This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations .(August 2018) |

Italicus (fl. 1st century AD) was a chieftain of the Germanic Cherusci. He is chiefly remembered as the nephew of Arminius.
This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations .(August 2018) |

Italicus (fl. 1st century AD) was a chieftain of the Germanic Cherusci. He is chiefly remembered as the nephew of Arminius.
Like his father Flavus and uncle Arminius, Italicus is only known by his Latin name, which means "the Italian". His original name is unknown.
Italicus was part of the royal family of the Cherusci tribe in ancient Germany, which was an ally of the early Roman Empire under Augustus. Italicus's father Flavus was a Roman citizen, served in the Roman military, and appears to have remained loyal to Rome when Italicus's grandfather Segimer and uncle Arminius ambushed three legions under P. Quinctilius Varus in the Teutoburg Forest in AD 9. Arminius seems to have succeeded Segimer as chieftain but was challenged by his uncle Inguiomer and the Marcomanni. During Germanicus's reprisal campaigns, Flavus also personally defeated Arminius at the Weser River. Arminius was killed by his father-in-law Segestes in AD 21.
Although Italicus's mother was also German, the daughter of the Chatti chieftain Actumerus, Tacitus wrote in his Annals that Italicus was entirely Romanized by his education. Nonetheless, in AD 47, the Cherusci requested that the emperor Claudius send him to rule them as the only surviving member of his dynasty. [1] Familiar with both Germanic and Roman ways of waging war, Italicus successfully established himself over the Cherusci at first but was then driven into exile. He returned to power with the assistance of the Lombards. He was succeeded as chieftain by Chariomerus, presumably his son, sometime before the Chatti victory over the Cherusci around AD 88.

Germanicus Julius Caesar was an ancient Roman general and politician most famously known for his campaigns against Arminius in Germania. The son of Nero Claudius Drusus and Antonia the Younger, Germanicus was born into an influential branch of the patrician gens Claudia. The agnomen Germanicus was added to his full name in 9 BC when it was posthumously awarded to his father in honor of his victories in Germania. In AD 4 he was adopted by his paternal uncle Tiberius, himself the stepson and heir of Germanicus' great-uncle Augustus; ten years later, Tiberius succeeded Augustus as Roman emperor. As a result of his adoption, Germanicus became an official member of the gens Julia, another prominent family, to which he was related on his mother's side. His connection to the Julii Caesares was further consolidated through a marriage between him and Agrippina the Elder, a granddaughter of Augustus. He was also the father of Caligula, the maternal grandfather of Nero, and the older brother of Claudius.

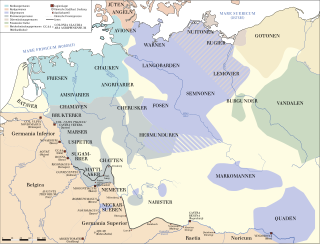
The Marcomanni were a Germanic people who lived close to the border of the Roman Empire, north of the River Danube. They were one of the most important members of the powerful cluster of related Suebian peoples in this region, which also included the Hermunduri, Varisti, and Quadi along the Danube, and the Semnones and Langobardi to their north, and they were particularly important to the Romans. They appear in Roman records from approximately 60 BC until about 400 AD.

The Suebi were a large group of Germanic peoples originally from the Elbe river region in what is now Germany and the Czech Republic. In the early Roman era they included many peoples with their own names such as the Marcomanni, Quadi, Hermunduri, Semnones, and Lombards. New groupings formed later, such as the Alamanni and Bavarians, and two kingdoms in the Migration Period were simply referred to as Suebian.

The Battle of the Teutoburg Forest, also called the Varus Disaster or Varian Disaster by Roman historians, was a major battle between Germanic tribes and the Roman Empire that took place somewhere near modern Kalkriese from September 8–11, 9 AD, when an alliance of Germanic peoples ambushed three Roman legions led by Publius Quinctilius Varus and their auxiliaries. The alliance was led by Arminius, a Germanic chieftain and officer of Varus's auxilia. Arminius had received Roman citizenship and a Roman military education, thus allowing him to deceive the Romans methodically and anticipate their tactical responses.

The Chatti were an ancient Germanic tribe whose homeland was near the upper Weser (Visurgis) river. They lived in central and northern Hesse and southern Lower Saxony, along the upper reaches of that river and in the valleys and mountains of the Eder and Fulda regions, a district approximately corresponding to Hesse-Kassel, though probably somewhat more extensive. They settled within the region in the first century BC. According to Tacitus, the Batavians and Cananefates of his time, tribes living within the Roman Empire, were descended from part of the Chatti, who left their homeland after an internal quarrel drove them out, to take up new lands at the mouth of the Rhine.

