peace who conspires to have his rival arrested on false charges.

It Is Never Too Late to Mend is a 1911 Australian feature-length silent film written and directed by W. J. Lincoln.

Griffith Gaunt, or Jealousy is an 1866 sensation novel by Charles Reade. A best-selling book in its day, it was thought by Reade to be his best novel, but critics and posterity have generally preferred The Cloister and the Hearth (1861).

George Hans Hamilton was Archdeacon of Lindisfarne from 1865 until 1882, when he became Archdeacon of Northumberland. He was also a Canon of Durham.
A convict melodrama is a type of melodrama set in Australia during the convict era. They normally revolved around stories of innocent people wrongly accused of a crime who were transported to Australia as convicts. The best known work in this field was the novel For the Term of His Natural Life, which was adapted into various plays and films.
It Is Never Too Late to Mend is a 1913 American silent film version of the 1856 novel by Charles Reade. The film was released by the Edison Company.
It Is Never Too Late to Mend may refer to:

A Damsel in Distress is 2015 musical written by Jeremy Sams and Robert Hudson, with music and lyrics by George Gershwin and Ira Gershwin. A romantic comedy, the musical is based on the novel A Damsel in Distress by P. G. Wodehouse, the 1928 play adapted from the novel, and the 1937 musical comedy film A Damsel in Distress based on the novel and play. The musical ran from 30 May to 27 June 2015 at Chichester Festival Theatre.
Frank Towers (1835–1886) was an English actor, playwright and stage producer.
George James Vining was an English actor and theatre manager, appearing in London theatres. For several years he was manager of the Princess's Theatre.