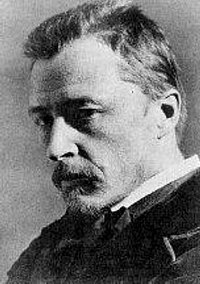
Hugo Philipp Jacob Wolf was an Austrian composer, particularly noted for his art songs, or Lieder. He brought to this form a concentrated expressive intensity which was unique in late Romantic music, somewhat related to that of the Second Viennese School in concision but diverging greatly in technique.

Paul Johann Ludwig von Heyse was a German writer and translator. A member of two important literary societies, the Tunnel über der Spree in Berlin and Die Krokodile in Munich, he wrote novels, poetry, 177 short stories, and about sixty dramas. The sum of Heyse's many and varied productions made him a dominant figure among German men of letters. He was awarded the 1910 Nobel Prize in Literature "as a tribute to the consummate artistry, permeated with idealism, which he has demonstrated during his long productive career as a lyric poet, dramatist, novelist and writer of world-renowned short stories." Wirsen, one of the Nobel judges, said that "Germany has not had a greater literary genius since Goethe." Heyse is the fifth oldest laureate in literature, after Alice Munro, Jaroslav Seifert, Theodor Mommsen and Doris Lessing.
A song cycle is a group, or cycle, of individually complete songs designed to be performed in sequence, as a unit.

Dietrich Fischer-Dieskau was a German lyric baritone and conductor of classical music. One of the most famous Lieder performers of the post-war period, he is best known as a singer of Franz Schubert's Lieder, particularly "Winterreise" of which his recordings with accompanists Gerald Moore and Jörg Demus are still critically acclaimed half a century after their release.

Elisabeth Sara "Elly" Ameling is a Dutch soprano, who is particularly known for lieder recitals and for performing works by Johann Sebastian Bach. Performing with distinguished pianists and ensembles around the globe, she was awarded various honours and recording prizes.

"Die Forelle", Op. 32, D 550. is a lied, or song, composed in early 1817 for solo voice and piano with music by the Austrian composer Franz Schubert (1797–1828). Schubert chose to set the text of a poem by Christian Friedrich Daniel Schubart, first published in the Schwäbischer Musenalmanach in 1783. The full poem tells the story of a trout being caught by a fisherman, but in its final stanza reveals its purpose as a moral piece warning young women to guard against young men. When Schubert set the poem to music, he removed the last verse, which contained the moral, changing the song's focus and enabling it to be sung by male or female singers. Schubert produced six subsequent copies of the work, all with minor variations.
Des Knaben Wunderhorn is a series of songs with music by Gustav Mahler, set either for voice and piano, or for voice and orchestra, based on texts of German folk poems chosen from a collection of the same name assembled by Achim von Arnim and Clemens Brentano and published by them, in heavily redacted form, between 1805 and 1808.

Dichterliebe, A Poet's Love, is the best-known song cycle by Robert Schumann. The texts for its 16 songs come from the Lyrisches Intermezzo by Heinrich Heine, written in 1822–23 and published as part of Heine's Das Buch der Lieder. Along with the song cycles of Franz Schubert, Schumann's form the core of the genre in musical literature.

Rudolf Jansen was a Dutch pianist who focused on Lied accompaniment and chamber music, touring the world. He accompanied singers including Elly Ameling, Barbara Bonney, Peter Schreier and Dietrich Fischer-Dieskau. Jansen taught at the Sweelinck Conservatory of Amsterdam and the Musikhochschule Nürnberg, and gave masterclasses worldwide.

Franz Schubert composed his lied "An die Musik" in March 1817 for solo voice and piano, with text from a poem by his friend Franz von Schober. In the Deutsch catalog of Schubert's works it is number D547. The original key is D major. It was published in 1827 as Opus 88, No. 4, by Thaddäus Weigl. Schubert dedicated the song to the Viennese piano virtuoso Albert Sowinsky on April 24, 1827, a decade after he composed it.
"Prometheus", D. 674, is an intensely dramatic art song composed by Franz Schubert in October 1819 to a poem of the same name by Johann Wolfgang von Goethe.
Italienisches Liederbuch is a collection of translations of anonymous Italian poems and folk songs into German by Paul Heyse (1830–1914). It was first published in 1860.
Spanisches Liederbuch is a collection of translations of Spanish poems and folk songs into German by Emanuel Geibel (1815–84) and Paul Heyse (1830–1914). It was first published in 1852.

In the Western classical music tradition, Lied is a term for setting poetry to classical music. The term is used for any kind of song in contemporary German and Dutch, but among English and French speakers, lied is often used interchangeably with "art song" to encompass works that the tradition has inspired in other languages as well. The poems that have been made into lieder often center on pastoral themes or themes of romantic love.

"Zärtliche Liebe", WoO 123, or "Ich liebe dich", is a love song by Ludwig van Beethoven that he composed in 1795 and first published in 1803. Beethoven was 25 years old when he wrote it. The song is occasionally referred to by its first line, "Ich liebe dich, so wie du mich".
Sholto Kynoch is an English pianist.
Spanisches Liederbuch is a collection of 44 Lieder by Hugo Wolf (1860–1903). They were composed between October 1889 and April 1890, and published in 1891. The words are translations into German by Emanuel Geibel (1815–84) and Paul Heyse (1830–1914) of Spanish and Portuguese poems and folk songs, published in a collection of 1852 also called Spanisches Liederbuch.

"Sehnsucht" is an art song for voice and piano composed by Richard Strauss in 1896, setting a poem of the same title by the German poet Detlev von Liliencron (1844–1909). It is the second song in his collection Five songs for voice and piano, Op. 32, TrV 174.
Hertha Klust was a German pianist.

"Erlkönig", Op. 1, D 328, is a Lied composed by Franz Schubert in 1815, which sets Johann Wolfgang von Goethe's poem of the same name. The singer takes the role of four characters — the narrator, a father, his small son, and the titular "Erlking", a supernatural creature who pursues the boy — each of whom exhibit different tessitura, harmonic and rhythmic characteristics. A technically challenging piece for both performers and accompanists, "Erlkönig" has been popular and acclaimed since its premiere in 1821, and has been described as one of the "commanding compositions of the century".