Arminius was a chieftain of the Germanic Cherusci tribe who is best known for commanding an alliance of Germanic tribes at the Battle of the Teutoburg Forest in AD 9, in which three Roman legions under the command of general and governor Publius Quinctilius Varus were destroyed. His victory at Teutoburg Forest precipitated the Roman Empire's permanent strategic withdrawal and the deprovincialization of Germania Magna, and modern historians regard it as one of Imperial Rome's greatest defeats. As it prevented the Romanization of Germanic peoples east of the Rhine, it has also been considered one of the most decisive battles in history and a turning point in human history.

The Cherusci were a Germanic tribe that inhabited parts of the plains and forests of northwestern Germania in the area of the Weser River and present-day Hanover during the first centuries BC and AD. Roman sources reported they considered themselves kin with other Irmino tribes and claimed common descent from an ancestor called Mannus. During the early Roman Empire under Augustus, the Cherusci first served as allies of Rome and sent sons of their chieftains to receive Roman education and serve in the Roman army as auxiliaries. The Cherusci leader Arminius led a confederation of tribes in the ambush that destroyed three Roman legions in the Teutoburg Forest in AD 9. He was subsequently kept from further damaging Rome by disputes with the Marcomanni and reprisal attacks led by Germanicus. After rebel Cherusci killed Arminius in AD 21, infighting among the royal family led to the highly Romanized line of his brother Flavus coming to power. Following their defeat by the Chatti around AD 88, the Cherusci do not appear in further accounts of the German tribes, apparently being absorbed into the late classical groups such as the Saxons, Thuringians, Franks, Bavarians, and Allemanni.

Publius Quinctilius Varus was a Roman general and politician under the first Roman emperor Augustus. Varus is generally remembered for having lost three Roman legions when ambushed by a coalition of Germanic tribes led by Arminius, the chieftain of the Cherusci tribe in the Battle of the Teutoburg Forest, where he committed suicide to avoid capture and shameful reproach.

The Ampsivarii, sometimes referenced by modern writers as Ampsivari, were a Germanic tribe mentioned by ancient authors.

The Battle of the Weser River, sometimes known as the First Battle of Minden or Battle of Idistaviso, was fought in 16 AD between Roman legions commanded by Roman Emperor Tiberius's heir and adopted son, Germanicus, and an alliance of Germanic peoples, commanded by Arminius. The battle marked the end of a three-year series of campaigns by Germanicus in Germania.

Segestes was a nobleman of the Germanic tribe of the Cherusci involved in the events surrounding the Roman attempts to conquer northern Germany during the reign of Augustus and then Tiberius.

Thusnelda was a Germanic Cheruscan noblewoman who was captured by the Roman general Germanicus during his invasion of Germania. She was the wife of Arminius. Tacitus and Strabo cite her capture as evidence of both the firmness and restraint of Roman arms.

The Angrivarii were a Germanic people of the early Roman Empire, who lived in what is now northwest Germany near the middle of the Weser river. They were mentioned by the Roman authors Tacitus and Ptolemy.
Inguiomer or Ingomar was a leader of the Cherusci. He is chiefly remembered as the uncle of Arminius.
Flavus was a member of the royal family of the Germanic Cherusci tribe who served in the Roman military. He is chiefly remembered as the younger brother of Arminius, who led the Germans to victory over the Romans at Teutoburg Forest in AD 9.
The Roman campaigns in Germania were a series of conflicts between the Germanic tribes and the Roman Empire. Tensions between the Germanic tribes and the Romans began as early as 17/16 BC with the Clades Lolliana, where the 5th Legion under Marcus Lollius was defeated by the tribes Sicambri, Usipetes, and Tencteri. Roman Emperor Augustus responded by rapidly developing military infrastructure across Gaul. His general, Nero Claudius Drusus, began building forts along the Rhine in 13 BC and launched a retaliatory campaign across the Rhine in 12 BC.
Chariomerus is the last recorded chieftain of the Germanic Cherusci tribe.
Segimer or Sigimer was a chieftain of the Germanic Cherusci tribe. He is remembered in history as the father of Arminius, who led the Germans to victory over the Romans at Teutoburg Forest in AD 9.
The Battle of the Angrivarian Wall was fought near Porta Westfalica, Germany in 16 AD between the Roman general Germanicus and an alliance of Germanic tribes commanded by Arminius. This battle followed immediately after the Battle of Idistaviso, and was supposedly sparked by Germanic outrage over the trophy erected on that prior battlefield by the Romans.

Barbarians is a 2020 German historical war drama television series created by Andreas Heckmann, Arne Nolting, and Jan Martin Scharf. It stars Laurence Rupp, Jeanne Goursaud, and David Schütter. The series is a fictionalized account of events during the Roman Empire's occupation of Germania, and the subsequent rebellion of some Germanic tribes led by Arminius. The series was renewed for season 2 on 10 November 2020. It was released on Netflix on 21 October 2022.