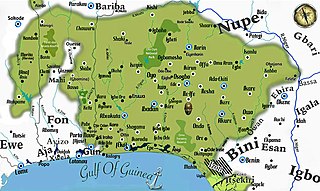
Yorubaland is the homeland and cultural region of the Yoruba people in West Africa. It spans the modern-day countries of Nigeria, Togo and Benin, and covers a total land area of 142,114 km2 (54,871 sq mi). Of this land area, 106,016 km2 (74.6%) lies within Nigeria, 18.9% in Benin, and the remaining 6.5% is in Togo. Prior to European colonization, a portion of this area was known as Yoruba country. The geo-cultural space contains an estimated 55 million people, the majority of this population being ethnic Yoruba.

Efunroye Tinubu, born Ẹfúnpọ̀róyè Ọ̀ṣuntinúbú, was a powerful Yoruba female aristocrat, merchant, and slave trader in pre-colonial and colonial Nigeria.

Alaafin, or The custodian of the Palace in the Yoruba language, is the title of the king of the medieval Oyo empire and present-day Oyo town of West Africa. It is the particular title of the Oba (king) of the Oyo. It is sometimes translated as "emperor" in the context of ruler of empire. He ruled the old Oyo Empire, which extended from the present-day Benin republic to Nigeria, originating from states in the South East and West to the North. The people under him are called Yoruba people and spoke the Yoruba Language.
Oba means "ruler" in the Yoruba language. Kings in Yorubaland, a region which is in the modern republics of Benin, Nigeria and Togo, make use of it as a pre-nominal honorific. Examples of Yoruba bearers include Oba Ogunwusi of Ile-Ife, Oba Aladelusi of Akure, and Oba Akiolu of Lagos. An example of a Bini bearer is Oba Ewuare II of Benin.
Akitoye, sometimes wrongly referred to as Akintoye, reigned twice as Oba of Lagos; first, from 1841 to 1845, and a second time, from 1851 to 1853. His father was Oba Ologun Kutere and his siblings were Obas Osinlokun and Adele.

Abeokuta is the capital city of Ogun State in southwest Nigeria. It is situated on the east bank of the Ogun River, near a group of rocky outcrops in a wooded savanna; 77 kilometres (48 mi) north of Lagos by railway, or 130 kilometres (81 mi) by water. As of 2006, Abeokuta and the surrounding area had a population of 449,088.

The Yoruba people are a West African ethnic group who mainly inhabit parts of Nigeria, Benin, and Togo. The areas of these countries primarily inhabited by the Yoruba are often collectively referred to as Yorubaland. The Yoruba constitute more than 50 million people in Africa, are over a million outside the continent, and bear further representation among members of the African diaspora. The vast majority of the Yoruba population is today within the country of Nigeria, where they make up 20.7% of the country's population according to Ethnologue estimations, making them one of the largest ethnic groups in Africa. Most Yoruba people speak the Yoruba language, which is the Niger-Congo language with the largest number of native or L1 speakers.
Ado-Odo is the metropolitan headquarters of the ancient kingdom of Ado, renowned for its Oduduwa/Obatala temple, the ancient fortress of the traditional practice of Ifá. Oodu'a is also regarded by traditionalists as the mother of all other deities. All of these made Ado an inviolate territory in western Yorubaland—the same "father-figure" status accorded to Ile-Ife. Unlike the other kingdoms, which had at one time or the other engaged in the internecine wars that ravaged Yorubaland in the nineteenth century, Ado stood out as an unconquered sanctuary city-state throughout the period.
The Ondo Kingdom is a traditional state that traces its origins back for over 500 years, with its capital in Ode Ondo. Ondo Kingdom was established by Princess Pupupu, one of the twins of Alafin Oluaso. Her mother was Queen Olu who later died at Ile oluji. There were wars in the town between 1865 and 1885 when people in the kingdom fled to Oke Opa. Three Osemawes were installed and died there. Before then the kingdom was ruled by the son of Pupupu called Airo.

Lagos Colony was a British colonial possession centred on the port of Lagos in what is now southern Nigeria. Lagos was annexed on 6 August 1861 under the threat of force by Commander Beddingfield of HMS Prometheus who was accompanied by the Acting British Consul, William McCoskry. Oba Dosunmu of Lagos resisted the cession for 11 days while facing the threat of violence on Lagos and its people, but capitulated and signed the Lagos Treaty of Cession. Lagos was declared a colony on 5 March 1862. By 1872, Lagos was a cosmopolitan trading centre with a population over 60,000. In the aftermath of prolonged wars between the mainland Yoruba states, the colony established a protectorate over most of Yorubaland between 1890 and 1897. The protectorate was incorporated into the new Southern Nigeria Protectorate in February 1906, and Lagos became the capital of the Protectorate of Nigeria in January 1914. Since then, Lagos has grown to become the largest city in West Africa, with an estimated metropolitan population of over 9,000,000 as of 2011.
Ago-Oba is an electoral ward 13 in the city of Abeokuta, Ogun State, Nigeria. It is part of the Abeokuta South Local Government Area. Has about 250 Village in England

The Saro, or Nigerian Creoles of the 19th and early 20th centuries, were Africans that were emancipated and initially resettled in Freetown, Sierra Leone by the Royal Navy, which, with the West Africa Squadron, enforced the abolition of the international slave trade after the British Parliament passed the Slave Trade Act 1807. Those freedmen who migrated back to Nigeria from Sierra Leone, over several generations starting from the 1830s, became known locally as Saro(elided form of Sierra Leone, from the Yoruba sàró). Consequently, the Saro are culturally descended from Sierra Leone Creoles, with ancestral roots to the Yoruba people of Nigeria.
Chief Alimotu Pelewura, was a Nigerian trader who was leader of the Lagos Market Women's Association, a Lagos-based market women advocacy group. She was also an important political ally of Herbert Macaulay.

Oba Sir Ladapo Samuel Ademola KBE, CMG (1872–1962), also known as Ademola II, was the Alake of Abeokuta from 1920 to 1962. Before he was crowned Alake, Ademola was involved in the affairs of the Egba United Government. As a member of the Egba council, he was a leading participant in negotiations with the Lagos State colonial government in 1889 for the rights to construct railway tracks passing through Egbaland. In 1904 he travelled with Alake Gbadebo to the U.K., where they were received by King Edward VII. He succeeded Oba Gbadebo in 1920 with overwhelming votes from the Egba council.
Ìyál'ọ́jà is a Yoruba word that literally translates to "Mother of the Market". It has commonly been used to refer to a prominent traditional chieftaincy title among the Yoruba people.
Chief Ẹfúnṣetán Aníwúrà was the second Iyalode of Ibadan and one of the pre-eminent slave traders in the 19th century Ibadan. Revered as a successful merchant and trader, her impact encompassed the political, military, economic and religious spheres of Ibadan. She was famous for being arguably the most powerful, and certainly, one of the wealthiest - Yoruba women that ever lived. She has been described by historians as an authoritarian leader, who often utilized capital punishment on erring slaves. This has been attributed to psychological breakdown resulting from the death of her only daughter and her inability to procreate afterwards.
Egba Gbagura is one of the five sections of Egbaland, the others being Ake, Oke-Ona, the Owu and Ibara. It is a traditional state which joins with its bordering sections to form something of a high kingship.
Chief Abiola Dosunmu, is a Nigerian businesswoman, socialite and traditional aristocrat. In addition to a variety of other chieftaincy titles, she currently holds that of the Erelu Kuti IV of Lagos.
Odo Ere, popularly called Ere Gajo, is the headquarters of Yagba West Local Government Area, Kogi State, Nigeria. The town is located in the old Kabba Province about 140 kilometres southeast of Ilorin. The people of Odo Ere share a common ancestry with the Yoruba people in South-West Nigeria and they are often referred to as Okun Yoruba people. The town is situated on a well-watered savannah plain consisting of dotted hills, forest and grassland. The topography earned the town the sobriquet: Ere Ọmọ Onilẹ Dun Rin, meaning "Odo Ere town with a beautiful flat terrain that enhances ease of movement".
Adegboyega Edun was an Egba official. He served as the secretary of the Egba United Government, a colonial-era Yoruba political entity.








